SLVSBC9C March 2012 – February 2016 TPS65177 , TPS65177A
PRODUCTION DATA.
- 1 Features
- 2 Applications
- 3 Description
- 4 Revision History
- 5 Pin Configuration and Functions
- 6 Specifications
-
7 Detailed Description
- 7.1 Overview
- 7.2 Functional Block Diagram
- 7.3 Feature Description
- 7.4
Device Functional Modes
- 7.4.1 Boost Converter (V(AVDD))
- 7.4.2 Buck 1 Converter (V(IO))
- 7.4.3 BUCK 2 CONVERTER (V(CORE))
- 7.4.4 Buck 3 Converter (V(HAVDD))
- 7.4.5 Positive Charge Pump Controller (V(GH)) with Temperature Compensation
- 7.4.6 Negative Charge Pump Controller (V(GL))
- 7.5 Gate Pulse Modulation (V(GHM))
- 7.6
Programming
- 7.6.1 I2C Serial Interface Description
- 7.6.2 Memory Description
- 7.6.3 Read / Write Description
- 7.6.4 Write Operation
- 7.6.5 READ OPERATION
- 7.6.6 Write Single Data to DAC:
- 7.6.7 Write Multiple Data to DAC (Auto Increment Address):
- 7.6.8 Write all DAC Data to EEPROM:
- 7.6.9 Read Single Data From DAC / EEPROM:
- 7.6.10 Read Multiple Data fFom DAC / EEPROM (Auto Increment Address):
- 7.7
Register Map
- 7.7.1
Registers and DAC Settings
- 7.7.1.1 Channel Register (with factory value) - 00h (00h)
- 7.7.1.2 Boost Output Voltage V(AVDD) Register (with factory value) - 01h (0Fh)
- 7.7.1.3 Boost HVS Offset Voltage Register (with factory value) - 02h (05h)
- 7.7.1.4 Boost Current Limit Negative Offset Current Register (with factory value) - 03h (00h)
- 7.7.1.5 Boost Soft-start Time Register (with factory value) - 04h (00h)
- 7.7.1.6 Buck 1 Output Voltage V(IO) Register (with factory value) - 05h (03h):
- 7.7.1.7 Buck 2 Output Voltage V(CORE) Register (with factory value) - 06h (02h)
- 7.7.1.8 Buck 3 Output Voltage V(HAVDD) Register (with factory value) - 07h (1Bh)
- 7.7.1.9 Pos. Charge Pump Low Output Voltage V(GH_L) Register (with factory value) - 08h (08h):
- 7.7.1.10 Positive Charge Pump Low Output Voltage V(GH_L) to V(GH_H) Positive Offset Voltage V(GH_OFS) Register (with factory value) - 09h (04h):
- 7.7.1.11 Gate Pulse Modulation Limit Voltage Register (with factory value) - 0Ah (00h)
- 7.7.1.12 Negative Charge Pump Output Voltage V(GL) Register (with factory value) - 0Bh (04h)
- 7.7.1.13 Buck 3 HVS Offset Voltage Register (with factory value) - 0Ch (00h):
- 7.7.1.14 Memory Write Remain Time Register (with factory value) - FEh (0Fh):
- 7.7.1
Registers and DAC Settings
- 8 Application and Implementation
- 9 Power Supply Recommendations
- 10Layout
- 11Device and Documentation Support
- 12Mechanical, Packaging, and Orderable Information
Package Options
Mechanical Data (Package|Pins)
- RHA|40
Thermal pad, mechanical data (Package|Pins)
Orderable Information
5 Pin Configuration and Functions
RHA Package
40 Pin (VQFN)
Top View
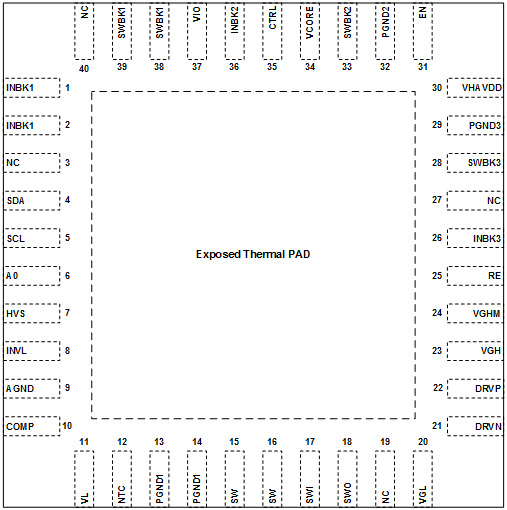
Pin Functions
| PIN | TYPE | DESCRIPTION | |
|---|---|---|---|
| NAME | NO. | ||
