SLVSBZ1A September 2013 – November 2015 TPS54340-Q1
PRODUCTION DATA.
- 1 Features
- 2 Applications
- 3 Description
- 4 Revision History
- 5 Pin Configuration and Functions
- 6 Specifications
-
7 Detailed Description
- 7.1 Overview
- 7.2 Functional Block Diagram
- 7.3
Feature Description
- 7.3.1 Fixed-Frequency PWM Control
- 7.3.2 Slope Compensation Output Current
- 7.3.3 Pulse Skip Eco-mode™
- 7.3.4 Low Dropout Operation and Bootstrap Voltage (BOOT)
- 7.3.5 Error Amplifier
- 7.3.6 Adjusting the Output Voltage
- 7.3.7 Enable and Adjusting Undervoltage Lockout
- 7.3.8 Internal Soft-Start
- 7.3.9 Constant Switching Frequency and Timing Resistor (RT/CLK) Pin)
- 7.3.10 Accurate Current Limit Operation and Maximum Switchign Frequency
- 7.3.11 Synchronization to RT/CLK Pin
- 7.3.12 Overvoltage Protection
- 7.3.13 Thermal Shutdown
- 7.3.14 Small-Signal Model for Loop Response
- 7.3.15 Simple Small-Signal Model for Peak-Current-Mode Control
- 7.3.16 Small-Signal Model for Frequency Compensation
- 7.4 Device Functional Modes
-
8 Application and Implementation
- 8.1 Application Information
- 8.2
Typical Applications
- 8.2.1
Buck Converter With 6-V to 42-V Input and 3.3-V at 3.5-A Output
- 8.2.1.1 Design Requirements
- 8.2.1.2
Detailed Design Procedure
- 8.2.1.2.1 Selecting the Switching Frequency
- 8.2.1.2.2 Output Inductor Selection (LO)
- 8.2.1.2.3 Output Capacitor
- 8.2.1.2.4 Catch Diode
- 8.2.1.2.5 Input Capacitor
- 8.2.1.2.6 Bootstrap-Capacitor Selection
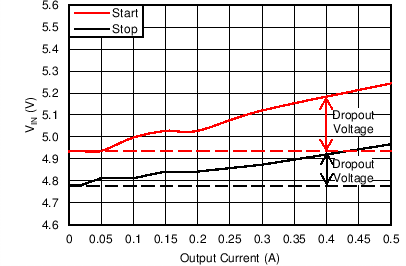
- 8.2.1.2.7 Undervoltage Lockout Set Point
- 8.2.1.2.8 Output Voltage and Feedback Resistors Selection
- 8.2.1.2.9 Compensation
- 8.2.1.2.10 Power Dissipation Estimate
- 8.2.1.2.11 Discontinuous Conduction Mode and Eco-mode™ Boundary
- 8.2.1.3 Application Curves
- 8.2.2 Inverting Power Supply
- 8.2.3 Split-Rail Power Supply
- 8.2.1
Buck Converter With 6-V to 42-V Input and 3.3-V at 3.5-A Output
- 9 Power Supply Recommendations
- 10Layout
- 11Device and Documentation Support
- 12Mechanical, Packaging, and Orderable Information
Package Options
Mechanical Data (Package|Pins)
- DDA|8
Thermal pad, mechanical data (Package|Pins)
- DDA|8
Orderable Information
6 Specifications
6.1 Absolute Maximum Ratings
over operating free-air temperature range (unless otherwise noted)(1)| MIN | MAX | UNIT | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Input voltage | VIN | –0.3 | 45 | V |
| EN | –0.3 | 8.4 | ||
| BOOT | 53 | |||
| FB | –0.3 | 3 | ||
| COMP | –0.3 | 3 | ||
| RT/CLK | –0.3 | 3.6 | ||
| Output voltage | BOOT-SW | 8 | V | |
| SW | –0.6 | 45 | ||
| SW, 10-ns Transient | –2 | 45 | ||
| Operating junction temperature | –40 | 150 | °C | |
| Storage temperature | –65 | 150 | °C | |
(1) Stresses beyond those listed under Absolute Maximum Ratings may cause permanent damage to the device. These are stress ratings only, which do not imply functional operation of the device at these or any other conditions beyond those indicated under Recommended Operating Conditions. Exposure to absolute-maximum-rated conditions for extended periods may affect device reliability.
6.2 ESD Ratings
| VALUE | UNIT | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| V(ESD) | Electrostatic discharge | Human body model (HBM), per ANSI/ESDA/JEDEC JS-001(1) | ±2000 | V |
| Charged device model (CDM), per JEDEC specification JESD22-C101(2) | ±500 | |||
(1) JEDEC document JEP155 states that 500-V HBM allows safe manufacturing with a standard ESD control process.
