JAJSDZ0J October 2011 – April 2016 AM3351 , AM3352 , AM3354 , AM3356 , AM3357 , AM3358 , AM3359
PRODUCTION DATA.
- 1デバイスの概要
- 2改訂履歴
- 3Device Comparison
- 4Terminal Configuration and Functions
-
5Specifications
- 5.1 Absolute Maximum Ratings
- 5.2 ESD Ratings
- 5.3 Power-On Hours (POH)
- 5.4 Operating Performance Points (OPPs)
- 5.5 Recommended Operating Conditions
- 5.6 Power Consumption Summary
- 5.7 DC Electrical Characteristics
- 5.8 Thermal Resistance Characteristics for ZCE and ZCZ Packages
- 5.9 External Capacitors
- 5.10 Touch Screen Controller and Analog-to-Digital Subsystem Electrical Parameters
- 6Power and Clocking
-
7Peripheral Information and Timings
- 7.1 Parameter Information
- 7.2 Recommended Clock and Control Signal Transition Behavior
- 7.3 OPP50 Support
- 7.4 Controller Area Network (CAN)
- 7.5 DMTimer
- 7.6 Ethernet Media Access Controller (EMAC) and Switch
- 7.7
External Memory Interfaces
- 7.7.1 General-Purpose Memory Controller (GPMC)
- 7.7.2
mDDR(LPDDR), DDR2, DDR3, DDR3L Memory Interface
- 7.7.2.1 mDDR (LPDDR) Routing Guidelines
- 7.7.2.2
DDR2 Routing Guidelines
- 7.7.2.2.1 Board Designs
- 7.7.2.2.2
DDR2 Interface
- 7.7.2.2.2.1 DDR2 Interface Schematic
- 7.7.2.2.2.2 Compatible JEDEC DDR2 Devices
- 7.7.2.2.2.3 PCB Stackup
- 7.7.2.2.2.4 Placement
- 7.7.2.2.2.5 DDR2 Keepout Region
- 7.7.2.2.2.6 Bulk Bypass Capacitors
- 7.7.2.2.2.7 High-Speed (HS) Bypass Capacitors
- 7.7.2.2.2.8 Net Classes
- 7.7.2.2.2.9 DDR2 Signal Termination
- 7.7.2.2.2.10 DDR_VREF Routing
- 7.7.2.2.3 DDR2 CK and ADDR_CTRL Routing
- 7.7.2.3
DDR3 and DDR3L Routing Guidelines
- 7.7.2.3.1 Board Designs
- 7.7.2.3.2 DDR3 Device Combinations
- 7.7.2.3.3
DDR3 Interface
- 7.7.2.3.3.1 DDR3 Interface Schematic
- 7.7.2.3.3.2 Compatible JEDEC DDR3 Devices
- 7.7.2.3.3.3 PCB Stackup
- 7.7.2.3.3.4 Placement
- 7.7.2.3.3.5 DDR3 Keepout Region
- 7.7.2.3.3.6 Bulk Bypass Capacitors
- 7.7.2.3.3.7 High-Speed Bypass Capacitors
- 7.7.2.3.3.8 Net Classes
- 7.7.2.3.3.9 DDR3 Signal Termination
- 7.7.2.3.3.10 DDR_VREF Routing
- 7.7.2.3.3.11 VTT
- 7.7.2.3.4 DDR3 CK and ADDR_CTRL Topologies and Routing Definition
- 7.7.2.3.5 Data Topologies and Routing Definition
- 7.7.2.3.6 Routing Specification
- 7.8 I2C
- 7.9 JTAG Electrical Data and Timing
- 7.10 LCD Controller (LCDC)
- 7.11 Multichannel Audio Serial Port (McASP)
- 7.12 Multichannel Serial Port Interface (McSPI)
- 7.13 Multimedia Card (MMC) Interface
- 7.14 Programmable Real-Time Unit Subsystem and Industrial Communication Subsystem (PRU-ICSS)
- 7.15 Universal Asynchronous Receiver Transmitter (UART)
- 8Device and Documentation Support
- 9Mechanical, Packaging, and Orderable Information
パッケージ・オプション
デバイスごとのパッケージ図は、PDF版データシートをご参照ください。
メカニカル・データ(パッケージ|ピン)
- ZCZ|324
- ZCE|298
サーマルパッド・メカニカル・データ
発注情報
5 Specifications
5.1 Absolute Maximum Ratings
over junction temperature range (unless otherwise noted)(1)(2)| MIN | MAX | UNIT | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| VDD_MPU(3) | Supply voltage for the MPU core domain | –0.5 | 1.5 | V | |
| VDD_CORE | Supply voltage for the core domain | –0.5 | 1.5 | V | |
| CAP_VDD_RTC(4) | Supply voltage for the RTC core domain | –0.5 | 1.5 | V | |
| VPP(5) | Supply voltage for the FUSE ROM domain | –0.5 | 2.2 | V | |
| VDDS_RTC | Supply voltage for the RTC domain | –0.5 | 2.1 | V | |
| VDDS_OSC | Supply voltage for the System oscillator | –0.5 | 2.1 | V | |
| VDDS_SRAM_CORE_BG | Supply voltage for the Core SRAM LDOs | –0.5 | 2.1 | V | |
| VDDS_SRAM_MPU_BB | Supply voltage for the MPU SRAM LDOs | –0.5 | 2.1 | V | |
| VDDS_PLL_DDR | Supply voltage for the DPLL DDR | –0.5 | 2.1 | V | |
| VDDS_PLL_CORE_LCD | Supply voltage for the DPLL Core and LCD | –0.5 | 2.1 | V | |
| VDDS_PLL_MPU | Supply voltage for the DPLL MPU | –0.5 | 2.1 | V | |
| VDDS_DDR | Supply voltage for the DDR I/O domain | –0.5 | 2.1 | V | |
| VDDS | Supply voltage for all dual-voltage I/O domains | –0.5 | 2.1 | V | |
| VDDA1P8V_USB0 | Supply voltage for USBPHY | –0.5 | 2.1 | V | |
| VDDA1P8V_USB1(6) | Supply voltage for USBPHY | –0.5 | 2.1 | V | |
| VDDA_ADC | Supply voltage for ADC | –0.5 | 2.1 | V | |
| VDDSHV1 | Supply voltage for the dual-voltage I/O domain | –0.5 | 3.8 | V | |
| VDDSHV2(6) | Supply voltage for the dual-voltage I/O domain | –0.5 | 3.8 | V | |
| VDDSHV3(6) | Supply voltage for the dual-voltage I/O domain | –0.5 | 3.8 | V | |
| VDDSHV4 | Supply voltage for the dual-voltage I/O domain | –0.5 | 3.8 | V | |
| VDDSHV5 | Supply voltage for the dual-voltage I/O domain | –0.5 | 3.8 | V | |
| VDDSHV6 | Supply voltage for the dual-voltage I/O domain | –0.5 | 3.8 | V | |
| VDDA3P3V_USB0 | Supply voltage for USBPHY | –0.5 | 4 | V | |
| VDDA3P3V_USB1(6) | Supply voltage for USBPHY | –0.5 | 4 | V | |
| USB0_VBUS(7) | Supply voltage for USB VBUS comparator input | –0.5 | 5.25 | V | |
| USB1_VBUS(6)(7) | Supply voltage for USB VBUS comparator input | –0.5 | 5.25 | V | |
| DDR_VREF | Supply voltage for the DDR SSTL and HSTL reference voltage | –0.3 | 1.1 | V | |
| Steady state max voltage at all I/O pins(8) | –0.5 V to I/O supply voltage + 0.3 V | ||||
| USB0_ID(9) | Steady state maximum voltage for the USB ID input | –0.5 | 2.1 | V | |
| USB1_ID(6)(9) | Steady state maximum voltage for the USB ID input | –0.5 | 2.1 | V | |
| Transient overshoot and undershoot specification at I/O terminal | 25% of corresponding I/O supply voltage for up to 30% of signal period | ||||
| Latch-up performance(10) | Class II (105°C) | 45 | mA | ||
| Storage temperature, Tstg(11) | –55 | 155 | °C | ||
- Stresses beyond those listed under Absolute Maximum Ratings may cause permanent damage to the device. These are stress ratings only, and functional operation of the device at these or any other conditions beyond those indicated under Recommended Operating Conditions is not implied. Exposure to absolute-maximum-rated conditions for extended periods may affect device reliability.
