SBAS683B August 2014 – May 2020 ADS1120-Q1
PRODUCTION DATA.
- 1 Features
- 2 Applications
- 3 Description
- 4 Revision History
- 5 Pin Configuration and Functions
- 6 Specifications
- 7 Parameter Measurement Information
-
8 Detailed Description
- 8.1 Overview
- 8.2 Functional Block Diagram
- 8.3
Feature Description
- 8.3.1 Multiplexer
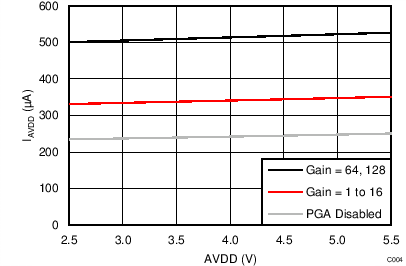
- 8.3.2 Low-Noise PGA
- 8.3.3 Modulator
- 8.3.4 Digital Filter
- 8.3.5 Output Data Rate
- 8.3.6 Voltage Reference
- 8.3.7 Clock Source
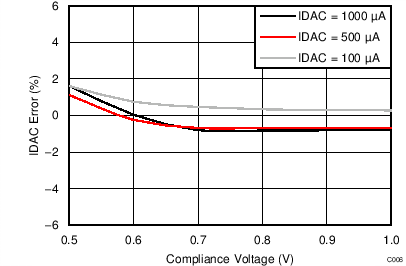
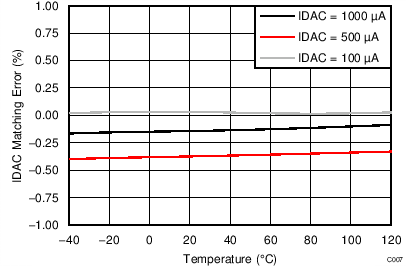
- 8.3.8 Excitation Current Sources
- 8.3.9 Low-Side Power Switch
- 8.3.10 Sensor Detection
- 8.3.11 System Monitor
- 8.3.12 Offset Calibration
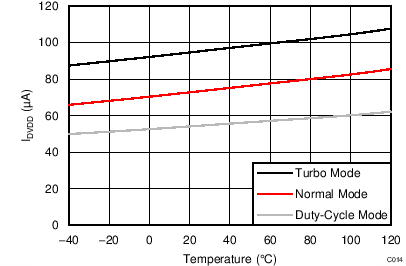
- 8.3.13 Power Supplies
- 8.3.14 Temperature Sensor
- 8.4 Device Functional Modes
- 8.5 Programming
- 8.6 Register Map
- 9 Application and Implementation
- 10Power Supply Recommendations
- 11Layout
- 12Device and Documentation Support
- 13Mechanical, Packaging, and Orderable Information
6.8 Typical Characteristics
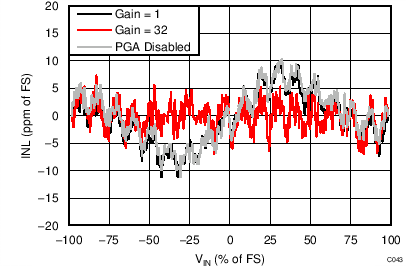
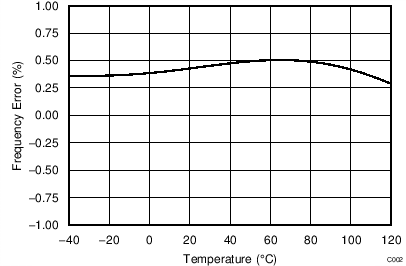
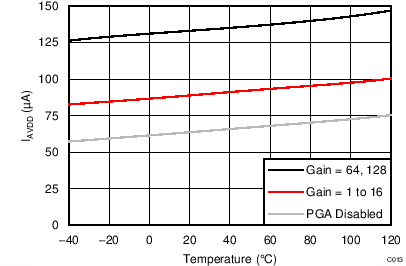
At TA = 25°C, AVDD = 3.3 V, AVSS = 0 V, and PGA enabled using external VREF = 2.5 V (unless otherwise noted).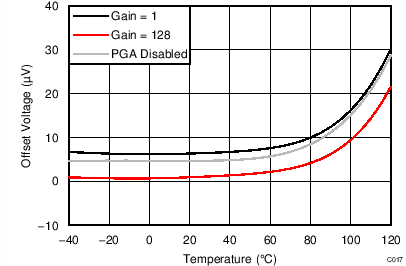
| AVDD = 3.3 V |
| AVDD = 3.3 V |
| AVDD = 3.3 V, external 2.5-V reference, normal mode |
Differential Input Signal
| AVDD = 3.3 V, internal reference, normal mode |
Differential Input Signal

