JAJSQ48A April 2023 – January 2025 DLP550HE
PRODUCTION DATA
- 1
- 1 特長
- 2 アプリケーション
- 3 概要
- 4 Pin Configuration and Functions
-
5 Specifications
- 5.1 Absolute Maximum Ratings
- 5.2 Storage Conditions
- 5.3 ESD Ratings
- 5.4 Recommended Operating Conditions
- 5.5 Thermal Information
- 5.6 Electrical Characteristics
- 5.7 Capacitance at Recommended Operating Conditions
- 5.8 Timing Requirements
- 5.9 System Mounting Interface Loads
- 5.10 Micromirror Array Physical Characteristics
- 5.11 Micromirror Array Optical Characteristics
- 5.12 Window Characteristics
- 5.13 Chipset Component Usage Specification
- 6 Detailed Description
- 7 Application and Implementation
- 8 Power Supply Recommendations
- 9 Layout
- 10Device and Documentation Support
- 11Revision History
- 12Mechanical, Packaging, and Orderable Information
5.8 Timing Requirements
| PARAMETER DESCRIPTION | SIGNAL | MIN | TYP | MAX | UNIT | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| LVDS(1) | |||||||
| tC | Clock Cycle | DCLK_A | LVDS | 4.34 | 5 | ns | |
| tC | Clock Cycle | DCLK_B | LVDS | 4.34 | 5 | ns | |
| tW | Pulse Width | DCLK_A | LVDS | 2.17 | 2.5 | ns | |
| tW | Pulse Width | DCLK_B | LVDS | 2.17 | 2.5 | ns | |
| tSU | Setup Time | D_A(15:0) before DCLK_A | LVDS | 0.35 | ns | ||
| tSU | Setup Time | D_A(15:0) before DCLK_B | LVDS | 0.35 | ns | ||
| tSU | Setup Time | SCTRL_A before DCLK_A | LVDS | 0.35 | ns | ||
| tSU | Setup Time | SCTRL_B before DCLK_B | LVDS | 0.35 | ns | ||
| tH | Hold Time | D_A(15:0) after DCLK_A | LVDS | 0.65 | ns | ||
| tH | Hold Time | D_B(15:0) after DCLK_B | LVDS | 0.65 | ns | ||
| tH | Hold Time | SCTRL_A after DCLK_A | LVDS | 0.65 | ns | ||
| tH | Hold Time | SCTRL_B after DCLK_B | LVDS | 0.65 | ns | ||
| tSKEW | Skew Time | Channel B relative to Channel A(2)(3) | LVDS | –1.25 | 1.25 | ns | |
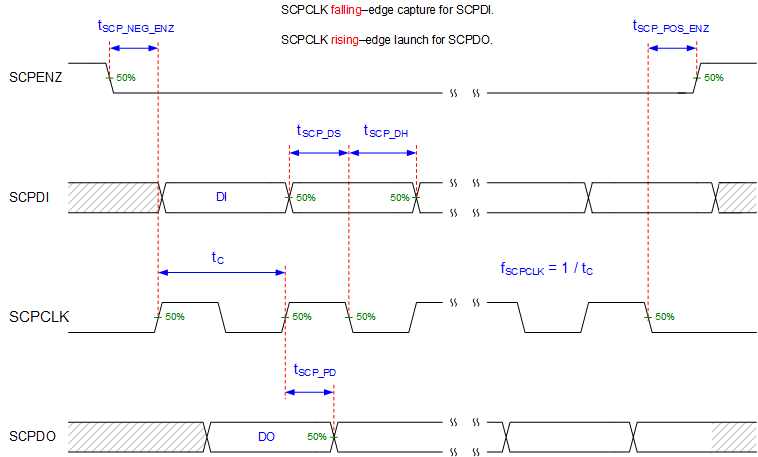 Figure 5-2 SCP
Timing Requirements
Figure 5-2 SCP
Timing RequirementsSee Section 5.4 for fSCPCLK, tSCP_DS, tSCP_DH, and tSCP_PD specifications.
See Section 5.4 for tr and tf specifications and conditions.
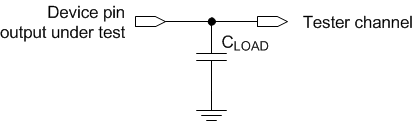 Figure 5-4 Test Load
Circuit for Output Propagation Measurement
Figure 5-4 Test Load
Circuit for Output Propagation MeasurementFor output timing analysis, the tester pin electronics and its transmission line effects must be considered. System designers must use IBIS or other simulation tools to correlate the timing reference load to a system environment. See Figure 5-4.
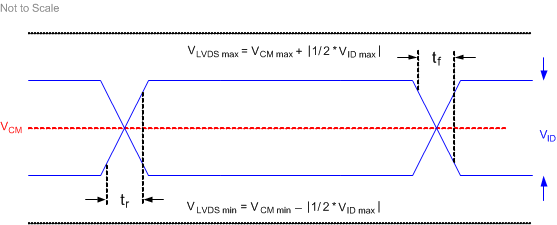 Figure 5-5 LVDS
Waveform Requirements
Figure 5-5 LVDS
Waveform RequirementsSee Section 5.4 for VCM, VID, and VLVDS specifications and conditions.
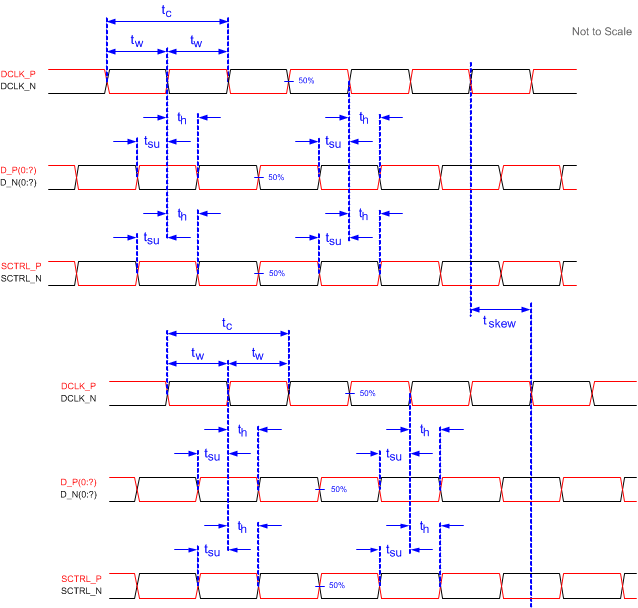 Figure 5-6 Timing
Requirements
Figure 5-6 Timing
RequirementsSee Section 5.8 for timing requirements and LVDS pairs per channel (bus) defining D_P(0:x) and D_N(0:x).