- All voltage values are with respect to their associated VSS or VSSA_x.
- Not available on the ZCE package. VDD_MPU is merged with VDD_CORE on the ZCE package.
- This supply is sourced from an internal LDO when RTC_KALDO_ENn is low. If RTC_KALDO_ENn is high, this supply must be sourced from an external power supply.
- During functional operation, this pin is a no connect.
- Not available on the ZCE package.
- This terminal is connected to a fail-safe I/O and does not have a dependence on any I/O supply voltage.
- This parameter applies to all I/O terminals which are not fail-safe and the requirement applies to all values of I/O supply voltage. For example, if the voltage applied to a specific I/O supply is 0 volts the valid input voltage range for any I/O powered by that supply will be –0.5 to +0.3 V. Apply special attention anytime peripheral devices are not powered from the same power sources used to power the respective I/O supply. It is important the attached peripheral never sources a voltage outside the valid input voltage range, including power supply ramp-up and ramp-down sequences.
- This terminal is connected to analog circuits in the respective USB PHY. The circuit sources a known current while measuring the voltage to determine if the terminal is connected to VSSA_USB with a resistance less than 10 Ω or greater than 100 kΩ. The terminal should be connected to ground for USB host operation or open-circuit for USB peripheral operation, and should never be connected to any external voltage source.
- Based on JEDEC JESD78D [IC Latch-Up Test].
- For tape and reel the storage temperature range is [–10°C; +50°C] with a maximum relative humidity of 70%. TI recommends returning to ambient room temperature before usage.
Fail-safe I/O terminals are designed such they do not have dependencies on the respective I/O power supply voltage. This allows external voltage sources to be connected to these I/O terminals when the respective I/O power supplies are turned off. The USB0_VBUS and USB1_VBUS are the only fail-safe I/O terminals. All other I/O terminals are not fail-safe and the voltage applied to them should be limited to the value defined by the steady state max. Voltage at all I/O pins parameter in Section 5.1.
5.2 ESD Ratings
| VALUE | UNIT | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| VESD | Electrostatic discharge (ESD) performance: | Human Body Model (HBM), per ANSI/ESDA/JEDEC JS001(1) | ±2000 | V | |
| Charged Device Model (CDM), per JESD22-C101(2) | ±500 | ||||
5.3 Power-On Hours (POH)
Table 5-1 Reliability Data(1)(2)(3)(4)
| OPERATING CONDITION | COMMERCIAL | INDUSTRIAL | EXTENDED | INDUSTRIAL EXTENDED | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| JUNCTION TEMP (TJ) | LIFETIME (POH)(5) | JUNCTION TEMP (TJ) | LIFETIME (POH)(5) | JUNCTION TEMP (TJ) | LIFETIME (POH)(5) | JUNCTION TEMP (TJ) | LIFETIME (POH)(5) | |
| Nitro | 0°C to 90°C | 100K | –40°C to 90°C | 100K | –40°C to 105°C | 37K | –40°C to 125°C | – |
| Turbo | 0°C to 90°C | 100K | –40°C to 90°C | 100K | –40°C to 105°C | 80K | –40°C to 125°C | – |
| OPP120 | 0°C to 90°C | 100K | –40°C to 90°C | 100K | –40°C to 105°C | 100K | –40°C to 125°C | – |
| OPP100 | 0°C to 90°C | 100K | –40°C to 90°C | 100K | –40°C to 105°C | 100K | –40°C to 125°C | 35K |
| OPP50 | 0°C to 90°C | 100K | –40°C to 90°C | 100K | –40°C to 105°C | 100K | –40°C to 125°C | 95K |
- The power-on hours (POH) information in this table is provided solely for your convenience and does not extend or modify the warranty provided under TI's standard terms and conditions for TI semiconductor products.
- To avoid significant degradation, the device power-on hours (POH) must be limited as described in this table.
- Logic functions and parameter values are not assured out of the range specified in the recommended operating conditions.
- The previous notations cannot be deemed a warranty or deemed to extend or modify the warranty under TI's standard terms and conditions for TI semiconductor products.
- POH = Power-on hours when the device is fully functional.
5.4 Operating Performance Points (OPPs)
Device OPPs are defined in Table 5-2 through Table 5-9.
Table 5-2 VDD_CORE OPPs for ZCZ Package
With Device Revision Code "Blank"(1)
| VDD_CORE OPP Device Rev. "Blank" |
VDD_CORE | DDR3, DDR3L(2) | DDR2(2) | mDDR(2) | L3 and L4 | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| MIN | NOM | MAX | |||||
| OPP100 | 1.056 V | 1.100 V | 1.144 V | 400 MHz | 266 MHz | 200 MHz | 200 and 100 MHz |
| OPP50 | 0.912 V | 0.950 V | 0.988 V | — | 125 MHz | 90 MHz | 100 and 50 MHz |
- Frequencies in this table indicate maximum performance for a given OPP condition.
- This parameter represents the maximum memory clock frequency. Because data is transferred on both edges of the clock, double-data rate (DDR), the maximum data rate is two times the maximum memory clock frequency defined in this table.
Table 5-3 VDD_MPU OPPs for ZCZ Package
With Device Revision Code "Blank"(1)
| VDD_MPU OPP Device Rev. "Blank" |
VDD_MPU | ARM (A8) | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| MIN | NOM | MAX | ||
| Turbo | 1.210 V | 1.260 V | 1.326 V | 720 MHz |
| OPP120 | 1.152 V | 1.200 V | 1.248 V | 600 MHz |
| OPP100(2) | 1.056 V | 1.100 V | 1.144 V | 500 MHz |
| OPP100(3) | 1.056 V | 1.100 V | 1.144 V | 275 MHz |
- Frequencies in this table indicate maximum performance for a given OPP condition.
- Applies to all orderable AM335__ZCZ_50 (500-MHz speed grade) or higher devices.
- Applies to all orderable AM335__ZCZ_27 (275-MHz speed grade) devices.
Table 5-4 Valid Combinations of VDD_CORE and VDD_MPU OPPs for ZCZ Package
With Device Revision Code "Blank"
| VDD_CORE | VDD_MPU |
|---|---|
| OPP50 | OPP100 |
| OPP100 | OPP100 |
| OPP100 | OPP120 |
| OPP100 | Turbo |
Table 5-5 VDD_CORE OPPs for ZCE Package
With Device Revision Code "Blank"(1)
| VDD_CORE OPP Device Rev. "Blank" |
VDD_MPU(2) | ARM (A8) | DDR3, DDR3L(3) | DDR2(3) | mDDR(3) | L3 and L4 | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| MIN | NOM | MAX | ||||||
| OPP100 | 1.056 V | 1.100 V | 1.144 V | 500 MHz | 400 MHz | 266 MHz | 200 MHz | 200 and 100 MHz |
| OPP100 | 1.056 V | 1.100 V | 1.144 V | 275 MHz | 400 MHz | 266 MHz | 200 MHz | 200 and 100 MHz |
- Frequencies in this table indicate maximum performance for a given OPP condition.
