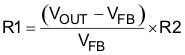SLUSD61A December 2017 – March 2019 TPS53119
PRODUCTION DATA.
- 1 Features
- 2 Applications
- 3 Description
- 4 Revision History
- 5 Pin Configuration and Functions
- 6 Specifications
-
7 Detailed Description
- 7.1 Overview
- 7.2 Functional Block Diagram
- 7.3
Feature Description
- 7.3.1 Enable and Soft-Start
- 7.3.2 Adaptive ON-Time D-CAP Control and Frequency Selection
- 7.3.3 Small Signal Model
- 7.3.4 Ramp Signal
- 7.3.5 Adaptive Zero Crossing
- 7.3.6 Output Discharge Control
- 7.3.7 Low-Side Driver
- 7.3.8 High-Side Driver
- 7.3.9 Power Good
- 7.3.10 Current Sense and Overcurrent Protection
- 7.3.11 Overvoltage and Undervoltage Protection
- 7.3.12 UVLO Protection
- 7.3.13 Thermal Shutdown
- 7.4 Device Functional Modes
- 8 Application and Implementation
- 9 Power Supply Recommendations
- 10Layout
- 11Device and Documentation Support
- 12Mechanical, Packaging, and Orderable Information
Package Options
Mechanical Data (Package|Pins)
- RGT|16
Thermal pad, mechanical data (Package|Pins)
- RGT|16
Orderable Information
8.2.2.2.1 External Parts Selection With All Ceramic Output Capacitors
When a ceramic output capacitor is used, the stability criteria in Equation 2 cannot be satisfied. The ripple injection approach as shown in Figure 22 is implemented to increase the ripple on the VFB pin and make the system stable. C2 can be fixed at 1 nF. The value of C1 can be selected between 10 nF to 200 nF.
The increased ripple on the VFB pin causes the increase of the VFB DC value. The AC ripple coupled to the VFB pin has two components, one coupled from SW node and the other coupled from VOUT and they can be calculated using Equation 13 and Equation 14.
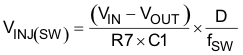

The DC value of VFB can be calculated by Equation 15.

And the resistor divider value can be determined by Equation 16.