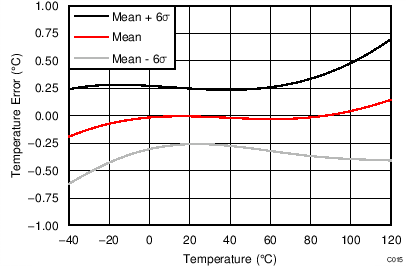
| TA = 25°C, data from 5490 devices |
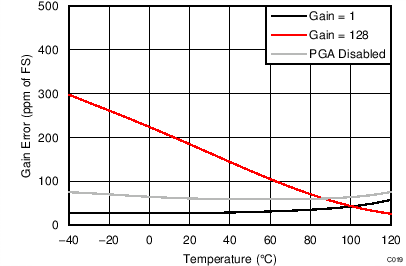
| DVDD = 3.3 V, normal mode |
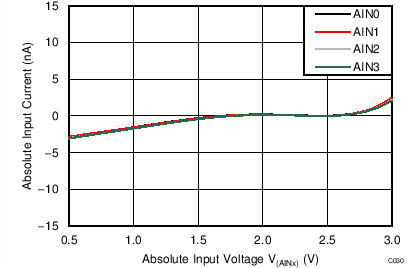
| AVDD = 3.3 V, PGA enabled, TA = –40°C |
Absolute Input Voltage
| AVDD = 3.3 V, PGA enabled, TA = 85°C |
Absolute Input Voltage
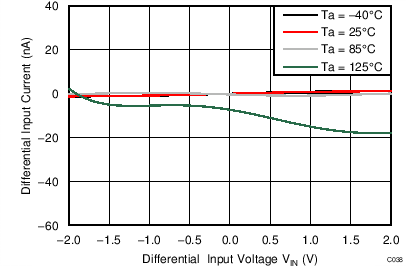
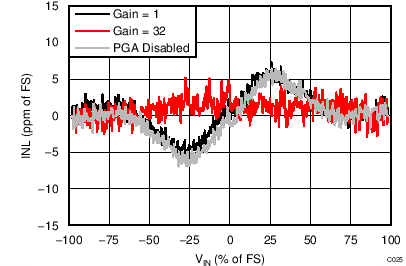
| AVDD = 3.3 V, PGA enabled, AINP = AIN0, AINN = AIN1 |
Differential Input Voltage
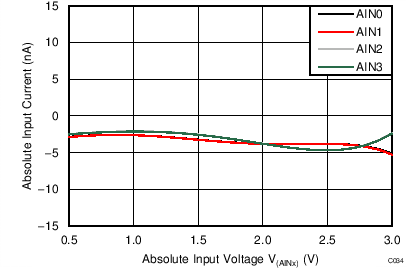
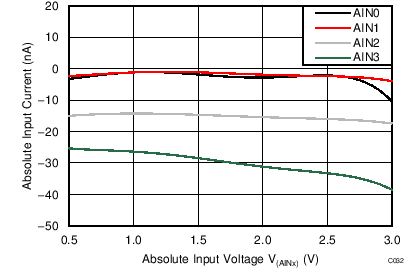
| AVDD = 3.3 V, PGA disabled, TA = –40°C |
Absolute Input Voltage
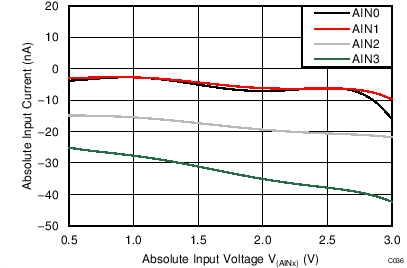
| AVDD = 3.3 V, PGA disabled, TA = 85°C |
Absolute Input Voltage
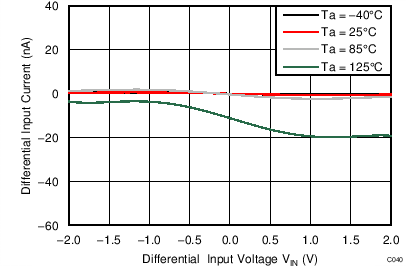
| AVDD = 3.3 V, PGA disabled, AINP = AIN0, AINN = AIN1 |
Differential Input Voltage

| AVDD = 3.3 V, internal reference, turbo mode |
| Normal mode, internal reference |
| DVDD = 3.3 V |
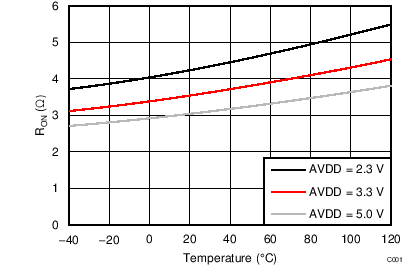
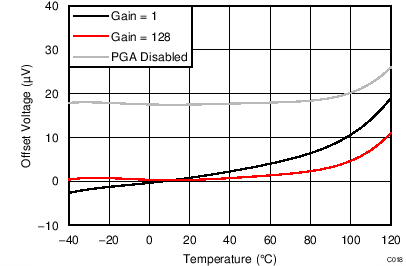
| AVDD = 5.0 V |