(2) JEDEC document JEP157 states that 250-V CDM allows safe manufacturing with a standard ESD control process.
6.3 Recommended Operating Conditions
over operating free-air temperature range (unless otherwise noted)| MIN | NOM | MAX | UNIT | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| VIN | Supply input voltage | 4.5 | 42 | V | |
| VO | Output voltage | 0.8 | 58.8 | V | |
| IO | Output current | 0 | 3.5 | A | |
| TJ | Junction Temperature | –40 | 150 | °C | |
6.4 Thermal Information
| THERMAL METRIC(1)(2) | TPS54340-Q1 | UNIT | |
|---|---|---|---|
| DDA (HSOP) | |||
| 8 PINS | |||
| RθJA | Junction-to-ambient thermal resistance (standard board) | 42 | °C/W |
| RθJC(top) | Junction-to-case(top) thermal resistance | 45.8 | °C/W |
| RθJB | Junction-to-board thermal resistance | 23.4 | °C/W |
| ψJT | Junction-to-top characterization parameter | 5.9 | °C/W |
| ψJB | Junction-to-board characterization parameter | 23.4 | °C/W |
| RθJC(bot) | Junction-to-case(bottom) thermal resistance | 3.6 | °C/W |
(1) For more information about traditional and new thermal metrics, see the Semiconductor and IC Package Thermal Metrics application report, SPRA953.
(2) Power rating at a specific ambient temperature TA should be determined with a junction temperature of 150°C. This is the point where distortion starts to substantially increase. See power dissipation estimate in application section of this data sheet for more information.
6.5 Electrical Characteristics
TJ = –40°C to 150°C, VIN = 4.5 V to 42 V (unless otherwise noted)| PARAMETER | TEST CONDITIONS | MIN | TYP | MAX | UNIT | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| SUPPLY VOLTAGE (VIN PIN) | |||||||
| Operating input voltage | 4.5 | 42 | V | ||||
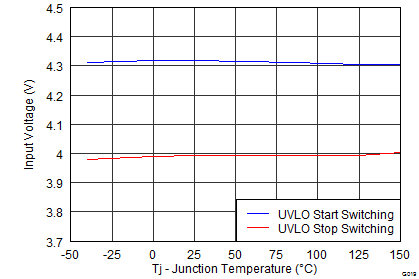
| Internal undervoltage lockout threshold | Rising | 4.1 | 4.3 | 4.48 | V | ||
| Internal undervoltage lockout threshold hysteresis | 325 | mV | |||||
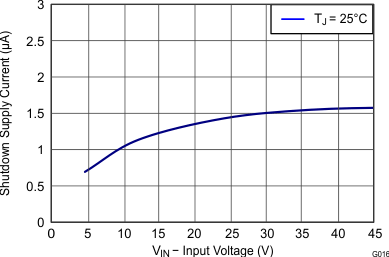
| Shutdown supply current | EN = 0 V, 25°C, 4.5 V ≤ VIN ≤ 42 V | 2.25 | 4.5 | μA | |||
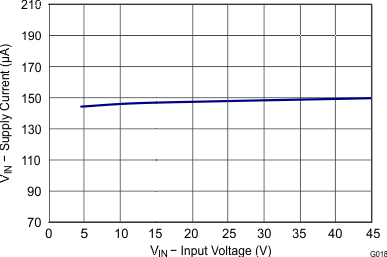
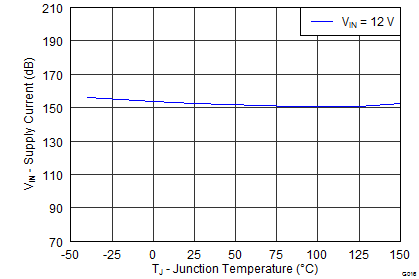
| Operating: nonswitching supply current | FB = 0.9 V, TA = 25°C | 146 | 175 | ||||
| ENABLE AND UVLO (EN PIN) | |||||||
