SBAS841 October 2017 ADS54J64
PRODUCTION DATA.
- 1 Features
- 2 Applications
- 3 Description
- 4 Revision History
- 5 Pin Configuration and Functions
-
6 Specifications
- 6.1 Absolute Maximum Ratings
- 6.2 ESD Ratings
- 6.3 Recommended Operating Conditions
- 6.4 Thermal Information
- 6.5 Electrical Characteristics
- 6.6 AC Performance
- 6.7 Digital Characteristics
- 6.8 Timing Characteristics
- 6.9 Typical Characteristics: DDC Bypass Mode
- 6.10 Typical Characteristics: Mode 2
- 6.11 Typical Characteristics: Mode 0
- 6.12 Typical Characteristics: Dual ADC Mode
-
7 Detailed Description
- 7.1 Overview
- 7.2 Functional Block Diagram
- 7.3 Feature Description
- 7.4
Device Functional Modes
- 7.4.1
Digital Functions
- 7.4.1.1 Numerically Controlled Oscillators (NCOs) and Mixers
- 7.4.1.2 Decimation Filter
- 7.4.1.3 Mode 0: Decimate-by-4 With IQ Outputs and fS / 4 Mixer
- 7.4.1.4 Mode 1: Decimate-by-4 With IQ Outputs and 16-Bit NCO
- 7.4.1.5 Mode 2: Decimate-by-4 With Real Output
- 7.4.1.6 Mode 3: Decimate-by-2 Real Output With Frequency Shift
- 7.4.1.7 Mode 4: Decimate-by-4 With Real Output
- 7.4.1.8 Mode 6: Decimate-by-4 With IQ Outputs for Up to 110 MHz of IQ Bandwidth
- 7.4.1.9 Mode 7: Decimate-by-4 With Real Output and Zero Stuffing
- 7.4.1.10 Mode 8: DDC Bypass Mode
- 7.4.1.11 Averaging Mode
- 7.4.1.12 Overrange Indication
- 7.4.1
Digital Functions
- 7.5 Programming
- 7.6
Register Maps
- 7.6.1
Register Map
- 7.6.1.1
Register Description
- 7.6.1.1.1
GLOBAL Page Register Description
- 7.6.1.1.1.1 Register 00h (address = 00h) [reset = 0h], GLOBAL Page
- 7.6.1.1.1.2 Register 04h (address = 04h) [reset = 0h], GLOBAL Page
- 7.6.1.1.1.3 Register 11h (address = 11h) [reset = 0h], GLOBAL Page
- 7.6.1.1.1.4 Register 12h (address = 12h) [reset = 0h], GLOBAL Page
- 7.6.1.1.1.5 Register 13h (address = 13h) [reset = 0h], GLOBAL Page
- 7.6.1.1.2
DIGTOP Page Register Description
- 7.6.1.1.2.1 Register 64h (address = 64h) [reset = 0h], DIGTOP Page
- 7.6.1.1.2.2 Register 8Dh (address = 8Dh) [reset = 0h], DIGTOP Page
- 7.6.1.1.2.3 Register 8Eh (address = 8Eh) [reset = 0h], DIGTOP Page
- 7.6.1.1.2.4 Register 8Fh (address = 8Fh) [reset = 0h], DIGTOP Page
- 7.6.1.1.2.5 Register 90h (address = 90h) [reset = 0h], DIGTOP Page
- 7.6.1.1.2.6 Register 91h (address = 91h) [reset = 0h], DIGTOP Page
- 7.6.1.1.2.7 Register A5h (address = A5h) [reset = 0h], DIGTOP Page
- 7.6.1.1.2.8 Register A6h (address = A6h) [reset = 0h], DIGTOP Page
- 7.6.1.1.2.9 Register ABh (address = ABh) [reset = 0h], DIGTOP Page
- 7.6.1.1.2.10 Register ACh (address = ACh) [reset = 0h], DIGTOP Page
- 7.6.1.1.2.11 Register ADh (address = ADh) [reset = 0h], DIGTOP Page
- 7.6.1.1.2.12 Register AEh (address = AEh) [reset = 0h], DIGTOP Page
- 7.6.1.1.2.13 Register B7h (address = B7h) [reset = 0h], DIGTOP Page
