SLAS950A May 2013 – June 2015 DAC7562-Q1 , DAC7563-Q1 , DAC8162-Q1 , DAC8163-Q1 , DAC8562-Q1 , DAC8563-Q1
PRODUCTION DATA.
- 1 Features
- 2 Applications
- 3 Description
- 4 Revision History
- 5 Device Comparison Table
- 6 Pin Configuration and Functions
- 7 Specifications
- 8 Detailed Description
- 9 Application and Implementation
- 10Power Supply Recommendations
- 11Layout
- 12Device and Documentation Support
- 13Mechanical, Packaging, and Orderable Information
11 Layout
11.1 Layout Guidelines
A precision analog component requires careful layout, adequate bypassing, and clean, well-regulated power supplies. The DAC756x-Q1, DAC816x-Q1, and DAC856x-Q1 devices offer single-supply operation, and are often used in close proximity with digital logic, microcontrollers, microprocessors, and digital signal processors. The more digital logic present in the design and the higher the switching speed, the more difficult it is to keep digital noise from appearing at the output. As a result of the single ground pin of the DAC756x-Q1, DAC816x-Q1, and DAC856x-Q1 devices, all return currents (including digital and analog return currents for the DAC) must flow through a single point. Ideally, GND would be connected directly to an analog ground plane. This plane would be separate from the ground connection for the digital components until they were connected at the power-entry point of the system. The power applied to AVDD should be well-regulated and low noise. Switching power supplies and dc-dc converters often have high-frequency glitches or spikes riding on the output voltage. In addition, digital components can create similar high-frequency spikes as their internal logic switches states. This noise can easily couple into the DAC output voltage through various paths between the power connections and analog output. As with the GND connection, AVDD should be connected to a power-supply plane or trace that is separate from the connection for digital logic until they are connected at the power-entry point. In addition, a pair of 100-pF to 1-nF capacitors and a 0.1-µF to 1-µF bypass capacitor are strongly recommended. In some situations, additional bypassing may be required, such as a 100-µF electrolytic capacitor or even a pi filter made up of inductors and capacitors – all designed essentially to provide low-pass filtering for the supply and remove the high-frequency noise.
11.2 Layout Example
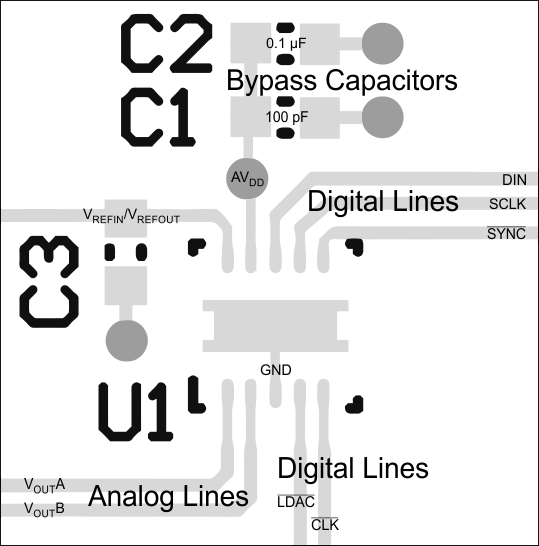 Figure 103. DACxx6x-Q1 Layout Example
Figure 103. DACxx6x-Q1 Layout Example