- VDD_MPU is merged with VDD_CORE on the ZCE package.
- This parameter represents the maximum memory clock frequency. Because data is transferred on both edges of the clock, double-data rate (DDR), the maximum data rate is two times the maximum memory clock frequency defined in this table.
Table 5-6 VDD_CORE OPPs for ZCZ Package
With Device Revision Code "A" or Newer(1)
| VDD_CORE OPP Rev "A" or Newer |
VDD_CORE | DDR3, DDR3L(2) | DDR2(2) | mDDR(2) | L3 and L4 | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| MIN | NOM | MAX | |||||
| OPP100 | 1.056 V | 1.100 V | 1.144 V | 400 MHz | 266 MHz | 200 MHz | 200 and 100 MHz |
| OPP50 | 0.912 V | 0.950 V | 0.988 V | — | 125 MHz | 90 MHz | 100 and 50 MHz |
- Frequencies in this table indicate maximum performance for a given OPP condition.
- This parameter represents the maximum memory clock frequency. Because data is transferred on both edges of the clock, double-data rate (DDR), the maximum data rate is two times the maximum memory clock frequency defined in this table.
Table 5-7 VDD_MPU OPPs for ZCZ Package
With Device Revision Code "A" or Newer(1)
| VDD_MPU OPP
Rev "A" or Newer |
VDD_MPU | ARM (A8) | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| MIN | NOM | MAX | ||
| Nitro | 1.272 V | 1.325 V | 1.378 V | 1 GHz |
| Turbo | 1.210 V | 1.260 V | 1.326 V | 800 MHz |
| OPP120 | 1.152 V | 1.200 V | 1.248 V | 720 MHz |
| OPP100(2) | 1.056 V | 1.100 V | 1.144 V | 600 MHz |
| OPP100(3) | 1.056 V | 1.100 V | 1.144 V | 300 MHz |
| OPP50 | 0.912 V | 0.950 V | 0.988 V | 300 MHz |
- Frequencies in this table indicate maximum performance for a given OPP condition.
- Applies to all orderable AM335__ZCZ_60 (600-MHz speed grade) or higher devices.
- Applies to all orderable AM335__ZCZ_30 (300-MHz speed grade) devices.
Table 5-8 Valid Combinations of VDD_CORE and VDD_MPU OPPs for ZCZ Package With Device Revision Code "A" or Newer
| VDD_CORE | VDD_MPU |
|---|---|
| OPP50 | OPP50 |
| OPP50 | OPP100 |
| OPP100 | OPP50 |
| OPP100 | OPP100 |
| OPP100 | OPP120 |
| OPP100 | Turbo |
| OPP100 | Nitro |
Table 5-9 VDD_CORE OPPs for ZCE Package
With Device Revision Code "A" or Newer(1)
| VDD_CORE OPP Rev "A" or newer |
VDD_MPU(2) | ARM (A8) | DDR3, DDR3L(3) | DDR2(3) | mDDR(3) | L3 and L4 | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| MIN | NOM | MAX | ||||||
| OPP100 | 1.056 V | 1.100 V | 1.144 V | 600 MHz | 400 MHz | 266 MHz | 200 MHz | 200 and 100 MHz |
| OPP100 | 1.056 V | 1.100 V | 1.144 V | 300 MHz | 400 MHz | 266 MHz | 200 MHz | 200 and 100 MHz |
| OPP50 | 0.912 V | 0.950 V | 0.988 V | 300 MHz | – | 125 MHz | 90 MHz | 100 and 50 MHz |
- Frequencies in this table indicate maximum performance for a given OPP condition.
- VDD_MPU is merged with VDD_CORE on the ZCE package.
- This parameter represents the maximum memory clock frequency. Because data is transferred on both edges of the clock, double-data rate (DDR), the maximum data rate is two times the maximum memory clock frequency defined in this table.
5.5 Recommended Operating Conditions
over junction temperature range (unless otherwise noted)| SUPPLY NAME | DESCRIPTION | MIN | NOM | MAX | UNIT |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| VDD_CORE(1) | Supply voltage range for core domain; OPP100 | 1.056 | 1.100 | 1.144 | V |
| Supply voltage range for core domain; OPP50 | 0.912 | 0.950 | 0.988 | ||
| VDD_MPU(1)(2) | Supply voltage range for MPU domain, Nitro | 1.272 | 1.325 | 1.378 | V |
| Supply voltage range for MPU domain; Turbo | 1.210 | 1.260 | 1.326 | ||
| Supply voltage range for MPU domain; OPP120 | 1.152 | 1.200 | 1.248 | ||
| Supply voltage range for MPU domain; OPP100 | 1.056 | 1.100 | 1.144 | ||
| Supply voltage range for MPU domain; OPP50 | 0.912 | 0.950 | 0.988 | ||
| CAP_VDD_RTC(3) | Supply voltage range for RTC domain input | 0.900 | 1.100 | 1.250 | V |
| VDDS_RTC | Supply voltage range for RTC domain | 1.710 | 1.800 | 1.890 | V |
| VDDS_DDR | Supply voltage range for DDR I/O domain (DDR2) | 1.710 | 1.800 | 1.890 | V |
| Supply voltage range for DDR I/O domain (DDR3) | 1.425 | 1.500 | 1.575 | ||
| Supply voltage range for DDR I/O domain (DDR3L) | 1.283 | 1.350 | 1.418 | ||
| VDDS(4) | Supply voltage range for all dual-voltage I/O domains | 1.710 | 1.800 | 1.890 | V |
| VDDS_SRAM_CORE_BG | Supply voltage range for Core SRAM LDOs, analog | 1.710 | 1.800 | 1.890 | V |
| VDDS_SRAM_MPU_BB | Supply voltage range for MPU SRAM LDOs, analog | 1.710 | 1.800 | 1.890 | V |
| VDDS_PLL_DDR(5) | Supply voltage range for DPLL DDR, analog | 1.710 | 1.800 | 1.890 | V |
| VDDS_PLL_CORE_LCD(5) | Supply voltage range for DPLL CORE and LCD, analog | 1.710 | 1.800 | 1.890 | V |
| VDDS_PLL_MPU(5) | Supply voltage range for DPLL MPU, analog | 1.710 | 1.800 | 1.890 | V |
| VDDS_OSC | Supply voltage range for system oscillator I/Os, analog | 1.710 | 1.800 | 1.890 | V |
| VDDA1P8V_USB0(5) | Supply voltage range for USBPHY and PER DPLL, analog, 1.8 V | 1.710 | 1.800 | 1.890 | V |
| VDDA1P8V_USB1(6) | Supply voltage range for USB PHY, analog, 1.8 V | 1.710 | 1.800 | 1.890 | V |
| VDDA3P3V_USB0 | Supply voltage range for USB PHY, analog, 3.3 V | 3.135 | 3.300 | 3.465 | V |
| VDDA3P3V_USB1(6) | Supply voltage range for USB PHY, analog, 3.3 V | 3.135 | 3.300 | 3.465 | V |
| VDDA_ADC | Supply voltage range for ADC, analog | 1.710 | 1.800 | 1.890 | V |
| VDDSHV1 | Supply voltage range for dual-voltage I/O domain (1.8-V operation) | 1.710 | 1.800 | 1.890 | V |
| VDDSHV2(6) | Supply voltage range for dual-voltage I/O domain (1.8-V operation) | 1.710 | 1.800 | 1.890 | V |
| VDDSHV3(6) | Supply voltage range for dual-voltage I/O domain (1.8-V operation) | 1.710 | 1.800 | 1.890 | V |
| VDDSHV4 | Supply voltage range for dual-voltage I/O domain (1.8-V operation) | 1.710 | 1.800 | 1.890 | V |
