JAJSIJ6F April 2011 – February 2020 AMC1204
PRODUCTION DATA.
- 1 特長
- 2 アプリケーション
- 3 概要
- 4 改訂履歴
- 5 概要(続き)
- 6 Pin Configuration and Functions
-
7 Specifications
- 7.1 Absolute Maximum Ratings
- 7.2 ESD Ratings
- 7.3 Recommended Operating Conditions
- 7.4 Thermal Information
- 7.5 Power Ratings
- 7.6 Insulation Specifications
- 7.7 Safety-Related Certifications
- 7.8 Safety Limiting Values
- 7.9 Electrical Characteristics
- 7.10 Timing Requirements
- 7.11 Insulation Characteristics Curves
- 7.12 Typical Characteristics
- 8 Detailed Description
- 9 Application and Implementation
- 10Power Supply Recommendations
- 11Layout
- 12デバイスおよびドキュメントのサポート
- 13メカニカル、パッケージ、および注文情報
パッケージ・オプション
メカニカル・データ(パッケージ|ピン)
サーマルパッド・メカニカル・データ
- DW|16
発注情報
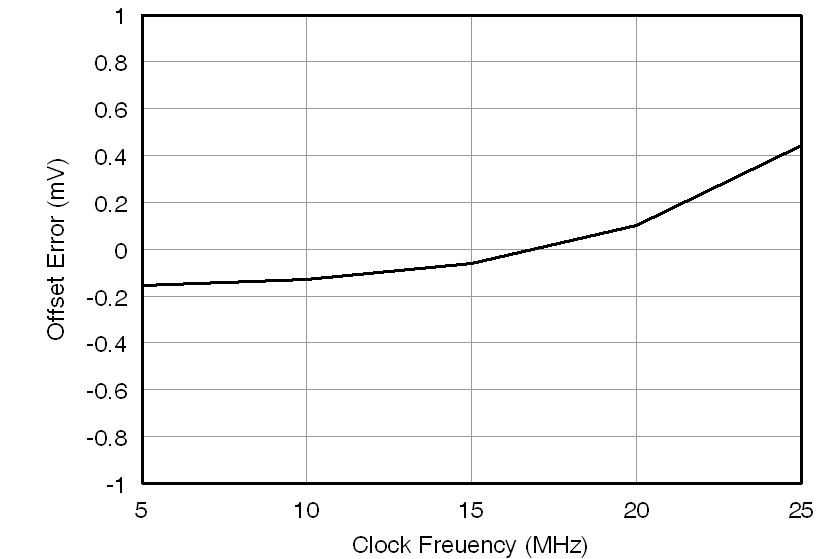
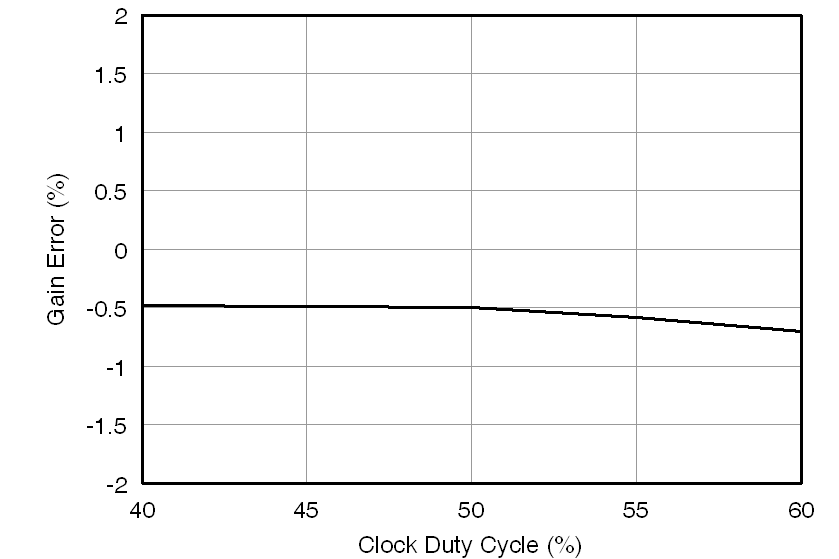
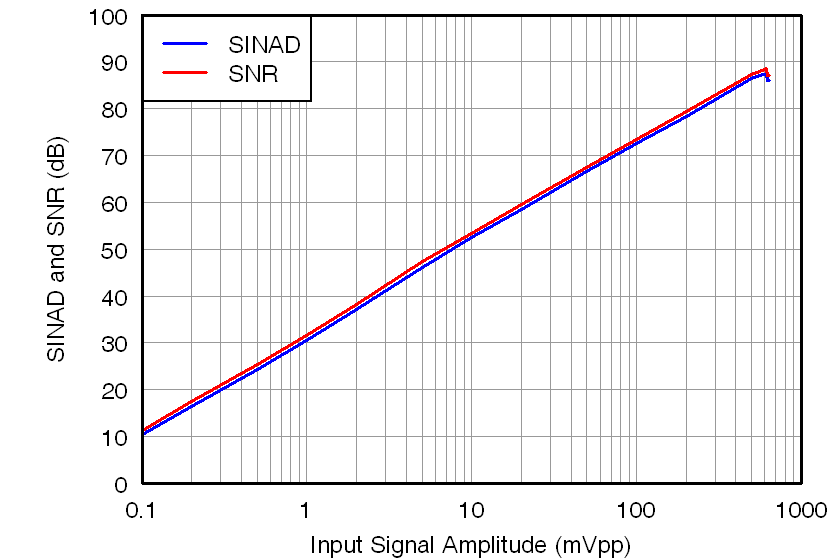
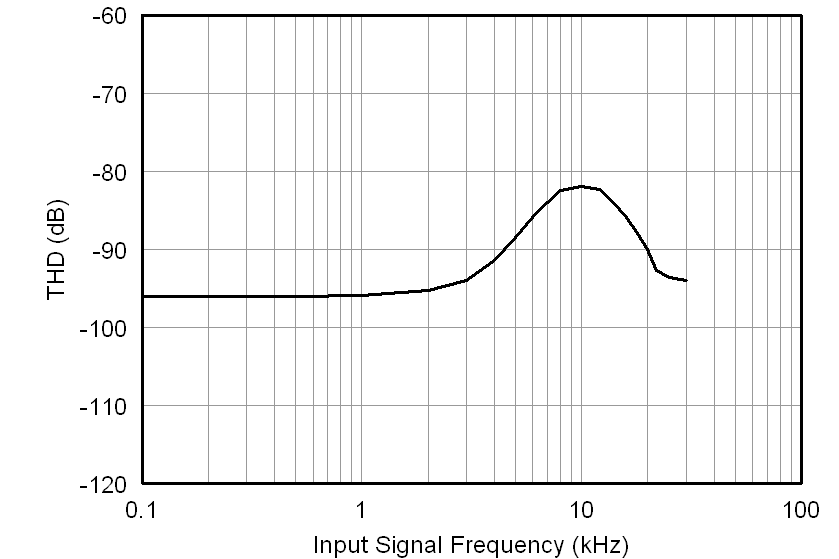
7.12 Typical Characteristics
at AVDD = 5 V, DVDD = 3.3 V, VINP = –250 mV to 250 mV, VINN = 0 V, and sinc3 filter with OSR = 256 (unless otherwise noted)