JAJS436D December 2009 – December 2019 BQ24610 , BQ24617
PRODUCTION DATA.
- 1 特長
- 2 アプリケーション
- 3 概要
- 4 改訂履歴
- 5 概要(続き)
- 6 Device Comparison Table
- 7 Pin Configuration and Functions
- 8 Specifications
-
9 Detailed Description
- 9.1 Overview
- 9.2 Functional Block Diagram
- 9.3
Feature Description
- 9.3.1 Battery Voltage Regulation
- 9.3.2 Battery Current Regulation
- 9.3.3 Input Adapter Current Regulation
- 9.3.4 Precharge
- 9.3.5 Charge Termination, Recharge, and Safety Timer
- 9.3.6 Power Up
- 9.3.7 Enable and Disable Charging
- 9.3.8 System Power Selector
- 9.3.9 Automatic Internal Soft-Start Charger Current
- 9.3.10 Converter Operation
- 9.3.11 Synchronous and Nonsynchronous Operation
- 9.3.12 Cycle-by-Cycle Charge Undercurrent Protection
- 9.3.13 Input Overvoltage Protection (ACOV)
- 9.3.14 Input Undervoltage Lockout (UVLO)
- 9.3.15 Battery Overvoltage Protection
- 9.3.16 Cycle-by-Cycle Charge Overcurrent Protection
- 9.3.17 Thermal Shutdown Protection
- 9.3.18 Temperature Qualification
- 9.3.19 Timer Fault Recovery
- 9.3.20 PG Output
- 9.3.21 CE (Charge Enable)
- 9.3.22 Charge Status Outputs
- 9.3.23 Battery Detection
- 9.4 Device Functional Modes
- 10Application and Implementation
- 11Power Supply Recommendations
- 12Layout
- 13デバイスおよびドキュメントのサポート
- 14メカニカル、パッケージ、および注文情報
パッケージ・オプション
メカニカル・データ(パッケージ|ピン)
- RGE|24
サーマルパッド・メカニカル・データ
- RGE|24
発注情報
7 Pin Configuration and Functions
RGE Package
24-Pin VQFN
Top View
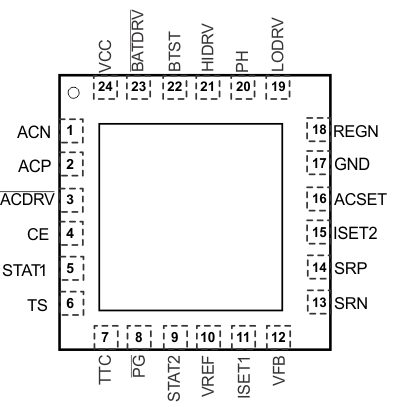
Pin Functions
| PIN | DESCRIPTION | |
|---|---|---|
| NAME | NO. | |
| ACDRV | 3 | AC adapter to system MOSFET driver output. Connect through a 1-kΩ resistor to the gate of the ACFET P-channel power MOSFET and the reverse conduction blocking P-channel power MOSFET. The internal gate drive is asymmetrical, allowing a quick turnoff and slow turnon, in addition to the internal break-before-make logic with respect to BATDRV. If needed, an optional capacitor from gate to source of the ACFET is used to slow down the ON and OFF times. |
| ACN | 1 | Adapter current-sense resistor, negative input. A 0.1-μF ceramic capacitor is placed from ACN to ACP to provide differential-mode filtering. An optional 0.1-μF ceramic capacitor is placed from the ACN pin to GND for common-mode filtering. |
| ACP | 2 | Adapter current-sense resistor, positive input. A 0.1-μF ceramic capacitor is placed from ACN to ACP to provide differential-mode filtering. A 0.1-μF ceramic capacitor is placed from the ACP pin to GND for common-mode filtering. |
| ACSET | 16 | Adapter current-set input. The voltage of the ACSET pin programs the input current regulation set point during Dynamic Power Management (DPM). |
| BATDRV | 23 | Battery-to-system MOSFET driver output. Gate drive for the battery-to-system load BAT PMOS power FET to isolate the system from the battery to prevent current flow from the system to the battery, while allowing a low-impedance path from battery to system. Connect this pin through a 1-kΩ resistor to the gate of the input BAT P-channel MOSFET. Connect the source of the FET to the system-load voltage node. Connect the drain of the FET to the battery pack positive terminal. The internal gate drive is asymmetrical to allow a quick turnoff and slow turnon, in addition to the internal break-before-make logic with respect to ACDRV. If needed, an optional capacitor from gate to source of the BATFET is used to slow down the ON and OFF times. |
| BTST | 22 | PWM high-side driver positive supply. Connect a 0.1-μF bootstrap capacitor from PH to BTST, and a bootstrap Schottky diode from REGN to BTST. |