| VDDSHV5 | Supply voltage range for dual-voltage I/O domain (1.8-V operation) | 1.710 | 1.800 | 1.890 | V |
| VDDSHV6 | Supply voltage range for dual-voltage I/O domain (1.8-V operation) | 1.710 | 1.800 | 1.890 | V |
| VDDSHV1 | Supply voltage range for dual-voltage I/O domain (3.3-V operation) | 3.135 | 3.300 | 3.465 | V |
| VDDSHV2(6) | Supply voltage range for dual-voltage I/O domain (3.3-V operation) | 3.135 | 3.300 | 3.465 | V |
| VDDSHV3(6) | Supply voltage range for dual-voltage I/O domain (3.3-V operation) | 3.135 | 3.300 | 3.465 | V |
| VDDSHV4 | Supply voltage range for dual-voltage I/O domain (3.3-V operation) | 3.135 | 3.300 | 3.465 | V |
| VDDSHV5 | Supply voltage range for dual-voltage I/O domain (3.3-V operation) | 3.135 | 3.300 | 3.465 | V |
| VDDSHV6 | Supply voltage range for dual-voltage I/O domain (3.3-V operation) | 3.135 | 3.300 | 3.465 | V |
| DDR_VREF | Voltage range for DDR SSTL and HSTL reference input (DDR2, DDR3, DDR3L) | 0.49 × VDDS_DDR | 0.50 × VDDS_DDR | 0.51 × VDDS_DDR | V |
| USB0_VBUS | Voltage range for USB VBUS comparator input | 0.000 | 5.000 | 5.250 | V |
| USB1_VBUS(6) | Voltage range for USB VBUS comparator input | 0.000 | 5.000 | 5.250 | V |
| USB0_ID | Voltage range for the USB ID input | (7) | V | ||
| USB1_ID(6) | Voltage range for the USB ID input | (7) | V | ||
| Operating temperature range, TJ | Commercial temperature | 0 | 90 | °C | |
| Industrial temperature | –40 | 90 | |||
| Extended temperature | –40 | 105 |
- The supply voltage defined by OPP100 should be applied to this power domain before the device is released from reset.
- Not available on the ZCE package. VDD_MPU is merged with VDD_CORE on the ZCE package.
- This supply is sourced from an internal LDO when RTC_KALDO_ENn is low. If RTC_KALDO_ENn is high, this supply must be sourced from an external power supply.
- VDDS should be supplied irrespective of 1.8- or 3.3-V mode of operation of the dual-voltage I/Os.
- For more details on power supply requirements, see Section 6.1.4.
- Not available on the ZCE package.
- This terminal is connected to analog circuits in the respective USB PHY. The circuit sources a known current while measuring the voltage to determine if the terminal is connected to VSSA_USB with a resistance less than 10 Ω or greater than 100 kΩ. The terminal should be connected to ground for USB host operation or open-circuit for USB peripheral operation, and should never be connected to any external voltage source.
5.6 Power Consumption Summary
Table 5-10 summarizes the power consumption at the AM335x power terminals.
Table 5-10 Maximum Current Ratings at AM335x Power Terminals(1)
| SUPPLY NAME | DESCRIPTION | MAX | UNIT | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| VDD_CORE(2) | Maximum current rating for the core domain; OPP100 | 400 | mA | |
| Maximum current rating for the core domain; OPP50 | 250 | |||
| VDD_MPU(2) | Maximum current rating for the MPU domain; Nitro | at 1 GHz | 1000 | mA |
| Maximum current rating for the MPU domain; Turbo | at 800 MHz | 800 | ||
| at 720 MHz | 720 | |||
| Maximum current rating for the MPU domain; OPP120 | at 720 MHz | 720 | ||
| at 600 MHz | 600 | |||
| Maximum current rating for the MPU domain; OPP100 | at 600 MHz | 600 | ||
| at 500 MHz | 500 | |||
| at 300 MHz | 380 | |||
| at 275 MHz | 350 | |||
| Maximum current rating for the MPU domain; OPP50 | at 300 MHz | 330 | ||
| at 275 MHz | 300 | |||
| CAP_VDD_RTC(3) | Maximum current rating for RTC domain input and LDO output | 2 | mA | |
| VDDS_RTC | Maximum current rating for the RTC domain | 5 | mA | |
| VDDS_DDR | Maximum current rating for DDR I/O domain | 250 | mA | |
| VDDS | Maximum current rating for all dual-voltage I/O domains | 50 | mA | |
| VDDS_SRAM_CORE_BG | Maximum current rating for core SRAM LDOs | 10 | mA | |
| VDDS_SRAM_MPU_BB | Maximum current rating for MPU SRAM LDOs | 10 | mA | |
| VDDS_PLL_DDR | Maximum current rating for the DPLL DDR | 10 | mA | |
| VDDS_PLL_CORE_LCD | Maximum current rating for the DPLL Core and LCD | 20 | mA | |
| VDDS_PLL_MPU | Maximum current rating for the DPLL MPU | 10 | mA | |
| VDDS_OSC | Maximum current rating for the system oscillator I/Os | 5 | mA | |
| VDDA1P8V_USB0 | Maximum current rating for USBPHY 1.8 V | 25 | mA | |
| VDDA1P8V_USB1(4) | Maximum current rating for USBPHY 1.8 V | 25 | mA | |
| VDDA3P3V_USB0 | Maximum current rating for USBPHY 3.3 V | 40 | mA | |
| VDDA3P3V_USB1(4) | Maximum current rating for USBPHY 3.3 V | 40 | mA | |
| VDDA_ADC | Maximum current rating for ADC | 10 | mA | |
| VDDSHV1(5) | Maximum current rating for dual-voltage I/O domain | 50 | mA | |
| VDDSHV2(4) | Maximum current rating for dual-voltage I/O domain | 50 | mA | |
| VDDSHV3(4) | Maximum current rating for dual-voltage I/O domain | 50 | mA | |
| VDDSHV4 | Maximum current rating for dual-voltage I/O domain | 50 | mA | |
| VDDSHV5 | Maximum current rating for dual-voltage I/O domain | 50 | mA | |
| VDDSHV6 | Maximum current rating for dual-voltage I/O domain | 100 | mA | |
- Current ratings specified in this table are worst-case estimates. Actual application power supply estimates could be lower. For more information, see AM335x Power Consumption Summary.
- VDD_MPU is merged with VDD_CORE and is not available separately on the ZCE package. The maximum current rating for VDD_CORE on the ZCE package is the sum of VDD_CORE and VDD_MPU shown in this table.
- This supply is sourced from an internal LDO when RTC_KALDO_ENn is low. If RTC_KALDO_ENn is high, this supply must be sourced from an external power supply.
- Not available on the ZCE package.
- VDDSHV1 and VDDSHV2 are merged in the ZCE package. The maximum current rating for VDDSHV1 on the ZCE package is the sum of VDDSHV1 and VDDSHV2 shown in this table.
Table 5-11 summarizes the power consumption of the AM335x low-power modes.
