SBVS298B September 2017 – July 2018 TPS7A53-Q1
PRODUCTION DATA.
- 1 Features
- 2 Applications
- 3 Description
- 4 Revision History
- 5 Pin Configuration and Functions
- 6 Specifications
- 7 Detailed Description
-
8 Application and Implementation
- 8.1
Application Information
- 8.1.1 Recommended Capacitor Types
- 8.1.2 Soft Start and Inrush Current
- 8.1.3 Optimizing Noise and PSRR
- 8.1.4 Charge Pump Noise
- 8.1.5 Current Sharing
- 8.1.6 Adjustable Operation
- 8.1.7 Power-Good Operation
- 8.1.8 Undervoltage Lockout (UVLO) Operation
- 8.1.9 Dropout Voltage (VDO)
- 8.1.10 Device Behavior During Transition From Dropout Into Regulation
- 8.1.11 Load Transient Response
- 8.1.12 Reverse Current Protection Considerations
- 8.1.13 Power Dissipation (PD)
- 8.1.14 Estimating Junction Temperature
- 8.2 Typical Application
- 8.1
Application Information
- 9 Power Supply Recommendations
- 10Layout
- 11Device and Documentation Support
- 12Mechanical, Packaging, and Orderable Information
Package Options
Refer to the PDF data sheet for device specific package drawings
Mechanical Data (Package|Pins)
- RGR|20
- RTK|20
Thermal pad, mechanical data (Package|Pins)
- RGR|20
Orderable Information
8.1.13 Power Dissipation (PD)
Circuit reliability demands that proper consideration be given to device power dissipation, location of the circuit on the printed circuit board (PCB), and correct sizing of the thermal plane. The PCB area around the regulator must be as free as possible of other heat-generating devices that cause added thermal stresses.
As a first-order approximation, power dissipation in the regulator depends on the input-to-output voltage difference and load conditions. Use Equation 5 to calculate PD:
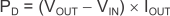
NOTE
Power dissipation can be minimized, and thus greater efficiency achieved, by proper selection of the system voltage rails. Proper selection allows the minimum input-to-output voltage differential to be obtained. The low dropout of the TPS7A53-Q1 allows for maximum efficiency across a wide range of output voltages.
The primary heat conduction path for the package is through the thermal pad to the PCB. Solder the thermal pad to a copper pad area under the device. This pad area contains an array of plated vias that conduct heat to any inner plane areas or to a bottom-side copper plane.
The maximum power dissipation determines the maximum allowable junction temperature (TJ) for the device. According to Equation 6, power dissipation and junction temperature are most often related by the junction-to-ambient thermal resistance (RθJA) of the combined PCB and device package and the temperature of the ambient air (TA). Equation 6 is rearranged in Equation 7 for output current.
Unfortunately, this thermal resistance (RθJA) is highly dependent on the heat-spreading capability built into the particular PCB design, and therefore varies according to the total copper area, copper weight, and location of the planes. The RθJA recorded in the Electrical Characteristics table is determined by the JEDEC standard, PCB, and copper-spreading area, and is only used as a relative measure of package thermal performance. For a well-designed thermal layout, RθJA is actually the sum of the VQFN package junction-to-case (bottom) thermal resistance (RθJC(bot)) plus the thermal resistance contribution by the PCB copper.