SLVSD80D November 2015 – May 2021 TPS65235
PRODUCTION DATA
- 1 Features
- 2 Applications
- 3 Description
- 4 Revision History
- 5 Pin Configuration and Functions
- 6 Specifications
-
7 Detailed Description
- 7.1 Overview
- 7.2 Functional Block Diagram
- 7.3
Feature Description
- 7.3.1 Boost Converter
- 7.3.2 Linear Regulator and Current Limit
- 7.3.3 Boost Converter Current Limit
- 7.3.4 Charge Pump
- 7.3.5 Slew Rate Control
- 7.3.6 Short Circuit Protection, Hiccup and Overtemperature Protection
- 7.3.7 Tone Generation
- 7.3.8 Tone Detection
- 7.3.9 Disable and Enable
- 7.3.10 Component Selection
- 7.4 Device Functional Modes
- 7.5 Programming
- 7.6 Register Maps
- 8 Application and Implementation
- 9 Power Supply Recommendations
- 10Layout
- 11Device and Documentation Support
- 12Mechanical, Packaging, and Orderable Information
Package Options
Mechanical Data (Package|Pins)
- RUK|20
Thermal pad, mechanical data (Package|Pins)
- RUK|20
Orderable Information
7.5.1 Serial Interface Description
I2C is a 2-wire serial interface developed by Philips Semiconductor (see I2C-Bus Specification, Version 2.1, January 2000). The bus consists of a data line (SDA) and a clock line (SCL) with pull-up structures. When the bus is idle, both SDA and SCL lines are pulled high external. All the I2C compatible devices connect to the I2C bus through open drain I/O pins, SDA and SCL. A master device, usually a microcontroller or a digital signal processor, controls the bus. The master is responsible for generating the SCL signal and device addresses. The master also generates specific conditions that indicate the START and STOP of data transfer. A slave device receives and/or transmits data on the bus under control of the master device.
The TPS65235 device works as a slave and supports the following data transfer modes, as defined in the I2CBus Specification: standard mode (100 kbps), and fast mode (400 kbps). The interface adds flexibility to the power supply solution, enabling most functions to be programmed to new values depending on the instantaneous application requirements. Register contents remain intact as long as supply voltage remains above 4.5 V (typical).
The data transfer protocol for standard and fast modes is exactly the same; therefore, they are referred to as F/S-mode in this document. The TPS65235 device supports 7-bit addressing; 10-bit addressing and general call address are not supported.
The TPS65235 device has a 7-bit address set by ADDR pin. Table 7-4 shows how to set the I2C address.
| ADDR PIN | I2C ADDRESS | Address Format (A6 ≥ A0) |
|---|---|---|
| Connect to VCC | 0x08H | 000 1000 |
| Floating | 0x09H | 000 1001 |
| Connected to GND | 0x10H | 001 0000 |
| Resistor divider to make ADDR pin voltage in 3 V ~ VCC - 0.8 V | 0x11H | 001 0001 |
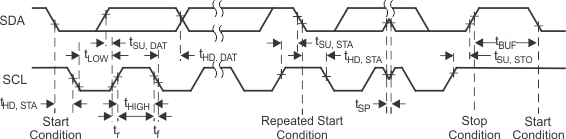 Figure 7-9 I2C Interface Timing Diagram
Figure 7-9 I2C Interface Timing Diagram