Table 5-11 AM335x Low-Power Modes Power Consumption Summary
| POWER MODES | APPLICATION STATE | POWER DOMAINS, CLOCKS, AND VOLTAGE SUPPLY STATES | NOM | MAX | UNIT |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Standby | DDR memory is in self-refresh and contents are preserved. Wake up from any GPIO. Cortex-A8 context/register contents are lost and must be saved before entering standby. On exit, context must be restored from DDR. For wakeup, boot ROM executes and branches to system resume. | Power supplies:
|
16.5 | 22.0 | mW |
| Deepsleep1 | On-chip peripheral registers are preserved. Cortex-A8 context/registers are lost, so the application must save them to the L3 OCMC RAM or DDR before entering DeepSleep. DDR is in self-refresh. For wakeup, boot ROM executes and branches to system resume. | Power supplies:
|
6.0 | 10.0 | mW |
| Deepsleep0 | PD_PER peripheral and Cortex-A8/MPU register information will be lost. On-chip peripheral register (context) information of PD-PER domain must be saved by application to SDRAM before entering this mode. DDR is in self-refresh. For wakeup, boot ROM executes and branches to peripheral context restore followed by system resume. | Power supplies:
|
3.0 | 4.3 | mW |
5.7 DC Electrical Characteristics
over recommended ranges of supply voltage and operating temperature (unless otherwise noted)(1)| PARAMETER | MIN | NOM | MAX | UNIT | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| DDR_RESETn,DDR_CSn0,DDR_CKE,DDR_CK,DDR_CKn,DDR_CASn,DDR_RASn,DDR_WEn,DDR_BA0,DDR_BA1,DDR_BA2,DDR_A0,DDR_A1,DDR_A2,DDR_A3,DDR_A4,DDR_A5,DDR_A6,DDR_A7,DDR_A8,DDR_A9,DDR_A10,DDR_A11,DDR_A12,DDR_A13,DDR_A14,DDR_A15,DDR_ODT,DDR_D0,DDR_D1,DDR_D2,DDR_D3,DDR_D4,DDR_D5,DDR_D6,DDR_D7,DDR_D8,DDR_D9,DDR_D10,DDR_D11,DDR_D12,DDR_D13,DDR_D14,DDR_D15,DDR_DQM0,DDR_DQM1,DDR_DQS0,DDR_DQSn0,DDR_DQS1,DDR_DQSn1 Pins (mDDR - LVCMOS Mode) | ||||||
| VIH | High-level input voltage | 0.65 × VDDS_DDR | V | |||
| VIL | Low-level input voltage | 0.35 × VDDS_DDR | V | |||
| VHYS | Hysteresis voltage at an input | 0.07 | 0.25 | V | ||
| VOH | High level output voltage, driver enabled, pullup or pulldown disabled | IOH = 8 mA | VDDS_DDR – 0.4 | V | ||
| VOL | Low level output voltage, driver enabled, pullup or pulldown disabled | IOL = 8 mA | 0.4 | V | ||
| II | Input leakage current, Receiver disabled, pullup or pulldown inhibited | 10 | µA | |||
| Input leakage current, Receiver disabled, pullup enabled | –240 | –80 | ||||
| Input leakage current, Receiver disabled, pulldown enabled | 80 | 240 | ||||
| IOZ | Total leakage current through the terminal connection of a driver-receiver combination that may include a pullup or pulldown. The driver output is disabled and the pullup or pulldown is inhibited. | 10 | µA | |||
| DDR_RESETn,DDR_CSn0,DDR_CKE,DDR_CK,DDR_CKn,DDR_CASn,DDR_RASn,DDR_WEn,DDR_BA0,DDR_BA1,DDR_BA2,DDR_A0,DDR_A1,DDR_A2,DDR_A3,DDR_A4,DDR_A5,DDR_A6,DDR_A7,DDR_A8,DDR_A9,DDR_A10,DDR_A11,DDR_A12,DDR_A13,DDR_A14,DDR_A15,DDR_ODT,DDR_D0,DDR_D1,DDR_D2,DDR_D3,DDR_D4,DDR_D5,DDR_D6,DDR_D7,DDR_D8,DDR_D9,DDR_D10,DDR_D11,DDR_D12,DDR_D13,DDR_D14,DDR_D15,DDR_DQM0,DDR_DQM1,DDR_DQS0,DDR_DQSn0,DDR_DQS1,DDR_DQSn1 Pins (DDR2 - SSTL Mode) | ||||||
| VIH | High-level input voltage | DDR_VREF + 0.125 | V | |||
| VHYS | Hysteresis voltage at an input | N/A | V | |||
| VOH | High-level output voltage, driver enabled, pullup or pulldown disabled | IOH = 8 mA | VDDS_DDR – 0.4 | V | ||
| VOL | Low-level output voltage, driver enabled, pullup or pulldown disabled | IOL = 8 mA | 0.4 | V | ||
| II | Input leakage current, Receiver disabled, pullup or pulldown inhibited | 10 | µA | |||
| Input leakage current, Receiver disabled, pullup enabled | –240 | –80 | ||||
| Input leakage current, Receiver disabled, pulldown enabled | 80 | 240 | ||||
| IOZ | Total leakage current through the terminal connection of a driver-receiver combination that may include a pullup or pulldown. The driver output is disabled and the pullup or pulldown is inhibited. | 10 | µA | |||
| DDR_RESETn,DDR_CSn0,DDR_CKE,DDR_CK,DDR_CKn,DDR_CASn,DDR_RASn,DDR_WEn,DDR_BA0,DDR_BA1,DDR_BA2,DDR_A0,DDR_A1,DDR_A2,DDR_A3,DDR_A4,DDR_A5,DDR_A6,DDR_A7,DDR_A8,DDR_A9,DDR_A10,DDR_A11,DDR_A12,DDR_A13,DDR_A14,DDR_A15,DDR_ODT,DDR_D0,DDR_D1,DDR_D2,DDR_D3,DDR_D4,DDR_D5,DDR_D6,DDR_D7,DDR_D8,DDR_D9,DDR_D10,DDR_D11,DDR_D12,DDR_D13,DDR_D14,DDR_D15,DDR_DQM0,DDR_DQM1,DDR_DQS0,DDR_DQSn0,DDR_DQS1,DDR_DQSn1 Pins (DDR3, DDR3L - HSTL Mode) | ||||||
| VIH | High-level input voltage | VDDS_DDR = 1.5 V | DDR_VREF + 0.1 | V | ||
| VDDS_DDR = 1.35 V | DDR_VREF + 0.09 | |||||
| VIL | Low-level input voltage | VDDS_DDR = 1.5 V | DDR_VREF – 0.1 | V | ||
| VDDS_DDR = 1.35 V | DDR_VREF – 0.09 | |||||
| VHYS | Hysteresis voltage at an input | N/A | V | |||
| VOH | High-level output voltage, driver enabled, pullup or pulldown disabled | IOH = 8 mA | VDDS_DDR – 0.4 | V | ||
| VOL | Low-level output voltage, driver enabled, pullup or pulldown disabled | IOL = 8 mA | 0.4 | V | ||
| II | Input leakage current, Receiver disabled, pullup or pulldown inhibited | 10 | µA | |||
| Input leakage current, Receiver disabled, pullup enabled | –240 | –80 | ||||
| Input leakage current, Receiver disabled, pulldown enabled | 80 | 240 | ||||
| IOZ | Total leakage current through the terminal connection of a driver-receiver combination that may include a pullup or pulldown. The driver output is disabled and the pullup or pulldown is inhibited. | 10 | µA | |||
| ECAP0_IN_PWM0_OUT,UART0_CTSn,UART0_RTSn,UART0_RXD,UART0_TXD,UART1_CTSn,UART1_RTSn,UART1_RXD,UART1_TXD,I2C0_SDA,I2C0_SCL,XDMA_EVENT_INTR0,XDMA_EVENT_INTR1,WARMRSTn,EXTINTn,TMS,TDO,USB0_DRVVBUS,USB1_DRVVBUS (VDDSHV6 = 1.8 V) | ||||||
| VIH | High-level input voltage | 0.65 × VDDSHV6 | V | |||
| VIL | Low-level input voltage | 0.35 × VDDSHV6 | V | |||
| VHYS | Hysteresis voltage at an input | 0.18 | 0.305 | V | ||
| VOH | High-level output voltage, driver enabled, pullup or pulldown disabled | IOH = 4 mA | VDDSHV6 – 0.45 | V | ||
| VOL | Low-level output voltage, driver enabled, pullup or pulldown disabled | IOL = 4 mA | 0.45 | V | ||
| II | Input leakage current, Receiver disabled, pullup or pulldown inhibited | 8 | µA | |||
| Input leakage current, Receiver disabled, pullup enabled | –161 | –100 | –52 | |||
| Input leakage current, Receiver disabled, pulldown enabled | 52 | 100 | 170 | |||
