SLUSBN5B August 2013 – July 2015 TPS53515
PRODUCTION DATA.
- 1 Features
- 2 Applications
- 3 Description
- 4 Revision History
- 5 Pin Configuration and Functions
- 6 Specifications
-
7 Detailed Description
- 7.1 Overview
- 7.2 Functional Block Diagram
- 7.3
Feature Description
- 7.3.1 5-V LDO and VREG Start-Up
- 7.3.2 Enable, Soft Start, and Mode Selection
- 7.3.3 Frequency Selection
- 7.3.4 D-CAP3 Control and Mode Selection
- 7.3.5 Power-Good
- 7.3.6 Current Sense and Overcurrent Protection
- 7.3.7 Overvoltage and Undervoltage Protection
- 7.3.8 Out-of-Bounds Operation
- 7.3.9 UVLO Protection
- 7.3.10 Thermal Shutdown
- 7.4 Device Functional Modes
- 8 Application and Implementation
- 9 Power Supply Recommendations
- 10Layout
- 11Device and Documentation Support
- 12Mechanical, Packaging, and Orderable Information
Package Options
Mechanical Data (Package|Pins)
- RVE|28
Thermal pad, mechanical data (Package|Pins)
- RVE|28
Orderable Information
8 Application and Implementation
NOTE
Information in the following applications sections is not part of the TI component specification, and TI does not warrant its accuracy or completeness. TI’s customers are responsible for determining suitability of components for their purposes. Customers should validate and test their design implementation to confirm system functionality.
8.1 Application Information
The TPS53515 device is a high-efficiency, single-channel, synchronous-buck converter. The device suits low-output voltage point-of-load applications with 12-A or lower output current in computing and similar digital consumer applications.
8.2 Typical Application
This design example describes a D-CAP3-mode, 8-A synchronous buck converter with integrated MOSFETs. The device provides a fixed 1.2-V output at up to 8 A from a 12-V input bus.
 Figure 43. Application Circuit Diagram
Figure 43. Application Circuit Diagram
8.2.1 Design Requirements
This design uses the parameters listed in Table 5.
Table 5. Design Example Specifications
| PARAMETER | TEST CONDITIONS | MIN | TYP | MAX | UNIT | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| INPUT CHARACTERISTIC | ||||||
| VIN | Voltage range | 5 | 12 | 18 | V | |
| IMAX | Maximum input current | VIN = 5 V, IOUT = 8 A | 2.5 | A | ||
| No load input current | VIN = 12 V, IOUT = 0 A with auto skip mode | 1 | mA | |||
| OUTPUT CHARACTERISTICS | ||||||
| VOUT | Output voltage | 1.2 | V | |||
| Output voltage regulation | Line regulation, 5 V ≤ VIN ≤ –14 V with FCCM |
0.2% | ||||
| Load regulation, VIN = 12 V, 0 A ≤ IOUT ≤ 8 A with FCCM |
0.5% | |||||
| VRIPPLE | Output voltage ripple | VIN = 12 V, IOUT = 8 A with FCCM | 10 | mVPP | ||
| ILOAD | Output load current | 0 | 12 | A | ||
| IOVER | Output over current | 11 | ||||
| tSS | Soft-start time | 1 | ms | |||
| SYSTEMS CHARACTERISTICS | ||||||
| fSW | Switching frequency | 1 | MHz | |||
| η | Peak efficiency | VIN = 12 V, VOUT = 1.2 V, IOUT = 4 A | 88.5% | |||
| η | Full load efficiency | VIN = 12 V, VOUT = 1.2 V, IOUT = 8 A | 86.9% | |||
| TA | Operating temperature | 25 | ºC | |||
8.2.2 Detailed Design Procedure
The external components selection is a simple process using D-CAP3 mode. Select the external components using the following steps
8.2.2.1 Choose the Switching Frequency
The switching frequency is configured by the resistor divider on the RF pin. Select one of eight switching frequencies from 250 kHz to 1 MHz. Refer to Table 1 for the relationship between the switching frequency and resistor-divider configuration.
8.2.2.2 Choose the Operation Mode
Select the operation mode using Table 4.
8.2.2.3 Choose the Inductor
Determine the inductance value to set the ripple current at approximately ¼ to ½ of the maximum output current. Larger ripple current increases output ripple voltage, improves signal-to-noise ratio, and helps to stabilize operation.

The inductor requires a low DCR to achieve good efficiency. The inductor also requires enough room above peak inductor current before saturation. The peak inductor current is estimated using Equation 8.

8.2.2.4 Choose the Output Capacitor
The output capacitor selection is determined by output ripple and transient requirement. When operating in CCM, the output ripple has two components as shown in Equation 9. Equation 10 and Equation 11 define these components.



8.2.2.5 Determine the Value of R1 and R2
The output voltage is programmed by the voltage-divider resistors, R1 and R2, shown in Equation 12. Connect R1 between the VFB pin and the output, and connect R2 between the VFB pin and GND. The recommended R2 value is from 1 kΩ to 20 kΩ. Determine R1 using Equation 12.

8.2.3 Application Curves
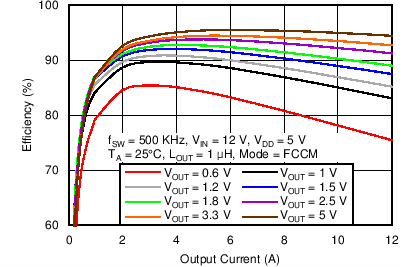 Figure 44. Efficiency vs. Output Current
Figure 44. Efficiency vs. Output Current
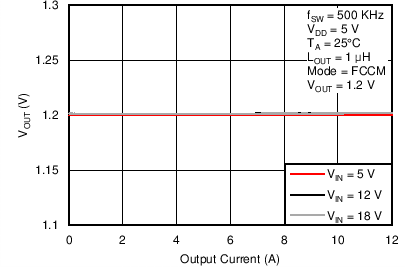 Figure 46. Output Voltage vs. Output Current
Figure 46. Output Voltage vs. Output Current

| ILOAD = 6 A |

| ILOAD from 0 A to 6 A | ||

| ILOAD from 0 A to 6A to 0 A | ||

| ILOAD = 6 A |
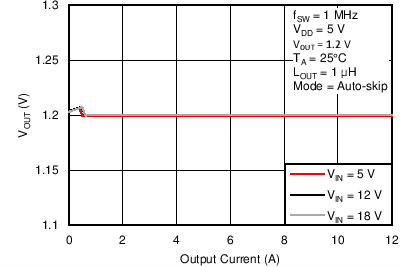 Figure 45. Output Voltage vs. Output Current
Figure 45. Output Voltage vs. Output Current
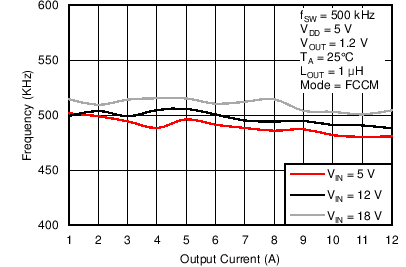 Figure 47. Switching Frequency vs. Output Current
Figure 47. Switching Frequency vs. Output Current

| ILOAD = 6 A |

| ILOAD from 6A to 0 A | ||

| ILOAD = 0 A |

| Preset VOUT = 0.5 V | ||