- 7.6.1.1.2.14 Register 8Ch (address = 8Ch) [reset = 0h], DIGTOP Page
- 7.6.1.1.3
ANALOG Page Register Description
- 7.6.1.1.3.1 Register 6Ah (address = 6Ah) [reset = 0h], ANALOG Page
- 7.6.1.1.3.2 Register 6Fh (address = 6Fh) [reset = 0h], ANALOG Page
- 7.6.1.1.3.3 Register 71h (address = 71h) [reset = 0h], ANALOG Page
- 7.6.1.1.3.4 Register 72h (address = 72h) [reset = 0h], ANALOG Page
- 7.6.1.1.3.5 Register 93h (address = 93h) [reset = 0h], ANALOG Page
- 7.6.1.1.3.6 Register 94h (address = 94h) [reset = 0h], ANALOG Page
- 7.6.1.1.3.7 Register 9Bh (address = 9Bh) [reset = 0h], ANALOG Page
- 7.6.1.1.3.8 Register 9Dh (address = 9Dh) [reset = 0h], ANALOG Page
- 7.6.1.1.3.9 Register 9Eh (address = 9Eh) [reset = 0h], ANALOG Page
- 7.6.1.1.3.10 Register 9Fh (address = 9Fh) [reset = 0h], ANALOG Page
- 7.6.1.1.3.11 Register AFh (address = AFh) [reset = 0h], ANALOG Page
- 7.6.1.1.4
SERDES_XX Page Register Description
- 7.6.1.1.4.1 Register 20h (address = 20h) [reset = 0h], SERDES_XX Page
- 7.6.1.1.4.2 Register 21h (address = 21h) [reset = 0h], SERDES_XX Page
- 7.6.1.1.4.3 Register 22h (address = 22h) [reset = 0h], SERDES_XX Page
- 7.6.1.1.4.4 Register 23h (address = 23h) [reset = 0h], SERDES_XX Page
- 7.6.1.1.4.5 Register 25h (address = 25h) [reset = 0h], SERDES_XX Page
- 7.6.1.1.4.6 Register 26h (address = 26h) [reset = 0h], SERDES_XX Page
- 7.6.1.1.4.7 Register 28h (address = 28h) [reset = 0h], SERDES_XX Page
- 7.6.1.1.4.8 Register 2Dh (address = 2Dh) [reset = 0h], SERDES_XX Page
- 7.6.1.1.4.9 Register 36h (address = 36h) [reset = 0h], SERDES_XX Page
- 7.6.1.1.4.10 Register 41h (address = 41h) [reset = 0h], SERDES_XX Page
- 7.6.1.1.4.11 Register 42h (address = 42h) [reset = 0h], SERDES_XX Page
- 7.6.1.1.5
CHX Page Register Description
- 7.6.1.1.5.1 Register 26h (address = 26h) [reset = 0h], CHX Page
- 7.6.1.1.5.2 Register 27h (address = 27h) [reset = 0h], CHX Page
- 7.6.1.1.5.3 Register 2Dh (address = 2Dh) [reset = 0h], CHX Page
- 7.6.1.1.5.4 Register 78h (address = 78h) [reset = 0h], CHX Page
- 7.6.1.1.5.5 Register 7Ah (address = 7Ah) [reset = 0h], CHX Page
- 7.6.1.1.5.6 Register 7Bh (address = 7Bh) [reset = 0h], CHX Page
- 7.6.1.1.5.7 Register 7Eh (address = 7Eh) [reset = 3h], CHX Page
- 7.6.1.1.6
ADCXX Page Register Description
- 7.6.1.1.6.1 Register 07h (address = 07h) [reset = FFh], ADCXX Page
- 7.6.1.1.6.2 Register 08h (address = 08h) [reset = 0h], ADCXX Page
- 7.6.1.1.6.3 Register D5h (address = D5h) [reset = 0h], ADCXX Page
- 7.6.1.1.6.4 Register 2Ah (address = 2Ah) [reset = 0h], ADCXX Page
- 7.6.1.1.6.5 Register CFh (address = CFh) [reset = 0h], ADCXX Page
- 7.6.1.1.1
GLOBAL Page Register Description
- 7.6.1.1
Register Description
- 7.6.1
Register Map
- 8 Application and Implementation
- 9 Power Supply Recommendations
- 10Layout
- 11Device and Documentation Support