| AVDD = 5.0 V |
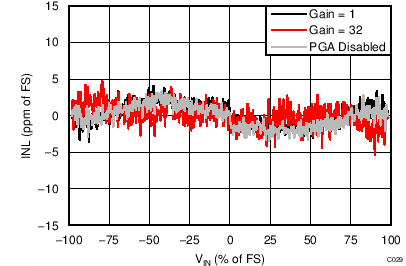
| AVDD = 5.0 V, external 2.5-V reference, normal mode |
Differential Input Signal

| AVDD = 5.0 V, internal reference, normal mode |
Differential Input Signal
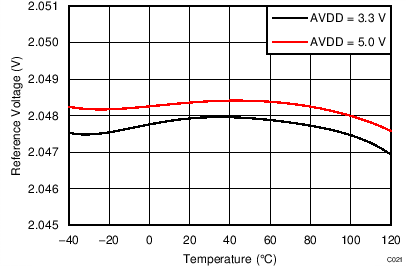
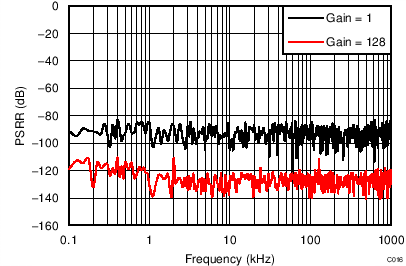
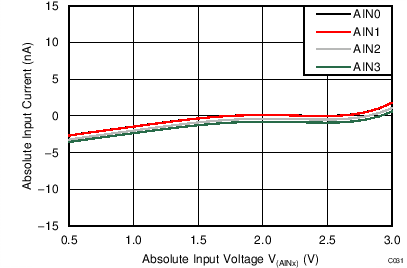
| AVDD = 3.3 V, PGA enabled, TA = 25°C |
Absolute Input Voltage
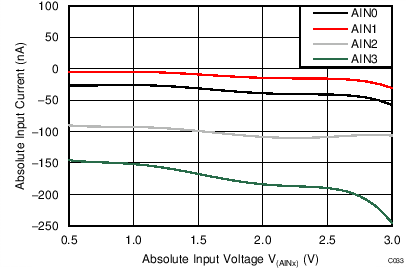
| AVDD = 3.3 V, PGA enabled, TA = 125°C |
Absolute Input Voltage
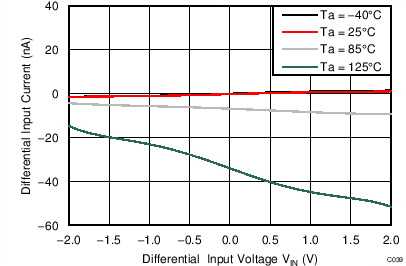
| AVDD = 3.3 V, PGA enabled, AINP = AIN3, AINN = AIN2 |
Differential Input Voltage
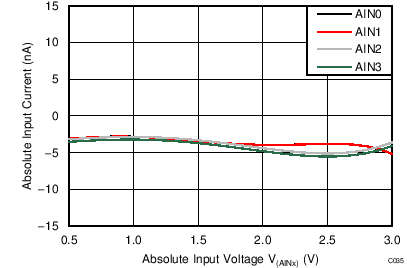
| AVDD = 3.3 V, PGA disabled, TA = 25°C |
Absolute Input Voltage
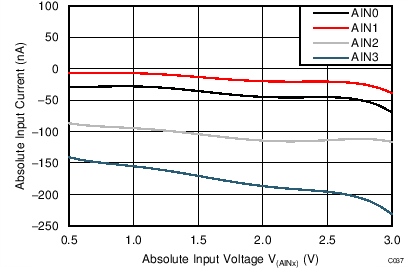
| AVDD = 3.3 V, PGA disabled, TA = 125°C |
Absolute Input Voltage

| AVDD = 3.3 V, PGA disabled, AINP = AIN3, AINN = AIN2 |
Differential Input Voltage
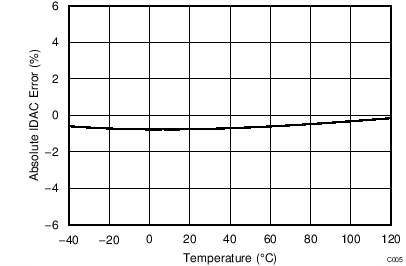
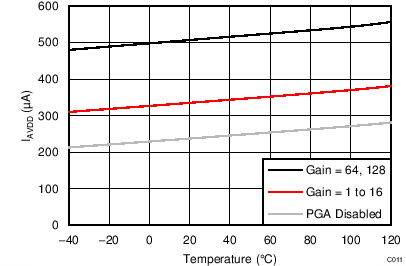
| AVDD = 3.3 V, internal reference, normal mode |
| AVDD = 3.3 V, internal reference, duty-cycle mode |