SLVSFM6A August 2020 – July 2021 TPS65994AD
PRODUCTION DATA
- 1 Features
- 2 Applications
- 3 Description
- 4 Revision History
- 5 Pin Configuration and Functions
-
6 Specifications
- 6.1 Absolute Maximum Ratings
- 6.2 ESD Ratings
- 6.3 Recommended Operating Conditions
- 6.4 Recommended Capacitance
- 6.5 Thermal Information
- 6.6 Power Supply Characteristics
- 6.7 Power Consumption
- 6.8 PP_5V Power Switch Characteristics
- 6.9 PP_EXT Power Switch Characteristics
- 6.10 Power Path Supervisory
- 6.11 CC Cable Detection Parameters
- 6.12 CC VCONN Parameters
- 6.13 CC PHY Parameters
- 6.14 Thermal Shutdown Characteristics
- 6.15 ADC Characteristics
- 6.16 Input/Output (I/O) Characteristics
- 6.17 I2C Requirements and Characteristics
- 6.18 Typical Characteristics
- 7 Parameter Measurement Information
-
8 Detailed Description
- 8.1 Overview
- 8.2 Functional Block Diagram
- 8.3
Feature Description
- 8.3.1 USB-PD Physical Layer
- 8.3.2 Power Management
- 8.3.3
Power Paths
- 8.3.3.1
Internal Sourcing Power Paths
- 8.3.3.1.1 PP_5Vx Current Clamping
- 8.3.3.1.2 PP_5Vx Local Overtemperature Shut Down (OTSD)
- 8.3.3.1.3 PP_5Vx Current Sense
- 8.3.3.1.4 PP_5Vx OVP
- 8.3.3.1.5 PP_5Vx UVLO
- 8.3.3.1.6 PP_5Vx Reverse Current Protection
- 8.3.3.1.7 Fast Role Swap
- 8.3.3.1.8 PP_CABLE Current Clamp
- 8.3.3.1.9 PP_CABLE Local Overtemperature Shut Down (OTSD)
- 8.3.3.1.10 PP_CABLE UVLO
- 8.3.3.2 Sink Path Control
- 8.3.3.1
Internal Sourcing Power Paths
- 8.3.4 Cable Plug and Orientation Detection
- 8.3.5 Default Behavior Configuration (ADCIN1, ADCIN2)
- 8.3.6 ADC
- 8.3.7 DisplayPort Hot-Plug Detect (HPD)
- 8.3.8 Digital Interfaces
- 8.3.9 Digital Core
- 8.3.10 I2C Interface
- 8.4 Device Functional Modes
- 9 Application and Implementation
- 10Power Supply Recommendations
- 11Layout
- 12Device and Documentation Support
- 13Mechanical, Packaging, and Orderable Information
Package Options
Refer to the PDF data sheet for device specific package drawings
Mechanical Data (Package|Pins)
- RSL|48
Thermal pad, mechanical data (Package|Pins)
Orderable Information
8.3.3.2.1 Overvoltage Protection (OVP)
The application firmware enables the OVP and
configures it based on the expected Px_VBUS
voltage. If the voltage on Px_VBUS surpasses
the configured threshold VOVP4VSYS = VOVP4RCP/rOVP,
then Px_GATE_VSYS is automatically disabled
within tPx_GATE_VSYS_FSD
to protect the system. If the voltage on Px_VBUS surpasses the configured threshold
VOVP4RCP then Px_GATE_VBUS is
automatically disabled within tPx_GATE_VBUS_OVP. When VPx_VBUS falls below
VOVP4RCP - VOVP4RCPH
Px_GATE_VBUS is automatically re-enabled
within
tPx_GATE_VBUS_ON since the OVP condition has cleared. This
allows two sinking power paths to be enabled simultaneously and Px_GATE_VBUS will be disabled when necessary
to ensure that VPx_VBUS remains
below VOVP4RCP.
While the TPS65994AD is in the BOOT mode in a dead-battery scenario (that is VIN_3V3 is low) it handles an OVP condition slightly differently. As long as the OVP condition is present Px_GATE_VBUS and Px_GATE_VSYS are disabled. Once the OVP condition clears, both Px_GATE_VBUS and Px_GATE_VSYS are re-enabled (unless ADCINx are configured in SafeMode). Since this is a dead-battery condition, the TPS65994AD will be drawing approximately IVIN_3V3,ActSnk from PA_VBUS or PB_VBUS during this time to help discharge it.
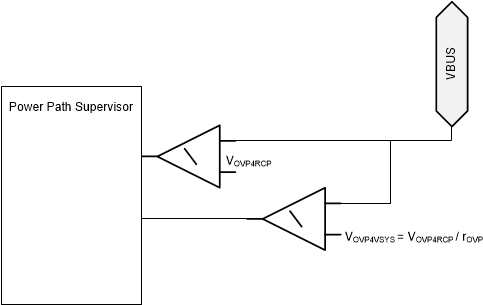 Figure 8-13 Diagram for OVP Comparators
Figure 8-13 Diagram for OVP Comparators