SLUSCZ8A July 2017 – July 2024 UCC27212A-Q1
PRODUCTION DATA
- 1
- 1 Features
- 2 Applications
- 3 Description
- 4 Pin Configuration and Functions
- 5 Specifications
- 6 Detailed Description
- 7 Application and Implementation
- 8 Power Supply Recommendations
- 9 Layout
- 10Device and Documentation Support
- 11Revision History
- 12Mechanical, Packaging, and Orderable Information
Package Options
Mechanical Data (Package|Pins)
- DDA|8
Thermal pad, mechanical data (Package|Pins)
- DDA|8
Orderable Information
4 Pin Configuration and Functions
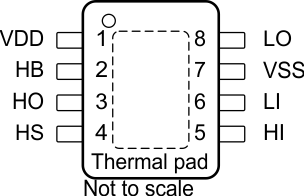 Figure 4-1 DDA Package8-Pin SO-PowerPADTop View
Figure 4-1 DDA Package8-Pin SO-PowerPADTop ViewTable 4-1 Pin Functions
| PIN | I/O | DESCRIPTION | |
|---|---|---|---|
| NO. | NAME | ||
| 2 | HB | P | High-side bootstrap supply. The bootstrap diode is on-chip but the external bootstrap capacitor is required. Connect positive side of the bootstrap capacitor to this pin. Typical range of HB bypass capacitor is 0.022µF to 0.1µF. The capacitor value is dependant on the gate charge of the high-side MOSFET and must also be selected based on speed and ripple criteria. |
| 5 | HI | I | High-side input.(1) |
| 3 | HO | O | High-side output. Connect to the gate of the high-side power MOSFET. |
| 4 | HS | P | High-side source connection. Connect to source of high-side power MOSFET. Connect the negative side of bootstrap capacitor to this pin. |
| 6 | LI | I | Low-side input.(1) |
| 8 | LO | O | Low-side output. Connect to the gate of the low-side power MOSFET. |
| 1 | VDD | P | Positive supply to the lower-gate driver. De-couple this pin to VSS (GND). Typical decoupling capacitor range is 0.22µF to 4.7µF (See (2)). |
| 7 | VSS | — | Negative supply terminal for the device that is generally grounded. |
| Pad | Thermal pad(3) | — | Electrically referenced to VSS (GND). Connect to a large thermal mass trace or GND plane to dramatically improve thermal performance. |
(1) HI or LI input is assumed to connect to a low impedance source
signal. The source output impedance is assumed less than 100Ω. If the source
impedance is greater than 100Ω, add a bypassing capacitor, each, between HI and
VSS and between LI and VSS. The added capacitor value depends on the noise
levels presented on the pins, typically from 1nF to 10nF should be effective to
eliminate the possible noise effect. When noise is present on two pins, HI or
LI, the effect is to cause HO and LO malfunctions to have wrong logic
outputs.
(2) For cold temperature applications TI recommends the upper
capacitance range. Follow the Section 9.1 for PCB layout.
(3) The thermal pad is not directly connected to any leads of the
package; however, it is electrically and thermally connected to the substrate
which is the ground of the device.