| INBK1 | 1, 2 | — | Buck 1 converter (V(IO)) supply pin. This pin is internally connected to INBK3. Place a buffer capacitor close to this pin. |
| NC | 3 | — | Not connected. |
| SDA | 4 | I / O | I2C data pin. |
| SCL | 5 | I | I2C clock pin. |
| A0 | 6 | I | I2C address select pin. |
| HVS | 7 | I | Boost and Buck 3 converter High Voltage Stress Mode enable pin. |
| INVL | 8 | — | Internal logic supply pin. Place a buffer capacitor close to this pin. |
| AGND | 9 | — | Analog Ground pin. Internal circuitry uses this ground. |
| COMP | 10 | I / O | Boost converter (V(AVDD)) compensation pin. |
| VL | 11 | I / O | Internal 5 V regulator output pin. Connect a buffer capacitor to this pin. |
| NTC | 12 | I | Thermal Resistor sense pin. |
| PGND1 | 13, 14 | — | Boost converter (V(AVDD)) Power Ground pin. |
| SW | 15, 16 | O | Boost converter (V(AVDD)) switch pin. Avoid long traces to the diode and inductor because this trace carries switching waveforms that generate noise. |
| SWI | 17 | I | Isolation Switch input pin. |
| SWO | 18 | O | Isolation Switch output pin. |
| NC | 19 | — | Not connected. |
| VGL | 20 | I | Negative Charge Pump (V(GL)) voltage sense pin. |
| DRVN | 21 | O | Negative Charge Pump (V(GL)) base drive pin. |
| DRVP | 22 | I | Positive charge pump (V(GH)) base drive pin. |
| VGH | 23 | I | Positive charge pump (V(GH)) output voltage sense and Gate Pulse Modulation supply pin. |
| VGHM | 24 | I / O | Gate Pulse Modulation output pin. |
| RE | 25 | O | Slope adjustment of Gate Pulse Modulation. |
| INBK3 | 26 | — | Buck 3 converter (V(HAVDD)) supply pin. This pin is internally connected to INBK1. Place a buffer capacitor close to this pin. |
| NC | 27 | — | Not connected. |
| SWBK3 | 28 | O | Buck 3 Converter (V(HAVDD)) switch pin. Avoid long traces to the inductor because this trace carries switching waveforms that generate noise. |
| PGND3 | 29 | — | Buck 3 Converter (V(HAVDD)) Power Ground pin. |
| VHAVDD | 30 | I | Buck 3 Converter (V(HAVDD)) voltage sense pin. |
| EN | 31 | I | Enable of Isolation Switch, Boost converter and Buck 3 converter. |
| PGND2 | 32 | — | Buck 2 converter (V(CORE)) Power Ground pin. |
| SWBK2 | 33 | O | Buck 2 converter (V(CORE)) switch pin. Avoid long traces to the inductor because this trace carries switching waveforms that generate noise. |
| VCORE | 34 | I | Buck 2 converter (V(CORE)) output voltage sense pin. |
| CTRL | 35 | I | Gate Pulse Modulation control pin. |
| INBK2 | 36 | — | Buck 2 converter (V(CORE)) supply pin. Place a buffer capacitor close to this pin. |
| VIO | 37 | I | Buck 1 converter (V(IO)) output voltage sense pin. |
| SWBK1 | 38, 39 | O | Buck 1 converter (V(IO)) switch pin. Avoid long traces to the diode and inductor because this trace carries switching waveforms that generate noise. |
| NC | 40 | — | Not connected. |
| Exposed thermal pad | — | The Exposed thermal pad is connected to AGND. | |