SLVSET0E May 2020 – October 2024 TPS61378-Q1
PRODUCTION DATA
- 1
- 1 Features
- 2 Applications
- 3 Description
- 4 Device Comparison Table
- 5 Pin Configuration and Functions
- 6 Specifications
-
7 Detailed Description
- 7.1 Overview
- 7.2 Functional Block Diagram
- 7.3
Feature Description
- 7.3.1 VCC Power Supply
- 7.3.2 Input Undervoltage Lockout (UVLO)
- 7.3.3 Enable and Soft Start
- 7.3.4 Shut Down
- 7.3.5 Switching Frequency Setting
- 7.3.6 Spread Spectrum Frequency Modulation
- 7.3.7 Adjustable Peak Current Limit
- 7.3.8 Bootstrap
- 7.3.9 Load Disconnect
- 7.3.10 MODE/SYNC Configuration
- 7.3.11 Overvoltage Protection (OVP)
- 7.3.12 Output Short Protection/Hiccup
- 7.3.13 Power-Good Indicator
- 7.3.14 Thermal Shutdown
- 7.4 Device Functional Modes
-
8 Application and Implementation
- 8.1 Application Information
- 8.2
Typical Application
- 8.2.1 Design Requirements
- 8.2.2 Detailed Design Procedure
- 8.2.3 Application Curves
- 9 Power Supply Recommendations
- 10Layout
- 11Device and Documentation Support
- 12Revision History
- 13Mechanical, Packaging, and Orderable Information
Package Options
Mechanical Data (Package|Pins)
- RTE|16
Thermal pad, mechanical data (Package|Pins)
- RTE|16
Orderable Information
7.3.7 Adjustable Peak Current Limit
The TPS61378-Q1 adopts a cycle-by-cycle peak current limit internally and changes its current limit with different working conditions. The low-side switch is turned off immediately as soon as the switch peak current triggers the peak current limit. The peak switch current limit can be set by a resistor from the ILIM pin to ground. The relationship between the peak current limit and the resistor is shown in Equation 2.
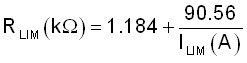
where
- RILIM is the resistance between the ILIM pin and the GND. This pin cannot be left floating or connected to VCC.
- ILIM is switch peak current limit
For instance, the current limit is set to 4.8 A if the RLIM is 20 kΩ.
Table 7-1 summarizes the peak current limit under various conditions. The current limit applies to the start-up phase.
| Behavior | Switch Peak Current Limit |
|---|---|
| Vin < VO (Not in Down Mode) | ILIM(1) |
| Vin < VO (In Down Mode) | 2/3 ILIM |
| 3V > Vin - VO > 0V | 4/9 ILIM |
| 6V > Vin - VO > 3V | 1/4 ILIM |
| Vin - VO > 6V | 1/4 ILIM & Fsw Clamp to 1.1MHz if FREQ pin setting is > 1.1MHz |
| FB ≤ 0.1V | 1/5 ILIM & Fsw Clamp to 1.1MHz if FREQ pin setting is > 1.1MHz |