SLVSC01A June 2013 – April 2015 TPS65133
PRODUCTION DATA.
- 1 Features
- 2 Applications
- 3 Description
- 4 Typical Application
- 5 Revision History
- 6 Pin Configuration and Functions
- 7 Specifications
- 8 Detailed Description
- 9 Application and Implementation
- 10Power Supply Recommendations
- 11Layout
- 12Device and Documentation Support
- 13Mechanical, Packaging, and Orderable Information
Package Options
Mechanical Data (Package|Pins)
- DPD|12
Thermal pad, mechanical data (Package|Pins)
- DPD|12
Orderable Information
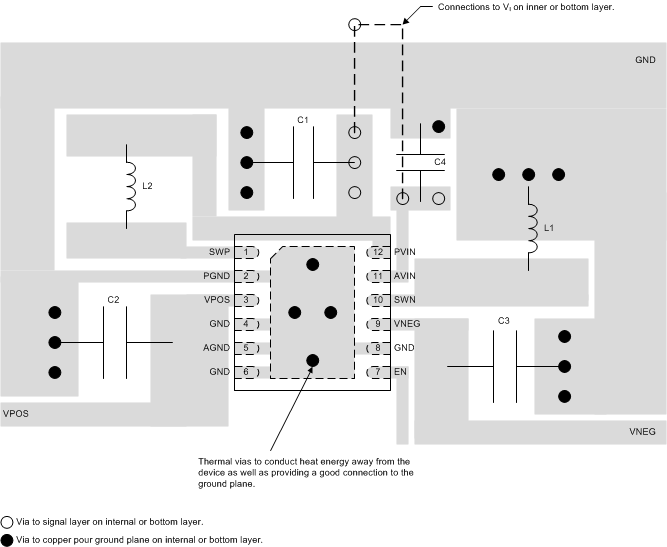
11 Layout
11.1 Layout Guidelines
No PCB layout is perfect, and compromises are always necessary. However, the basic principles listed below (in order of importance) go a long way to achieving the full performance of the TPS65133 device.
- Route discontinuous switching currents on the top layer using short, wide traces. Avoid routing these signals through vias, which have relatively high parasitic inductance and resistance.
- Place C1 as close as possible to pin 12.
- Place C2 as close as possible to pin 3. Place C3 as close as possible to pin 9.
- Use the exposed thermal pad to connect GND, AGND and PGND.
- Use a copper pour (preferably on layer 2) as a thermal spreader and connect it to the exposed thermal pad using a number of thermal vias.
Figure 28 illustrates how a PCB layout following the above principles may be realized in practice.