| CE | 4 | Charge enable active HIGH logic input. HI enables charge. LO disables charge. It has an internal 1-MΩ pulldown resistor. |
| GND | 17 | Low-current sensitive analog and digital ground. On PCB layout, connect with the thermal pad underneath the IC. |
| HIDRV | 21 | PWM high-side driver output. Connect to the gate of the high-side power MOSFET with a short trace. |
| ISET1 | 11 | Fast-charge current-set input. The voltage of the ISET1 pin programs the fast-charge current regulation set point. |
| ISET2 | 15 | Precharge and termination current set input. The voltage of the ISET2 pin programs the precharge current regulation set point and termination current trigger point. |
| LODRV | 19 | PWM low-side driver output. Connect to the gate of the low-side power MOSFET with a short trace. |
| PG | 8 | Open-drain power-good status output. Active LOW when IC has a valid VCC (not in UVLO or ACOV or SLEEP mode). Active HIGH when IC has an invalid VCC. PG can be used to drive an LED or communicate with a host processor. |
| PH | 20 | PWM high-side driver negative supply. Connect to the phase-switching node (junction of the low-side power MOSFET drain, high-side power MOSFET source, and output inductor). |
| REGN | 18 | PWM low-side driver positive 6-V supply output. Connect a 1-μF ceramic capacitor from REGN to the GND pin, close to the IC. Use for low-side driver and high-side driver bootstrap voltage by connecting a small-signal Schottky diode from REGN to BTST. |
| SRN | 13 | Charge current-sense resistor, negative input. A 0.1-μF ceramic capacitor is placed from SRN to SRP to provide differential-mode filtering. An optional 0.1-μF ceramic capacitor is placed from the SRN pin to GND for common-mode filtering. |
| SRP | 14 | Charge current sense resistor, positive input. A 0.1-μF ceramic capacitor is placed from SRN to SRP to provide differential-mode filtering. A 0.1-μF ceramic capacitor is placed from the SRP pin to GND for common-mode filtering. |
| STAT1 | 5 | Open-drain charge status pin to indicate various charger operation (see Table 2). |
| STAT2 | 9 | Open-drain charge status pin to indicate various charger operations (see Table 2). |
| Thermal pad | — | Exposed pad beneath the IC. Always solder the thermal pad to the board, and have vias on the thermal pad plane star-connecting to GND and ground plane for high-current power converter. It also serves as a thermal pad to dissipate the heat. |
| TS | 6 | Temperature qualification voltage input for battery pack negative temperature coefficient thermistor. Program the hot and cold temperature window with a resistor divider from VREF to TS to GND (see Figure 16). |
| TTC | 7 | SafetyTimer and termination control. Connect a capacitor from this node to GND to set the timer. When this input is LOW, the timer and termination are disabled. When this input is HIGH, the timer is disabled but termination is allowed. |
| VCC | 24 | IC power positive supply. Connect through a 10-Ω resistor to the common-source (diode-OR) point: source of high-side P-channel MOSFET and source of reverse-blocking power P-channel MOSFET. Place a 1-μF ceramic capacitor from VCC to the GND pin close to the IC. |
| VFB | 12 | Output voltage analog feedback adjustment. Connect the output of a resistive voltage divider from the battery terminals to this node to adjust the output battery regulation voltage. |
| VREF | 10 | 3.3-V regulated voltage output. Place a 1-μF ceramic capacitor from VREF to GND pin close to the IC. This voltage could be used for programming of voltage and current regulation and for programming the TS threshold. |