SLUSER8C June 2022 – March 2023 UCC28C50 , UCC28C51 , UCC28C52 , UCC28C53 , UCC28C54 , UCC28C55 , UCC28C56H , UCC28C56L , UCC28C57H , UCC28C57L , UCC28C58 , UCC28C59 , UCC38C50 , UCC38C51 , UCC38C52 , UCC38C53 , UCC38C54 , UCC38C55
PRODUCTION DATA
- 1 Features
- 2 Applications
- 3 Description
- 4 Revision History
- 5 Device Comparison Table
- 6 Pin Configuration and Functions
- 7 Specifications
-
8 Detailed Description
- 8.1 Overview
- 8.2 Functional Block Diagram
- 8.3
Feature Description
- 8.3.1 Detailed Pin Description
- 8.3.2 Undervoltage Lockout
- 8.3.3 ±1% Internal Reference Voltage
- 8.3.4 Current Sense and Overcurrent Limit
- 8.3.5 Reduced-Discharge Current Variation
- 8.3.6 Oscillator Synchronization
- 8.3.7 Soft-Start Timing
- 8.3.8 Enable and Disable
- 8.3.9 Slope Compensation
- 8.3.10 Voltage Mode
- 8.4 Device Functional Modes
-
9 Application and Implementation
- 9.1 Application Information
- 9.2
Typical Application
- 9.2.1 Design Requirements
- 9.2.2
Detailed Design Procedure
- 9.2.2.1 Input Bulk Capacitor and Minimum Bulk Voltage
- 9.2.2.2 Transformer Turns Ratio and Maximum Duty Cycle
- 9.2.2.3 Transformer Inductance and Peak Currents
- 9.2.2.4 Output Capacitor
- 9.2.2.5 Current Sensing Network
- 9.2.2.6 Gate Drive Resistor
- 9.2.2.7 VREF Capacitor
- 9.2.2.8 RT/CT
- 9.2.2.9 Start-Up Circuit
- 9.2.2.10 Voltage Feedback Compensation
- 9.2.3 Application Curves
- 9.3 Power Supply Recommendations
- 9.4 Layout
- 10Device and Documentation Support
- 11Mechanical, Packaging, and Orderable Information
Package Options
Mechanical Data (Package|Pins)
- D|8
Thermal pad, mechanical data (Package|Pins)
Orderable Information
9.2.2.5 Current Sensing Network
The current sensing network consists of the primary-side current sensing resistor (RCS), filtering components RCSF and CCSF, and optional RP. Typically, the direct current sense signal contains a large amplitude leading edge spike associated with the turnon of the main power MOSFET, reverse recovery of the output rectifier, and other factors including charging and discharging of parasitic capacitances. Therefore, CCSF and RCSF form a low-pass filter that provides immunity to suppress the leading edge spike. For this converter, CCSF is chosen to be 100 pF.
Without RP, RCS sets the maximum peak current in the transformer primary based on the maximum amplitude of the CS pin, which is specified to be 1 V. To achieve 1.36-A primary side peak current, a 0.75-Ω resistor is chosen for RCS.
The high current sense threshold of CS helps to provide better noise immunity to the system but also results in higher losses in the current sense resistor. These current sense losses can be minimized by injecting an offset voltage into the current sense signal using RP. RP and RCSF form a resistor divider network from the current sense signal to the reference voltage of the controller (VVREF) which adds an offset to the current sense voltage. This technique still achieves current mode control with cycle-by-cycle over-current protection. To calculate required offset value (VOFFSET), use Equation 16.
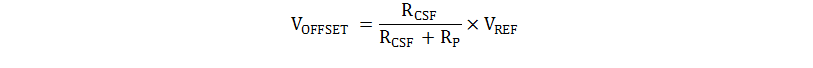
After adding the RP resistance, adjust the RCS value accordingly.