| IOZ | Total leakage current through the terminal connection of a driver-receiver combination that may include a pullup or pulldown. The driver output is disabled and the pullup or pulldown is inhibited. | 8 | µA | |||
| ECAP0_IN_PWM0_OUT,UART0_CTSn,UART0_RTSn,UART0_RXD,UART0_TXD,UART1_CTSn,UART1_RTSn,UART1_RXD,UART1_TXD,I2C0_SDA,I2C0_SCL,XDMA_EVENT_INTR0,XDMA_EVENT_INTR1,WARMRSTn,EXTINTn,TMS,TDO,USB0_DRVVBUS,USB1_DRVVBUS (VDDSHV6 = 3.3 V) | ||||||
| VIH | High-level input voltage | 2 | V | |||
| VIL | Low-level input voltage | 0.8 | V | |||
| VHYS | Hysteresis voltage at an input | 0.265 | 0.44 | V | ||
| VOH | High-level output voltage, driver enabled, pullup or pulldown disabled | IOH = 4 mA | VDDSHV6 – 0.45 | V | ||
| VOL | Low-level output voltage, driver enabled, pullup or pulldown disabled | IOL = 4 mA | 0.45 | V | ||
| II | Input leakage current, Receiver disabled, pullup or pulldown inhibited | 18 | µA | |||
| Input leakage current, Receiver disabled, pullup enabled | –243 | –100 | –19 | |||
| Input leakage current, Receiver disabled, pulldown enabled | 51 | 110 | 210 | |||
| IOZ | Total leakage current through the terminal connection of a driver-receiver combination that may include a pullup or pulldown. The driver output is disabled and the pullup or pulldown is inhibited. | 18 | µA | |||
| TCK (VDDSHV6 = 1.8 V) | ||||||
| VIH | High-level input voltage | 1.45 | V | |||
| VIL | Low-level input voltage | 0.46 | V | |||
| VHYS | Hysteresis voltage at an input | 0.4 | V | |||
| II | Input leakage current, Receiver disabled, pullup or pulldown inhibited | 8 | µA | |||
| Input leakage current, Receiver disabled, pullup enabled | –161 | –100 | –52 | |||
| Input leakage current, Receiver disabled, pulldown enabled | 52 | 100 | 170 | |||
| TCK (VDDSHV6 = 3.3 V) | ||||||
| VIH | High-level input voltage | 2.15 | V | |||
| VIL | Low-level input voltage | 0.46 | V | |||
| VHYS | Hysteresis voltage at an input | 0.4 | V | |||
| II | Input leakage current, Receiver disabled, pullup or pulldown inhibited | 18 | µA | |||
| Input leakage current, Receiver disabled, pullup enabled | –243 | –100 | –19 | |||
| Input leakage current, Receiver disabled, pulldown enabled | 51 | 110 | 210 | |||
| PWRONRSTn (VDDSHV6 = 1.8 or 3.3 V)(2) | ||||||
| VIH | High-level input voltage | 1.35 | V | |||
| VIL | Low-level input voltage | 0.5 | V | |||
| VHYS | Hysteresis voltage at an input | 0.07 | V | |||
| II | Input leakage current | VI = 1.8 V | 0.1 | µA | ||
| VI = 3.3 V | 2 | |||||
| RTC_PWRONRSTn | ||||||
| VIH | High-level input voltage | 0.65 × VDDS_RTC | V | |||
| VIL | Low-level input voltage | 0.35 × VDDS_RTC | V | |||
| VHYS | Hysteresis voltage at an input | 0.065 | V | |||
| II | Input leakage current | –1 | 1 | µA | ||
| PMIC_POWER_EN | ||||||
| VOH | High-level output voltage, driver enabled, pullup or pulldown disabled | IOH = 6 mA | VDDS_RTC – 0.45 | V | ||
| VOL | Low-level output voltage, driver enabled, pullup or pulldown disabled | IOL = 6 mA | 0.45 | V | ||
| II | Input leakage current, Receiver disabled, pullup or pulldown inhibited | –1 | 1 | µA | ||
| Input leakage current, Receiver disabled, pullup enabled | –200 | –40 | ||||
| Input leakage current, Receiver disabled, pulldown enabled | 40 | 200 | ||||
| IOZ | Total leakage current through the terminal connection of a driver-receiver combination that may include a pullup or pulldown. The driver output is disabled and the pullup or pulldown is inhibited. | –1 | 1 | µA | ||
| EXT_WAKEUP | ||||||
| VIH | High-level input voltage | 0.65 × VDDS_RTC | V | |||
| VIL | Low-level input voltage | 0.35 × VDDS_RTC | V | |||
| VHYS | Hysteresis voltage at an input | 0.15 | V | |||
| II | Input leakage current, Receiver disabled, pullup or pulldown inhibited | –1 | 1 | µA | ||
| Input leakage current, Receiver disabled, pullup enabled | –200 | –40 | ||||
| Input leakage current, Receiver disabled, pulldown enabled | 40 | 200 | ||||
| XTALIN (OSC0) | ||||||
| VIH | High-level input voltage | 0.65 × VDDS_OSC | V | |||
| VIL | Low-level input voltage | 0.35 × VDDS_OSC | V | |||
| RTC_XTALIN (OSC1) | ||||||
| VIH | High-level input voltage | 0.65 × VDDS_RTC | V | |||
| VIL | Low-level input voltage | 0.35 × VDDS_RTC | V | |||
| All other LVCMOS pins (VDDSHVx = 1.8 V; x = 1 to 6) | ||||||
| VIH | High-level input voltage | 0.65 × VDDSHVx | V | |||
| VIL | Low-level input voltage | 0.35 × VDDSHVx | V | |||
| VHYS | Hysteresis voltage at an input | 0.18 | 0.305 | V | ||
| VOH | High-level output voltage, driver enabled, pullup or pulldown disabled | IOH = 6 mA | VDDSHVx – 0.45 | V | ||
| VOL | Low-level output voltage, driver enabled, pullup or pulldown disabled | IOL = 6 mA | 0.45 | V | ||
| II | Input leakage current, Receiver disabled, pullup or pulldown inhibited | 8 | µA | |||
| Input leakage current, Receiver disabled, pullup enabled | –161 | –100 | –52 | |||
| Input leakage current, Receiver disabled, pulldown enabled | 52 | 100 | 170 | |||
| IOZ | Total leakage current through the terminal connection of a driver-receiver combination that may include a pullup or pulldown. The driver output is disabled and the pullup or pulldown is inhibited. | 8 | µA | |||
| All other LVCMOS pins (VDDSHVx = 3.3 V; x = 1 to 6) | ||||||
| VIH | High-level input voltage | 2 | V | |||
| VIL | Low-level input voltage | 0.8 | V | |||
| VHYS | Hysteresis voltage at an input | 0.265 | 0.44 | V | ||
| VOH | High-level output voltage, driver enabled, pullup or pulldown disabled | IOH = 6 mA | VDDSHVx – 0.45 | V | ||
| VOL | Low-level output voltage, driver enabled, pullup or pulldown disabled | IOL = 6 mA | 0.45 | V | ||
| II | Input leakage current, Receiver disabled, pullup or pulldown inhibited | 18 | µA | |||
| Input leakage current, Receiver disabled, pullup enabled | –243 | –100 | –19 | |||
| Input leakage current, Receiver disabled, pulldown enabled | 51 | 110 | 210 | |||
| IOZ | Total leakage current through the terminal connection of a driver-receiver combination that may include a pullup or pulldown. The driver output is disabled and the pullup or pulldown is inhibited. | 18 | µA | |||
- The interfaces or signals described in this table correspond to the interfaces or signals available in multiplexing mode 0. All interfaces or signals multiplexed on the terminals described in this table have the same DC electrical characteristics.
