SLVSF01B November 2018 – December 2020 TPS55288
PRODUCTION DATA
- 1 Features
- 2 Applications
- 3 Description
- 4 Revision History
- 5 Pin Configuration and Functions
- 6 Specifications
-
7 Detailed Description
- 7.1 Overview
- 7.2 Functional Block Diagram
- 7.3
Feature Description
- 7.3.1 VCC Power Supply
- 7.3.2 Operation Mode Setting
- 7.3.3 Input Undervoltage Lockout
- 7.3.4 Enable and Programmable UVLO
- 7.3.5 Soft Start
- 7.3.6 Shutdown and Load Discharge
- 7.3.7 Switching Frequency
- 7.3.8 Switching Frequency Dithering
- 7.3.9 Inductor Current Limit
- 7.3.10 Internal Charge Path
- 7.3.11 Output Voltage Setting
- 7.3.12 Output Current Monitoring and Cable Voltage Droop Compensation
- 7.3.13 Integrated Gate Drivers
- 7.3.14 Output Current Limit
- 7.3.15 Overvoltage Protection
- 7.3.16 Output Short Circuit Protection
- 7.3.17 Thermal Shutdown
- 7.4 Device Functional Modes
- 7.5 I2C Serial Interface
- 7.6
Register Maps
- 7.6.1 REF Register (Address = 0h, 1h) [reset = 11010010h, 00000000h]
- 7.6.2 IOUT_LIMIT Register (Address = 2h) [reset = 11100100h]
- 7.6.3 VOUT_SR Register (Address = 3h) [reset = 00000001h]
- 7.6.4 VOUT_FS Register (Address = 4h) [reset = 00000011h]
- 7.6.5 CDC Register (Address = 5h) [reset = 11100000h]
- 7.6.6 MODE Register (Address = 6h) [reset = 00100000h]
- 7.6.7 STATUS Register (Address = 7h) [reset = 00000011h]
- 7.6.8 Register Summary
- 8 Application and Implementation
- 9 Power Supply Recommendations
- 10Layout
- 11Device and Documentation Support
- 12Mechanical, Packaging, and Orderable Information
Package Options
Mechanical Data (Package|Pins)
- RPM|26
Thermal pad, mechanical data (Package|Pins)
- RPM|26
Orderable Information
5 Pin Configuration and Functions
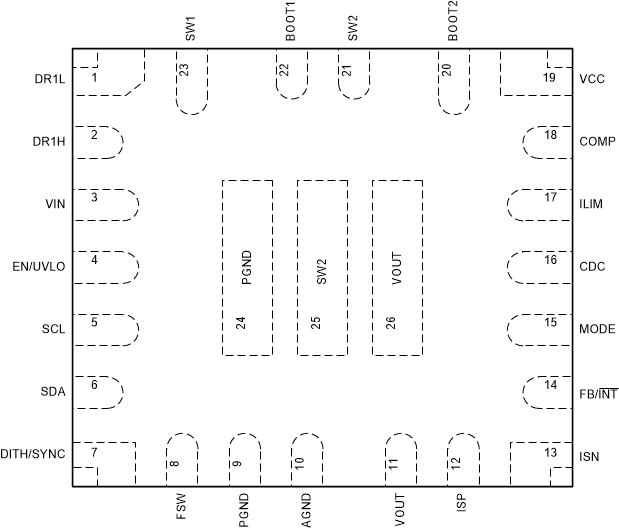 Figure 5-1 26-pin VQFN-HR, RPM Package
(Transparent Top View)
Figure 5-1 26-pin VQFN-HR, RPM Package
(Transparent Top View)Table 5-1 Pin Functions
| PIN | I/O | DESCRIPTION | |
|---|---|---|---|
| NO. | NAME | ||
| 1 | DR1L | O | Gate driver output for low-side MOSFET in buck side |
| 2 | DR1H | O | Gate driver output for high-side MOSFET in buck side |
| 3 | VIN | PWR | Input power supply for the IC |
| 4 | EN/UVLO | I | Enable logic input and programmable input voltage undervoltage lockout (UVLO) input. Logic high level enables the device. Logic low level disables the device and turns it into shutdown mode. After the voltage at the EN/UVLO pin is above the logic high voltage of 1.15 V, this pin acts as programmable UVLO input with 1.23-V internal reference. |
| 5 | SCL | I | Clock of I2C interface |
| 6 | SDA | I/O | Data of I2C interface |
| 7 | DITH/SYNC | I | Dithering frequency setting and synchronous clock input. Use a capacitor between this pin and ground to set the dithering frequency. When this pin is short to ground or pulled above 1.2 V, there is no dithering function. An external clock can be applied at this pin to synchronize the switching frequency. |
| 8 | FSW | O | The switching frequency is programmed by a resistor between this pin and the AGND pin. |
| 9, 24 | PGND | PWR | Power ground of the IC. It is connected to the source of the low-side MOSFET. |
| 10 | AGND | PWR | Signal ground of the IC |
| 11, 26 | VOUT | PWR | Output of the buck-boost converter |
| 12 | ISP | I | Positive input of the current sense amplifier. An optional current sense resistor connected between the ISP pin and the ISN pin can limit the output current. If the sensed voltage reaches the current limit setting value in the register, a slow constant current control loop becomes active and starts to regulate the voltage between the ISP pin and the ISN pin. Connecting the ISP pin and the ISN pin together with the VOUT pin can disable the output current limit function. |
| 13 | ISN | I | Negative input of the current sense amplifier. An optional current sense resistor connected between the ISP pin and the ISN pin can limit the output current. If the sensed voltage reaches the current limit setting value in the register, a slow constant current control loop becomes active and starts to regulate the voltage between the ISP pin and the ISN pin. Connecting the ISP pin and the ISN pin together with the VOUT pin can disable the output current limit function. |
| 14 | FB/INT | I/O | When the device is set to use external output voltage feedback, connect to the center tap of a resistor divider to program the output voltage. When the device is set to use internal feedback, this pin is a fault indicator output. When there is an internal fault happening, this pin outputs logic low level. |
| 15 | MODE | I | Set the operation modes of the TPS55288 by a resistor between this pin and AGND to select PFM mode, or forced PWM mode in light load condition to select the internal LDO or external 5 V for VCC, and to select different I2C address. |
| 16 | CDC | O | Voltage output proportional to the sensed voltage between the ISP pin and the ISN pin. Use a resistor between this pin and AGND to increase the output voltage to compensate voltage droop across the cable caused by the cable resistance. |
| 17 | ILIM | O | Average inductor current limit setting pin. Connect an external resistor between this pin and the AGND pin. |
| 18 | COMP | I | Output of the internal error amplifier. Connect the loop compensation network between this pin and the AGND pin. |
| 19 | VCC | O | Output of the internal regulator. A ceramic capacitor of more than 4.7 μF is required between this pin and the AGND pin. |
| 20 | BOOT2 | O | Power supply for high-side MOSFET gate driver in boost side. A ceramic capacitor of 0.1 µF must be connected between this pin and the SW2 pin. |
| 21, 25 | SW2 | I | The switching node pin of the boost side. It is connected to the drain of the internal low-side power MOSFET and the source of internal high-side power MOSFET. |
| 22 | BOOT1 | I | Power supply for high-side MOSFET gate driver in buck side. A ceramic capacitor of 0.1 µF must be connected between this pin and the SW1 pin. |
| 23 | SW1 | I | The switching node pin of the buck side. It is connected to the drain of the external low-side power MOSFET and the source of external high-side power MOSFET. |