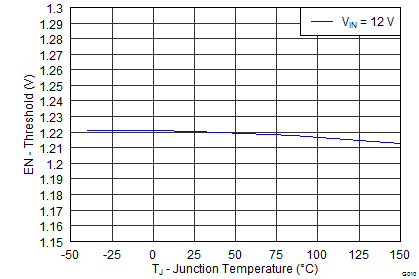
| Enable threshold voltage | No voltage hysteresis, rising and falling | 1.1 | 1.2 | 1.3 | V | ||
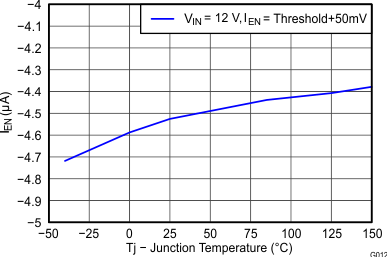
| Input current | Enable threshold 50 mV | –4.6 | μA | ||||
| Enable threshold –50 mV | –0.58 | –1.2 | -1.8 | ||||
| Hysteresis current | –2.2 | –3.4 | -4.5 | μA | |||
| Enable to COMP active | VIN = 12 V , TA = 25°C | 540 | µs | ||||
| INTERNAL SOFT-START TIME | |||||||
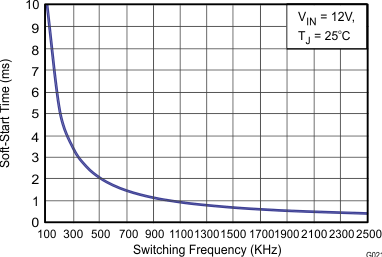
| Soft-Start Time | fSW = 500 kHz, 10% to 90% | 2.1 | ms | ||||
| Soft-Start Time | fSW = 2.5 MHz, 10% to 90% | 0.42 | ms | ||||
| VOLTAGE REFERENCE | |||||||
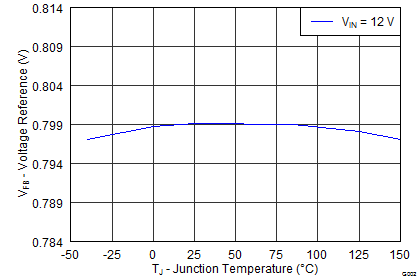
| Voltage reference | 0.792 | 0.8 | 0.808 | V | |||
| HIGH-SIDE MOSFET | |||||||
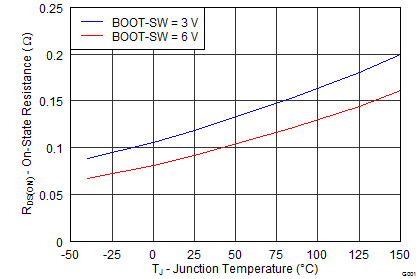
| On-resistance | VIN = 12 V, BOOT-SW = 6 V | 92 | 190 | mΩ | |||
| ERROR AMPLIFIER | |||||||
| Input current | 50 | nA | |||||
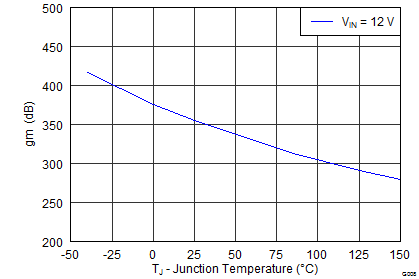
| Error amplifier transconductance (gM) | –2 μA < ICOMP < 2 μA, VCOMP = 1 V | 350 | μS | ||||
| Error amplifier transconductance (gM) during soft-start | –2 μA < ICOMP < 2 μA, VCOMP = 1 V, VFB = 0.4 V | 77 | μS | ||||
| Error amplifier DC gain | VFB = 0.8 V | 10,000 | V/V | ||||
| Min unity gain bandwidth | 2500 | kHz | |||||
| Error amplifier source and sink | V(COMP) = 1 V, 100-mV overdrive | ±30 | μA | ||||
| COMP to SW current transconductance | 12 | A/V | |||||
| CURRENT LIMIT | |||||||
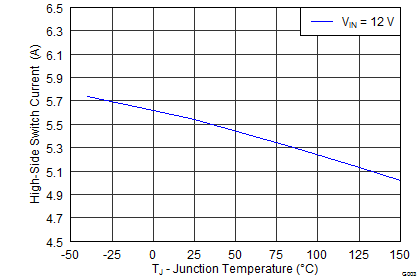
| Current limit threshold | All VIN and temperatures, Open Loop(1) | 4.5 | 5.5 | 6.8 | A | ||
| All temperatures, VIN = 12 V, Open Loop(1) | 4.5 | 5.5 | 6.25 | ||||
| VIN = 12 V, TA = 25°C, Open Loop(1) | 5.2 | 5.5 | 5.85 | ||||
| Current limit threshold delay | 60 | ns | |||||
| THERMAL SHUTDOWN | |||||||
| Thermal shutdown | 176 | °C | |||||
| Thermal shutdown hysteresis | 12 | °C | |||||
| TIMING RESISTOR AND EXTERNAL CLOCK (RT/CLK PIN) | |||||||
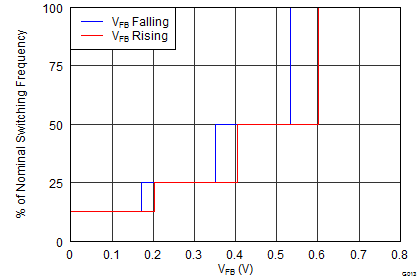
| RT/CLK high threshold | 1.55 | 2 | V | ||||
| RT/CLK low threshold | 0.5 | 1.2 | V | ||||
(1) Open Loop current limit measured directly at the SW pin and is independent of the inductor value and slope compensation.