- 12Mechanical, Packaging, and Orderable Information
Package Options
Mechanical Data (Package|Pins)
- RMP|72
Thermal pad, mechanical data (Package|Pins)
Orderable Information
1 Features
- Quad Channel, 14-Bit Resolution
- Maximum Sampling Rate: 1 GSPS
- Maximum Output Sample Rate: 500 MSPS
- High-Impedance Analog Input Buffer
- Analog Input Bandwidth (–3 dB): 1 GHz
- Output Options:
- Digital Down Conversion (DDC) Using 16-Bit NCO
- DDC Bypass With Full Rate Output Up to 500 MSPS
- Differential Full-Scale Input: 1.1 VPP
- JESD204B Interface:
- Subclass 1 Support
- 1 Lane per ADC Up to 10 Gbps
- Dedicated SYNC Pin for Pair of Channels
- Support for Multi-Chip Synchronization
- Spectral Performance:
- fIN = 190-MHz IF at –1 dBFS:
- SNR: 69 dBFS
- NSD: –153 dBFS/Hz
- SFDR: 86 dBc (HD2, HD3),
95 dBFS (Non HD2, HD3)
- fIN = 370-MHz IF at –3 dBFS:
- SNR: 68.5 dBFS
- NSD: –152.5 dBFS/Hz
- SFDR: 80 dBc (HD2, HD3),
86 dBFS (Non HD2, HD3)
- fIN = 190-MHz IF at –1 dBFS:
- 72-Pin VQFN Package (10 mm × 10 mm)
- Power Consumption: 625 mW/Ch, 2.5 W Total
- Power Supplies: 1.15 V, 1.15 V, 1.9 V
2 Applications
- Multi-Carrier Multi-Mode, GSM Cellular Infrastructure Base Stations
- Telecommunications Receivers
- Radar and Antenna Arrays
- Cable CMTS, DOCSIS 3.1 Receivers
- Communications Test Equipment
- Microwave Receivers
- Software Defined Radio (SDR)
- Digitizers
- Medical Imaging and Diagnostics
3 Description
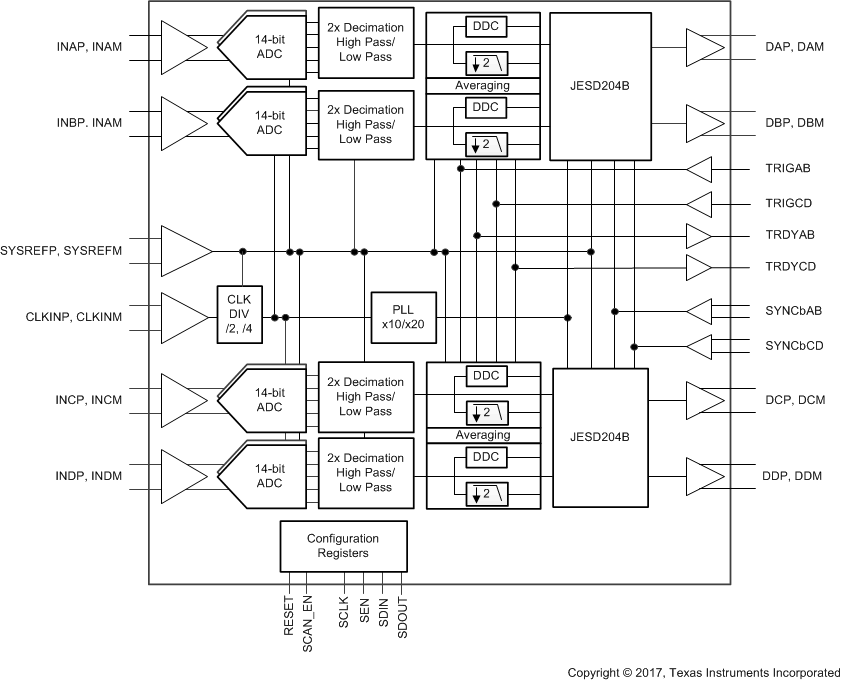
The ADS54J64 device is a quad-channel, 14-bit,
1-GSPS, analog-to-digital converter (ADC) offering wide-bandwidth, 2x oversampling and high SNR. The ADS54J64 supports a JESD204B serial interface with data rates up to 10 Gbps with one lane per channel. The buffered analog input provides uniform impedance across a wide frequency range and minimizes sample-and-hold glitch energy. The ADS54J64 provides excellent spurious-free dynamic range (SFDR) over a large input frequency range with very low power consumption. The digital signal processing block includes complex mixers followed by low-pass filters with decimate-by-2 and -4 options supporting up to a 200-MHz receive bandwidth. The ADS54J64 also supports a 14-bit, 500-MSPS output in DDC bypass mode.
A four-lane JESD204B interface simplifies connectivity, allowing high system integration density. An internal phase-locked loop (PLL) multiplies the incoming ADC sampling clock to derive the bit clock that is used to serialize the 14-bit data from each channel.
Device Information(1)
| PART NUMBER | PACKAGE | BODY SIZE (NOM) |
|---|---|---|
| ADS54J64 | VQFN (72) | 10.00 mm × 10.00 mm |
- For all available packages, see the orderable addendum at the end of the data sheet.
SPACE
SPACE
Simplified Block Diagram
4 Revision History
| DATE | REVISION | NOTES |
|---|---|---|
| October 2017 | * | Initial release. |