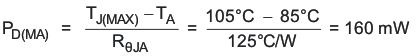SLVS871D February 2010 – June 2016 TPS62660 , TPS62665
PRODUCTION DATA.
- 1 Features
- 2 Applications
- 3 Description
- 4 Revision History
- 5 Pin Configuration and Functions
- 6 Specifications
- 7 Parameter Measurement Information
- 8 Detailed Description
- 9 Application and Implementation
- 10Power Supply Recommendations
- 11Layout
- 12Device and Documentation Support
- 13Mechanical, Packaging, and Orderable Information
Package Options
Mechanical Data (Package|Pins)
- YFF|6
Thermal pad, mechanical data (Package|Pins)
Orderable Information
11 Layout
11.1 Layout Guidelines
As for all switching power supplies, the layout is an important step in the design. High-speed operation of the TPS6266x devices demand careful attention to PCB layout. Take care in board layout to get the specified performance. If the layout is not carefully done, the regulator could show poor line or load regulation, stability and switching frequency issues, as well as EMI problems. It is critical to provide a low-inductance, impedance ground path. Therefore, use wide and short traces for the main current paths.
The input capacitor must be placed as close as possible to the IC pins as well as the inductor and output capacitor. In order to get an optimum ESL step, the output voltage feedback point (FB) must be taken in the output capacitor path, approximately 1 mm away for it. The feedback line must be routed away from noisy components and traces (that is, SW line).
11.2 Layout Example
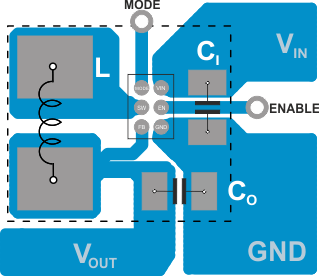 Figure 41. Suggested Layout (Top)
Figure 41. Suggested Layout (Top)
11.3 Thermal Considerations
Implementation of integrated circuits in low-profile and fine-pitch surface-mount packages typically requires special attention to power dissipation. Many system-dependant issues such as thermal coupling, airflow, added heat sinks, and convection surfaces, and the presence of other heat-generating components, affect the power dissipation limits of a given component
Three basic approaches for enhancing thermal performance are listed below:
- Improving the power dissipation capability of the PCB design
- Improving the thermal coupling of the component to the PCB
- Introducing airflow in the system
The maximum recommended junction temperature (TJ) of the TPS6266x devices is 105°C. The thermal resistance of the 6-pin DSBGA package (YFF-6) is RθJA = 125°C/W. Regulator operation is specified to a maximum ambient temperature TA of 85°C. Therefore, the maximum steady-state power dissipation is about
160 mW.