SBVS360A February 2020 – November 2020 TPS7B85-Q1
PRODUCTION DATA
- 1 Features
- 2 Applications
- 3 Description
- 4 Revision History
- 5 Pin Configuration and Functions
- 6 Specifications
- 7 Detailed Description
- 8 Application and Implementation
- 9 Power Supply Recommendations
- 10Layout
- 11Device and Documentation Support
Package Options
Mechanical Data (Package|Pins)
- DRC|10
Thermal pad, mechanical data (Package|Pins)
- DRC|10
Orderable Information
8.1.6.1 Calculating the Sense Input (SI) Pin Threshold
To use the SI pin, connect this pin to the rail being monitored through a resistor divider. This input can be configured as an undervoltage supervisor that can monitor voltage rails greater than 1.2 V or used as an overvoltage supervisor with an inverted output. Table 8-1 lists typical 1% resistor values for undervoltage monitoring where the trip point is a 5% threshold. The resistor values can be scaled to decrease the amount of current flowing through the resistor divider, but increasing the resistor values also decreases the accuracy of the resistor divider. General practice is for the current flowing through the resistor divider to be 100 times greater than the current going into the SI pin. This practice ensures the highest possible accuracy. Equation 6 can be used to calculate the resistors required in the resistor divider for any desired falling threshold. Figure 8-4 depicts the typical timing for this comparator and Figure 8-5 illustrates a block diagram for the adjustable operation.
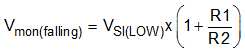
| INPUT VOLTAGE (V) | 5% THRESHOLD | ||
|---|---|---|---|
| R1 (kΩ) | R2 (kΩ) | THRESHOLD VOLTAGE (V) | |
| 3.3 | 18.2 | 10 | 3.13 |
| 5 | 32.4 | 10 | 4.71 |
| 6 | 41.2 | 10 | 5.68 |
| 7 | 49.9 | 10 | 6.65 |
| 8 | 59 | 10 | 7.66 |
| 9 | 66.5 | 10 | 8.49 |
| 10 | 75.5 | 10 | 9.49 |
| 11 | 80.6 | 10 | 10.06 |
| 12 | 93.1 | 10 | 11.44 |
| 13.5 | 105 | 10 | 12.77 |
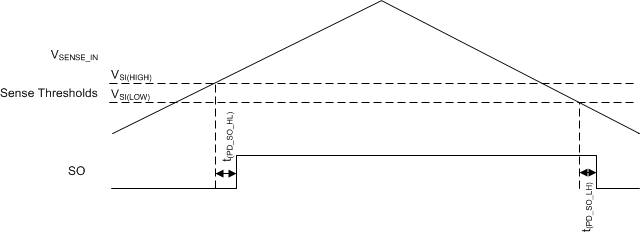 Figure 8-4 SI Timing Diagram
Figure 8-4 SI Timing Diagram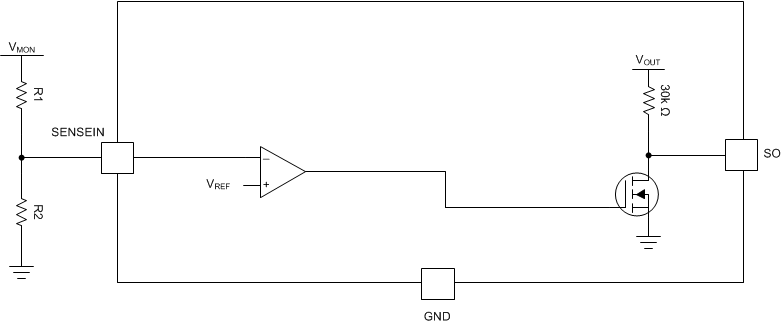 Figure 8-5 SI Basic Block Diagram
Figure 8-5 SI Basic Block Diagram