SLVSG72 September 2021 TPSM560R6H
PRODUCTION DATA
- 1 Features
- 2 Applications
- 3 Description
- 4 Revision History
- 5 Pin Configuration and Functions
-
6 Specifications
- 6.1 Absolute Maximum Ratings
- 6.2 ESD Ratings
- 6.3 Recommended Operating Conditions
- 6.4 Thermal Information
- 6.5 Electrical Characteristics
- 6.6 Typical Characteristics (VIN = 12 V)
- 6.7 Typical Characteristics (VIN = 24 V)
- 6.8 Typical Characteristics (VIN = 48 V)
- 6.9 Typical Characteristics (VIN = 60 V)
- 7 Detailed Description
- 8 Applications and Implementation
- 9 Power Supply Recommendations
- 10Layout
- 11Device and Documentation Support
- 12Mechanical, Packaging, and Orderable Information
Package Options
Mechanical Data (Package|Pins)
- RDA|15
Thermal pad, mechanical data (Package|Pins)
Orderable Information
10.2.1 Theta JA Versus PCB Area
The amount of PCB copper as well as airflow affects the thermal performance of the device. Figure 10-5 shows the effects of copper area and airflow on the junction-to-ambient thermal resistance (RθJA) of the TPSM560R6H. The junction-to-ambient thermal resistance versus PCB area is plotted for a 4-layer PCB.
To determine the required copper area for an application:
- Determine the maximum power dissipation of the device in the application by referencing the power dissipation graphs in the Typical Characteristics.
- Calculate the maximum θJA using Equation 3 and the maximum ambient temperature of the application.
Equation 3.
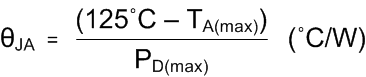
- Reference Figure 10-5 to determine the minimum required PCB area for the application conditions.
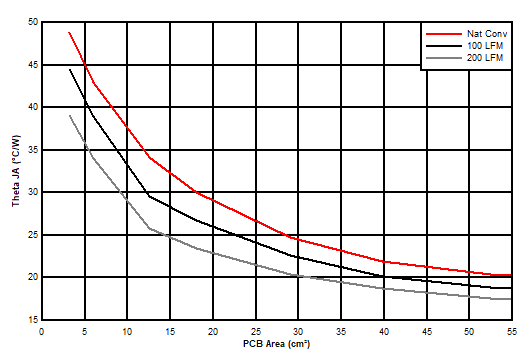 Figure 10-5 θJA Versus PCB Area
Figure 10-5 θJA Versus PCB Area