SLUSD61A December 2017 – March 2019 TPS53119
PRODUCTION DATA.
- 1 Features
- 2 Applications
- 3 Description
- 4 Revision History
- 5 Pin Configuration and Functions
- 6 Specifications
-
7 Detailed Description
- 7.1 Overview
- 7.2 Functional Block Diagram
- 7.3
Feature Description
- 7.3.1 Enable and Soft-Start
- 7.3.2 Adaptive ON-Time D-CAP Control and Frequency Selection
- 7.3.3 Small Signal Model
- 7.3.4 Ramp Signal
- 7.3.5 Adaptive Zero Crossing
- 7.3.6 Output Discharge Control
- 7.3.7 Low-Side Driver
- 7.3.8 High-Side Driver
- 7.3.9 Power Good
- 7.3.10 Current Sense and Overcurrent Protection
- 7.3.11 Overvoltage and Undervoltage Protection
- 7.3.12 UVLO Protection
- 7.3.13 Thermal Shutdown
- 7.4 Device Functional Modes
- 8 Application and Implementation
- 9 Power Supply Recommendations
- 10Layout
- 11Device and Documentation Support
- 12Mechanical, Packaging, and Orderable Information
Package Options
Mechanical Data (Package|Pins)
- RGT|16
Thermal pad, mechanical data (Package|Pins)
- RGT|16
Orderable Information
8.2.1.2.2 External Components Selection
Selecting external components is a simple process using D-CAP mode.
- Choose the Inductor
- Choose the Output Capacitor
- D is the duty factor
- the required output ripple slope is approximately 10 mV per tSW (switching period) in terms of VFB terminal voltage
- Determine the Value of R1 and R2
The inductance should be determined to give the ripple current of approximately ¼ to ½ of maximum output current. Larger ripple current increases output ripple voltage and improves the signal-to-noise ratio and helps stable operation.
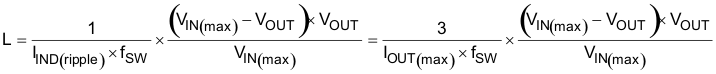
The inductor also requires a low DCR to achieve good efficiency. It also requires enough room above the peak inductor current before saturation. The peak inductor current can be estimated in Equation 10.
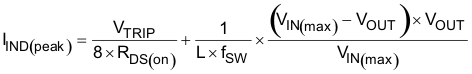
When organic semiconductor capacitors or specialty polymer capacitors are used, for loop stability, capacitance and ESR should satisfy Equation 2. For jitter performance, Equation 11 is a good starting point to determine ESR.
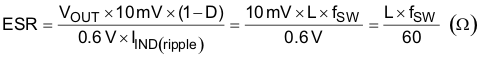
where
The output voltage is programmed by the voltage-divider resistor, R1 and R2 shown in Figure 17. R1 is connected between the VFB pin and the output, and R2 is connected between the VFB pin and GND. Recommended R2 value is between 10 kΩ and 20 kΩ. Determine R1 using Equation 12.
