SLVSD80D November 2015 – May 2021 TPS65235
PRODUCTION DATA
- 1 Features
- 2 Applications
- 3 Description
- 4 Revision History
- 5 Pin Configuration and Functions
- 6 Specifications
-
7 Detailed Description
- 7.1 Overview
- 7.2 Functional Block Diagram
- 7.3
Feature Description
- 7.3.1 Boost Converter
- 7.3.2 Linear Regulator and Current Limit
- 7.3.3 Boost Converter Current Limit
- 7.3.4 Charge Pump
- 7.3.5 Slew Rate Control
- 7.3.6 Short Circuit Protection, Hiccup and Overtemperature Protection
- 7.3.7 Tone Generation
- 7.3.8 Tone Detection
- 7.3.9 Disable and Enable
- 7.3.10 Component Selection
- 7.4 Device Functional Modes
- 7.5 Programming
- 7.6 Register Maps
- 8 Application and Implementation
- 9 Power Supply Recommendations
- 10Layout
- 11Device and Documentation Support
- 12Mechanical, Packaging, and Orderable Information
Package Options
Mechanical Data (Package|Pins)
- RUK|20
Thermal pad, mechanical data (Package|Pins)
- RUK|20
Orderable Information
7.3.7 Tone Generation
22 kHz tone signal is implemented at the LNB output voltage as a carrier for DiSEqC command. This tone signal can be generated by feeding an external 22-kHz clock at the EXTM pin, and it can also be generated with its internal tone generator controlled by EXTM pin. If EXTM pin is toggled to high, the internal tone signal will be superimposed at the LNB output, if EXTM pin is low, there will be no tone superimposed at the output stage of the regulator facilitates a push-pull circuit, so even at zero loading; the 22-kHz tone at the output is still clean without distortion.
There are two ways to generate the 22 kHz tone signal at the output.
For option1, if the EXTM has 44-kHz tone input, and the bit EXTM TONE of the Control Register 1 is set to "1", the LNB tone output is 44 kHz.
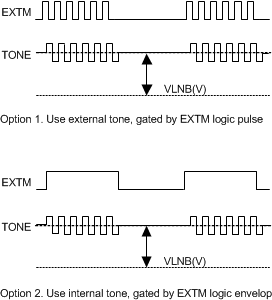 Figure 7-2 Two Ways to Generate 22 kHz Tone
Figure 7-2 Two Ways to Generate 22 kHz Tone