- The input voltage thresholds for this input are not a function of VDDSHV6.
5.8 Thermal Resistance Characteristics for ZCE and ZCZ Packages
Failure to maintain a junction temperature within the range specified in Section 5.5 reduces operating lifetime, reliability, and performance—and may cause irreversible damage to the system. Therefore, the product design cycle should include thermal analysis to verify the maximum operating junction temperature of the device. It is important this thermal analysis is performed using specific system use cases and conditions. TI provides an application report to aid users in overcoming some of the existing challenges of producing a good thermal design. For more information, see AM335x Thermal Considerations.
Table 5-12 provides thermal characteristics for the packages used on this device.
NOTE
Table 5-12 provides simulation data and may not represent actual use-case values.
Table 5-12 Thermal Resistance Characteristics (PBGA Package) [ZCE and ZCZ]
| ZCE (°C/W)(1)(2) | ZCZ (°C/W)(1)(2) | AIR FLOW (m/s)(3) | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| RΘJC | Junction-to-case | 10.3 | 10.2 | N/A |
| RΘJB | Junction-to-board | 11.6 | 12.1 | N/A |
| RΘJA | Junction-to-free air | 24.7 | 24.2 | 0 |
| 20.5 | 20.1 | 1.0 | ||
| 19.7 | 19.3 | 2.0 | ||
| 19.2 | 18.8 | 3.0 | ||
| φJT | Junction-to-package top | 0.4 | 0.3 | 0.0 |
| 0.6 | 0.6 | 1.0 | ||
| 0.7 | 0.7 | 2.0 | ||
| 0.9 | 0.8 | 3.0 | ||
| φJB | Junction-to-board | 11.9 | 12.7 | 0.0 |
| 11.7 | 12.3 | 1.0 | ||
| 11.7 | 12.3 | 2.0 | ||
| 11.6 | 12.2 | 3.0 |
- JESD51-2, Integrated Circuits Thermal Test Method Environmental Conditions - Natural Convection (Still Air)
- JESD51-3, Low Effective Thermal Conductivity Test Board for Leaded Surface Mount Packages
- JESD51-7, High Effective Thermal Conductivity Test Board for Leaded Surface Mount Packages
- JESD51-9, Test Boards for Area Array Surface Mount Package Thermal Measurements
5.9 External Capacitors
To improve module performance, decoupling capacitors are required to suppress the switching noise generated by high frequency and to stabilize the supply voltage. A decoupling capacitor is most effective when it is close to the device, because this minimizes the inductance of the circuit board wiring and interconnects.
5.9.1 Voltage Decoupling Capacitors
Table 5-13 summarizes the Core voltage decoupling characteristics.
5.9.1.1 Core Voltage Decoupling Capacitors
To improve module performance, decoupling capacitors are required to suppress high-frequency switching noise and to stabilize the supply voltage. A decoupling capacitor is most effective when located close to the AM335x device, because this minimizes the inductance of the circuit board wiring and interconnects.
Table 5-13 Core Voltage Decoupling Characteristics
| PARAMETER | TYP | UNIT |
|---|---|---|
| CVDD_CORE(1) | 10.08 | μF |
| CVDD_MPU(2)(3) | 10.05 | μF |
- The typical value corresponds to one capacitor of 10 μF and eight capacitors of 10 nF.
- Not available on the ZCE package. VDD_MPU is merged with VDD_CORE on the ZCE package.
- The typical value corresponds to one capacitor of 10 μF and five capacitors of 10 nF.
5.9.1.2 I/O and Analog Voltage Decoupling Capacitors
Table 5-14 summarizes the power-supply decoupling capacitor recommendations.
Table 5-14 Power-Supply Decoupling Capacitor Characteristics
| PARAMETER | TYP | UNIT |
|---|---|---|
| CVDDA_ADC | 10 | nF |
| CVDDA1P8V_USB0 | 10 | nF |
| CCVDDA3P3V_USB0 | 10 | nF |
| CVDDA1P8V_USB1(1) | 10 | nF |
| CVDDA3P3V_USB1(1) | 10 | nF |
| CVDDS(2) | 10.04 | μF |
| CVDDS_DDR | (3) | |
| CVDDS_OSC | 10 | nF |
| CVDDS_PLL_DDR | 10 | nF |
| CVDDS_PLL_CORE_LCD | 10 | nF |
| CVDDS_SRAM_CORE_BG(4) | 10.01 | μF |
| CVDDS_SRAM_MPU_BB(5) | 10.01 | μF |
| CVDDS_PLL_MPU | 10 | nF |
| CVDDS_RTC | 10 | nF |
| CVDDSHV1(6) | 10.02 | μF |
| CVDDSHV2(1)(6) | 10.02 | μF |
| CVDDSHV3(1)(6) | 10.02 | μF |
| CVDDSHV4(6) | 10.02 | μF |
| CVDDSHV5(6) | 10.02 | μF |
| CVDDSHV6(7) | 10.06 | μF |
- Not available on the ZCE package.
- Typical values consist of one capacitor of 10 μF and four capacitors of 10 nF.
- For more details on decoupling capacitor requirements for the mDDR(LPDDR), DDR2, DDR3, DDR3L memory interface, see Section 7.7.2.1.2.6 and Section 7.7.2.1.2.7 when using mDDR(LPDDR) memory devices, Section 7.7.2.2.2.6 and Section 7.7.2.2.2.7 when using DDR2 memory devices, or Section 7.7.2.3.3.6 and Section 7.7.2.3.3.7 when using DDR3 or DDR3L memory devices.
- VDDS_SRAM_CORE_BG supply powers an internal LDO for SRAM supplies. Inrush currents could cause voltage drop on the VDDS_SRAM_CORE_BG supplies when the SRAM LDO is enabled after powering up VDDS_SRAM_CORE_BG terminals. A 10 µF is recommended to be placed close to the terminal and routed with widest traces possible to minimize the voltage drop on VDDS_SRAM_CORE_BG terminals.
- VDDS_SRAM_MPU_BB supply powers an internal LDO for SRAM supplies. Inrush currents could cause voltage drop on the VDDS_SRAM_MPU_BB supplies when the SRAM LDO is enabled after powering up VDDS_SRAM_MPU_BB terminals. A 10 µF is recommended to be placed close to the terminal and routed with widest traces possible to minimize the voltage drop on VDDS_SRAM_MPU_BB terminals.
- Typical values consist of one capacitor of 10 μF and two capacitors of 10 nF.
- Typical values consist of one capacitor of 10 μF and six capacitors of 10 nF.
5.9.2 Output Capacitors
Internal low dropout output (LDO) regulators require external capacitors to stabilize their outputs. These capacitors should be placed as close as possible to the respective terminals of the AM335x device. Table 5-15 summarizes the LDO output capacitor recommendations.
