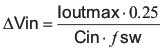SLVSFN6 December 2020 TPS54622-EP
PRODUCTION DATA
- 1 Features
- 2 Applications
- 3 Description
- 4 Revision History
- 5 Pin Configurations and Functions
- 6 Specifications
-
7 Detailed Description
- 7.1 Overview
- 7.2 Functional Block Diagram
- 7.3
Feature Description
- 7.3.1 Fixed-Frequency PWM Control
- 7.3.2 Continuous Current Mode Operation (CCM)
- 7.3.3 VIN and Power VIN Pins (VIN and PVIN)
- 7.3.4 Voltage Reference
- 7.3.5 Adjusting the Output Voltage
- 7.3.6 Safe Start-Up Into Prebiased Outputs
- 7.3.7 Error Amplifier
- 7.3.8 Slope Compensation
- 7.3.9 Enable and Adjusting Undervoltage Lockout
- 7.3.10 Adjustable Switching Frequency and Synchronization (RT/CLK)
- 7.3.11 Slow Start (SS/TR)
- 7.3.12 Power Good (PWRGD)
- 7.3.13 Output Overvoltage Protection (OVP)
- 7.3.14 Overcurrent Protection
- 7.3.15 Thermal Shutdown
- 7.3.16 Small Signal Model for Loop Response
- 7.3.17 Simple Small Signal Model for Peak Current Mode Control
- 7.3.18 Small Signal Model for Frequency Compensation
- 7.4 Device Functional Modes
-
8 Application and Implementation
- 8.1 Application Information
- 8.2
Typical Application
- 8.2.1 Design Requirements
- 8.2.2
Detailed Design Procedures
- 8.2.2.1 Custom Design With WEBENCH® Tools
- 8.2.2.2 Operating Frequency
- 8.2.2.3 Output Inductor Selection
- 8.2.2.4 Output Capacitor Selection
- 8.2.2.5 Input Capacitor Selection
- 8.2.2.6 Slow-Start Capacitor Selection
- 8.2.2.7 Bootstrap Capacitor Selection
- 8.2.2.8 Undervoltage Lockout Setpoint
- 8.2.2.9 Output Voltage Feedback Resistor Selection
- 8.2.2.10 Compensation Component Selection
- 8.2.2.11 Fast Transient Considerations
- 8.2.3 Application Curves
- 9 Power Supply Recommendations
- 10Layout
- 11Device and Documentation Support
- 12Mechanical, Packaging, and Orderable Information
Package Options
Mechanical Data (Package|Pins)
- RHL|14
Thermal pad, mechanical data (Package|Pins)
Orderable Information
8.2.2.5 Input Capacitor Selection
The TPS54622-EP requires a high-quality ceramic, type X5R or X7R, input decoupling capacitor of at least 4.7 µF of effective capacitance on the PVIN input voltage pins and 4.7 µF on the Vin input voltage pin. In some applications, additional bulk capacitance may also be required for the PVIN input. The effective capacitance includes any DC bias effects. The voltage rating of the input capacitor must be greater than the maximum input voltage. The capacitor must also have a ripple current rating greater than the maximum input current ripple of the TPS54622-EP. The input ripple current can be calculated using Equation 26.
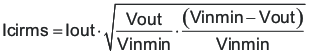
The value of a ceramic capacitor varies significantly over temperature and the amount of DC bias applied to the capacitor. The capacitance variations due to temperature can be minimized by selecting a dielectric material that is stable over temperature. X5R and X7R ceramic dielectrics are usually selected for power regulator capacitors because they have a high capacitance to volume ratio and are fairly stable over temperature. The output capacitor must also be selected with the DC bias taken into account. The capacitance value of a capacitor decreases as the DC bias across a capacitor increases. For this example design, a ceramic capacitor with at least a 25 V voltage rating is required to support the maximum input voltage. For this example, one 10 μF and one 4.7 µF 25-V capacitors in parallel have been selected as the VIN and PVIN inputs are tied together so the TPS54622-EP may operate from a single supply. The input capacitance value determines the input ripple voltage of the regulator. The input voltage ripple can be calculated using Equation 27. Using the design example values, Ioutmax = 6 A, Cin = 14.7 μF, Fsw = 480 kHz, yields an input voltage ripple of 213 mV and a RMS input ripple current of 2.95 A.