SLUSDG2 October 2018 TPS92515AHV-Q1
PRODUCTION DATA.
- 1 Features
- 2 Applications
- 3 Description
- 4 Revision History
- 5 Device Comparison Table
- 6 Pin Configuration and Functions
- 7 Specifications
-
8 Detailed Description
- 8.1 Overview
- 8.2 Functional Block Diagram
- 8.3
Feature Description
- 8.3.1 General Operation
- 8.3.2 Current Sense Comparator
- 8.3.3 OFF Timer
- 8.3.4 OFF-Timer, Shunt FET Dimming or Shunted Output Condition
- 8.3.5 Internal N-channel MOSFET
- 8.3.6 VCC Internal Regulator and Undervoltage Lockout (UVLO)
- 8.3.7 Analog Adjust Input
- 8.3.8 Thermal Protection
- 8.3.9 Junction Temperature Relative Estimation
- 8.3.10 BOOT and BOOT UVLO
- 8.3.11 PWM (UVLO and Enable)
- 8.4 Device Functional Modes
-
9 Application and Implementation
- 9.1 Application Information
- 9.2
Typical Application
- 9.2.1 General Design Procedure
- 9.2.2 Design Requirements
- 9.2.3
Detailed Design Procedure
- 9.2.3.1 Calculating Duty Cycle
- 9.2.3.2 Calculate OFF-Time Estimate
- 9.2.3.3 Calculate OFF-Time Resistor ROFF
- 9.2.3.4 Calculate the Inductance Value
- 9.2.3.5 Calculate the Sense Resistance
- 9.2.3.6 Calculate Input Capacitance
- 9.2.3.7 Verify Peak Current for Inductor Selection
- 9.2.3.8 Calculate Output Capacitance
- 9.2.3.9 Calculate UVLO Resistance Values
- 9.2.4 Application Curves
- 9.3 Dos and Don'ts
- 10Power Supply Recommendations
- 11Layout
- 12Device and Documentation Support
- 13Mechanical, Packaging, and Orderable Information
Package Options
Mechanical Data (Package|Pins)
- DGQ|10
Thermal pad, mechanical data (Package|Pins)
- DGQ|10
Orderable Information
9.2.4 Application Curves
Buck LED driver example: VOUT = 22 V (7 LEDs), IOUT = 1 A

| VLED = 22 V | IOUT = 1.0 A |

A. Ch1: SW Voltage; Ch2: VIN (DC Coupled);
Ch4: Inductor current; UVLO designed limit attained.
Time: 1 ms/div
Figure 36. Startup Transient Ch4: Inductor current; UVLO designed limit attained.
Time: 1 ms/div
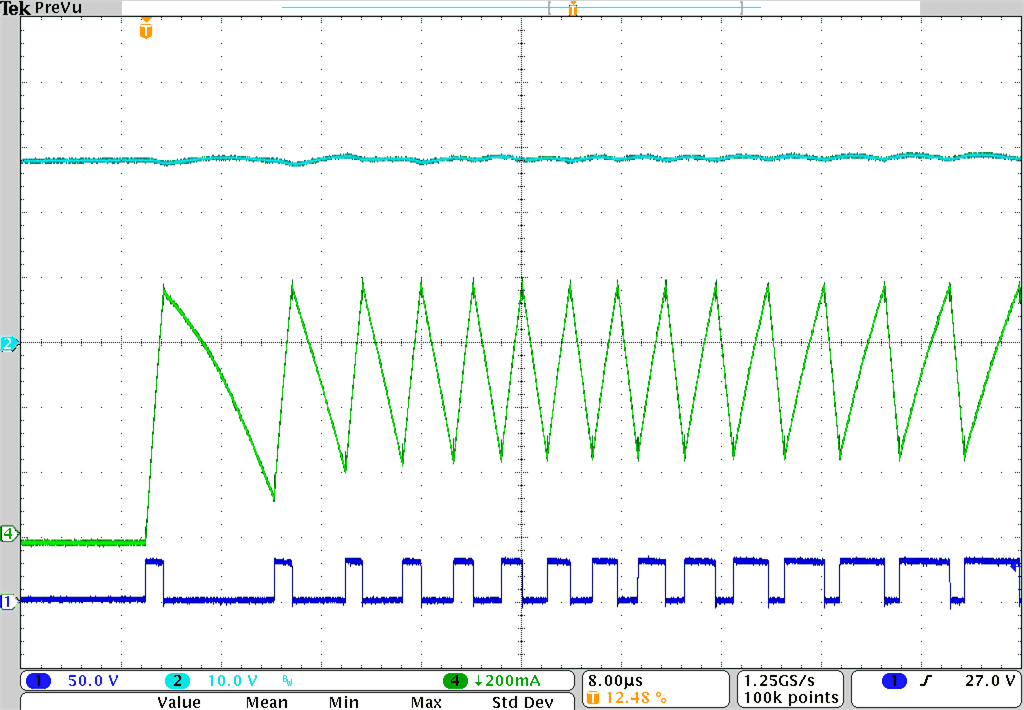
A. Ch1: SW Voltage; Ch2: VIN (DC Coupled);
Ch4: Inductor current;
Time: 8 µs/div
Figure 38. First 15 SW Node Pulses at Turn-On Ch4: Inductor current;
Time: 8 µs/div

A. Ch1: SW Voltage; Ch2: PWM pin;
Ch4: Inductor current;
Time: 10 µs/div
Figure 40. PWM Dimming: 250Hz, 1% Duty Cycle Ch4: Inductor current;
Time: 10 µs/div

A. Ch1: PWM Signal
Ch4: Inductor current; ΔIL-PP Maintained
Time: 20 µs/div
Figure 42. Shunt FET Dimming - Optimized Inductor Current Waveform Ch4: Inductor current; ΔIL-PP Maintained
Time: 20 µs/div

A. Ch1: SW Voltage; Ch2: VIN Ripple Voltage (AC Coupled);
Ch3: ILED-PP; Ch4: Inductor current;
Time: 1 µs/div
Figure 35. Normal Operation Ch3: ILED-PP; Ch4: Inductor current;
Time: 1 µs/div

A. Ch1: SW Voltage; Ch2: VIN (DC Coupled);
Ch4: Inductor current; UVLO designed limit attained.
Time: 1 ms/div
Figure 37. Shut-Down Transient Ch4: Inductor current; UVLO designed limit attained.
Time: 1 ms/div

A. Ch1: SW Voltage; Ch2: PWM pin;
Ch4: Inductor current;
Time: 10 µs/div
Figure 39. PWM Dimming: 250Hz, 0.25% Duty Cycle Ch4: Inductor current;
Time: 10 µs/div

A. Ch1: SW Voltage; Ch2: PWM pin;
Ch4: Inductor current;
Time: 1 ms/div
Figure 41. PWM Dimming: 250Hz, 50% Duty Cycle Ch4: Inductor current;
Time: 1 ms/div

A. Ch1: PWM Signal
Ch4: Inductor current; OFF-time reaching Maximum OFF-Time
Time: 400 µs/div
Figure 43. Shunt FET Dimming - Non-Optimized Inductor Current Ch4: Inductor current; OFF-time reaching Maximum OFF-Time
Time: 400 µs/div