SBOS375D October 2006 – October 2024 XTR111
PRODUCTION DATA
- 1
- 1 Features
- 2 Applications
- 3 Description
- 4 Pin Configurations and Functions
- 5 Specifications
- 6 Detailed Description
- 7 Application and Implementation
- 8 Device and Documentation Support
- 9 Revision History
- 10Mechanical, Packaging, and Orderable Information
Package Options
Refer to the PDF data sheet for device specific package drawings
Mechanical Data (Package|Pins)
- DRC|10
- DGQ|10
Thermal pad, mechanical data (Package|Pins)
Orderable Information
7.1.1 Input Voltage
The input voltage range for a given output current span is set by RSET according to the transfer function. Select a precise and low-drift resistor for best performance because resistor drift directly converts into drift of the output current. Careful layout must also minimize any series resistance with RSET and the VIN reference point.
The input voltage is referred to the grounding point of RSET. Therefore, this point must not be distorted from other currents. Assuming a 5V full-scale input signal for a 20mA output current, RSET is 2.5kΩ. A resistance uncertainty of just 2.5Ω already degrades the accuracy to below 0.1%.
The linear input voltage range extends from 0V to 12V, or 2.3V less than the positive supply voltage (whichever is smaller). The lowest rated supply voltage accommodates an input voltage range of up to 5V. Potential clipping is not detected by an error signal; therefore, safe design guard banding is recommended.
Do not drive the input negative (referred to GND) greater than 300mV. Higher negative voltages turn on the internal protection diodes. Insert a resistor in series with the input if negative signals can occur eventually during power on or power off, or during other transient conditions. Select a resistor value that limits the possible current to 0.3mA. Higher currents are nondestructive (see Absolute Maximum Ratings), but can produce output current glitches unless in disable mode.
More protection against negative input signals is provided using a standard diode and a 2.2kΩ resistor, as shown in Figure 7-1.
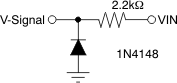 Figure 7-1 Enhanced
Protection Against Negative Overload of VIN
Figure 7-1 Enhanced
Protection Against Negative Overload of VIN