6.6 RT/CLK Timing Requirements
| MIN | NOM | MAX | UNIT | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Minimum CLK input pulse width | 15 | ns | |||
6.7 Switching Characteristics
over operating free-air temperature range (unless otherwise noted)| PARAMETER | TEST CONDITIONS | MIN | TYP | MAX | UNIT | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| TIMING RESISTOR AND EXTERNAL CLOCK (RT/CLK PIN) | ||||||
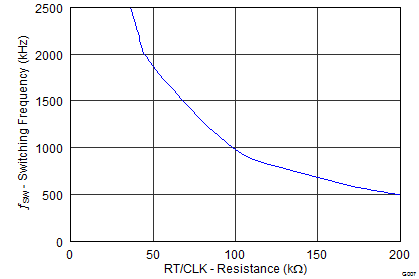
| Switching frequency range using RT mode | 100 | 2500 | kHz | |||
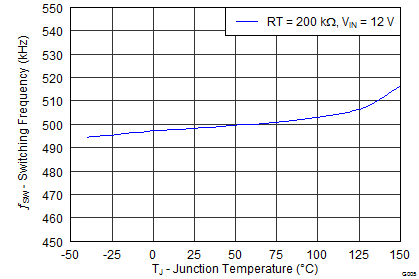
| ƒSW | Switching frequency | RT = 200 kΩ | 450 | 500 | 550 | kHz |
| Switching frequency range using CLK mode | 160 | 2300 | kHz | |||
| RT/CLK falling edge to SW rising edge delay | Measured at 500 kHz with RT resistor in series | 55 | ns | |||
| PLL lock in time | Measured at 500 kHz | 78 | μs | |||
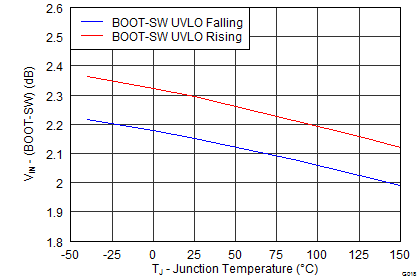
6.8 Typical Characteristics
High-Frequency Range
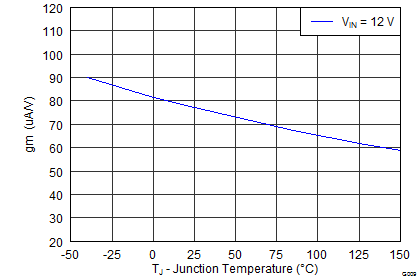
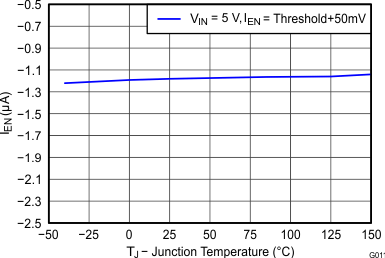
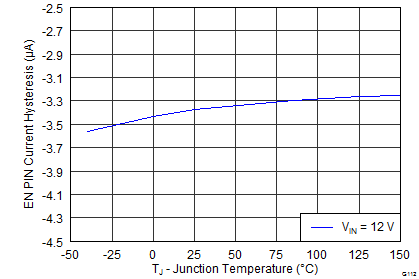
Junction Temperature
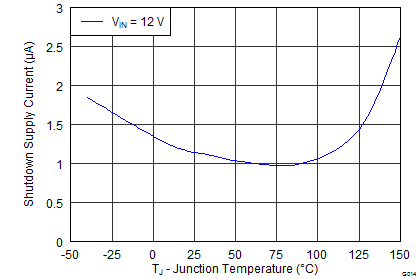
Junction Temperature
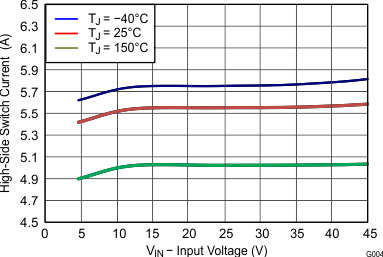
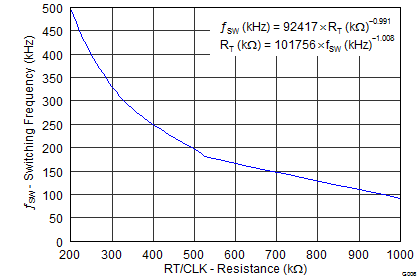
Low-Frequency Range