SLVSG66 November 2022 TPSM82902
PRODUCTION DATA
- 1 Features
- 2 Applications
- 3 Description
- 4 Revision History
- 5 Pin Configuration and Functions
- 6 Specifications
-
7 Detailed Description
- 7.1 Overview
- 7.2 Functional Block Diagram
- 7.3
Feature Description
- 7.3.1 Mode Selection and Device Configuration (MODE/S-CONF)
- 7.3.2 Adjustable VO Operation (External Voltage Divider)
- 7.3.3 Setable VO Operation (VSET and Internal Voltage Divider)
- 7.3.4 Soft Start/Tracking (SS/TR)
- 7.3.5 Smart Enable with Precise Threshold
- 7.3.6 Power Good (PG)
- 7.3.7 Undervoltage Lockout (UVLO)
- 7.3.8 Current Limit And Short Circuit Protection
- 7.3.9 Thermal Shutdown
- 7.4 Device Functional Modes
- 8 Application and Implementation
- 9 Device and Documentation Support
- 10Mechanical, Packaging, and Orderable Information
Package Options
Mechanical Data (Package|Pins)
- SIS|11
Thermal pad, mechanical data (Package|Pins)
Orderable Information
7.4.3 Power Save Mode Operation (Auto PFM/PWM)
When the MODE/S-CONF pin is configured for power save mode (auto PFM/PWM), the device operates in PWM mode as long the output current is higher than half of the ripple current of the inductor. To maintain high efficiency at light loads, the device enters power save mode at the boundary to discontinuous conduction mode (DCM). This happens if the output current becomes smaller than half of the ripple current of the inductor. The power save mode is entered seamlessly when the load current decreases. This makes sure there is a high efficiency in light load operation. The device remains in power save mode as long as the inductor current is discontinuous.
In power save mode, the switching frequency decreases linearly with the load current maintaining high efficiency. The transition in and out of power save mode is seamless in both directions.
In addition to adjusting the switching, the TPSM82902 adjusts the on time (TON) in power save mode, depending on the input voltage and the output voltage to maintain the highest efficiency using the AEE function when 2.5 MHz is selected as described in Section 7.4.2.
In power save mode, the TON time can be estimated using Equation 3 for 1 MHz and Equation 5 for 2.5 MHz (given the AEE is enabled for 2.5 MHz).
For very small output voltages, an absolute minimum on time of about 50 ns is kept to limit switching losses. The operating frequency is thereby reduced from its nominal value, which keeps efficiency high. Using TON, the typical peak inductor current in power save mode is approximated by Equation 7:

There is a minimum off time that limits the duty cycle of the TPSM82902. When VIN decreases to typically 15% above VOUT, the TPSM82902 does not enter power save mode, regardless of the load current. The device maintains output regulation in PWM mode.
The output voltage ripple in power save mode is given by Equation 8:
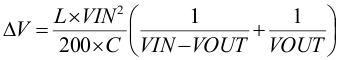
where
- L is the effective inductance (approximately 0.9 μF).
- C is the output effective capacitance.