Table 5-15 Output Capacitor Characteristics
| PARAMETER | TYP | UNIT |
|---|---|---|
| CCAP_VDD_SRAM_CORE(1) | 1 | μF |
| CCAP_VDD_RTC(1)(2) | 1 | μF |
| CCAP_VDD_SRAM_MPU(1) | 1 | μF |
| CCAP_VBB_MPU(1) | 1 | μF |
- LDO regulator outputs should not be used as a power source for any external components.
- The CAP_VDD_RTC terminal operates as an input to the RTC core voltage domain when the RTC_KLDO_ENn terminal is high.
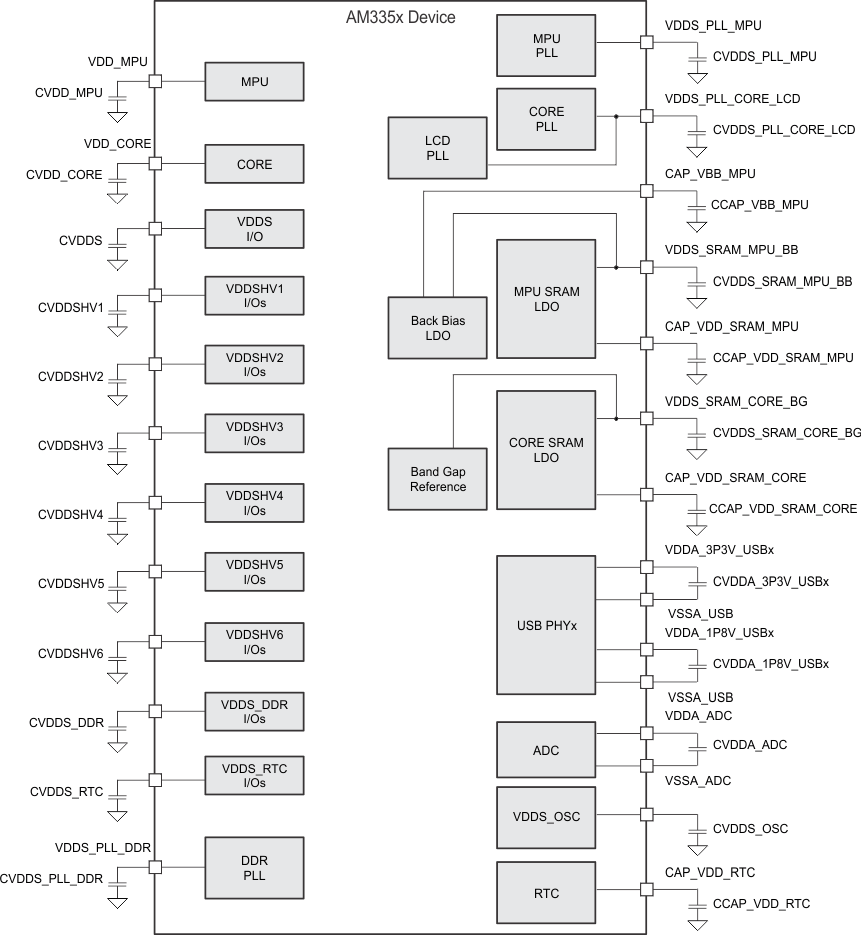
Figure 5-1 shows an example of the external capacitors.
5.10 Touch Screen Controller and Analog-to-Digital Subsystem Electrical Parameters
The touch screen controller (TSC) and analog-to-digital converter (ADC) subsystem (TSC_ADC) is an 8-channel general-purpose ADC with optional support for interleaving TSC conversions for 4-wire, 5-wire, or 8-wire resistive panels. The TSC_ADC subsystem can be configured for use in one of the following applications:
- 8 general-purpose ADC channels
- 4-wire TSC with 4 general-purpose ADC channels
- 5-wire TSC with 3 general-purpose ADC channels
- 8-wire TSC.
Table 5-16 summarizes the TSC_ADC subsystem electrical parameters.
Table 5-16 TSC_ADC Electrical Parameters
| PARAMETER | TEST CONDITIONS | MIN | NOM | MAX | UNIT |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Analog Input | |||||
| VREFP(1) | (0.5 × VDDA_ADC) + 0.25 | VDDA_ADC | V | ||
| VREFN(1) | 0 | (0.5 × VDDA_ADC) – 0.25 | V | ||
| VREFP + VREFN(1) | VDDA_ADC | V | |||
| Full-scale input range | Internal voltage reference | 0 | VDDA_ADC | V | |
| External voltage reference | VREFN | VREFP | |||
| Differential nonlinearity (DNL) | Internal voltage reference: VDDA_ADC = 1.8 V External voltage reference: VREFP – VREFN = 1.8 V |
–1 | 0.5 | 1 | LSB |
| Integral nonlinearity (INL) | Source impedance = 50 Ω Internal voltage reference: VDDA_ADC = 1.8 V External voltage reference: VREFP – VREFN = 1.8 V |
–2 | ±1 | 2 | LSB |
| Source impedance = 1 kΩ Internal voltage reference: VDDA_ADC = 1.8 V External voltage reference: VREFP – VREFN = 1.8 V |
±1 | ||||
| Gain error | Internal voltage reference: VDDA_ADC = 1.8 V External voltage reference: VREFP – VREFN = 1.8 V |
±2 | LSB | ||
| Offset error | Internal voltage reference: VDDA_ADC = 1.8 V External voltage reference: VREFP – VREFN = 1.8 V |
±2 | LSB | ||
| Input sampling capacitance | 5.5 | pF | |||
| Signal-to-noise ratio (SNR) | Internal voltage reference: VDDA_ADC = 1.8 V External voltage reference: VREFP – VREFN = 1.8 V Input signal: 30-kHz sine wave at –0.5-dB full scale |
70 | dB | ||
| Total harmonic distortion (THD) | Internal voltage reference: VDDA_ADC = 1.8 V External voltage reference: VREFP – VREFN = 1.8 V Input signal: 30-kHz sine wave at –0.5-dB full scale |
75 | dB | ||
| Spurious free dynamic range | Internal voltage reference: VDDA_ADC = 1.8 V External voltage reference: VREFP – VREFN = 1.8 V Input signal: 30-kHz sine wave at –0.5-dB full scale |
80 | dB | ||
| Signal-to-noise plus distortion | Internal voltage reference: VDDA_ADC = 1.8 V External voltage reference: VREFP – VREFN = 1.8 V Input signal: 30-kHz sine wave at –0.5-dB full scale |
69 | dB | ||
| VREFP and VREFN input impedance | 20 | kΩ | |||
| Input impedance of AIN[7:0](2) | ƒ = Input frequency | [1 / ((65.97 × 10–12) × ƒ)] | Ω | ||
| Sampling Dynamics | |||||
| Conversion time | 15 | ADC clock cycles | |||
| Acquisition time | 2 | ADC clock cycles | |||
| Sampling rate | ADC clock = 3 MHz | 200 | kSPS | ||
| Channel-to-channel isolation | 100 | dB | |||
| Touch Screen Switch Drivers | |||||
| Pullup and pulldown switch ON resistance (Ron) | 2 | Ω | |||
| Pullup and pulldown switch current leakage Ileak | Source impedance = 500 Ω | 0.5 | uA | ||
| Drive current | 25 | mA | |||
| Touch screen resistance | 6 | kΩ | |||
| Pen touch detect | 2 | kΩ | |||
- VREFP and VREFN must be tied to ground if the internal voltage reference is used.
- This parameter is valid when the respective AIN terminal is configured to operate as a general-purpose ADC input.