JAJSFJ1 May 2018 DLPA4000
PRODUCTION DATA.
- 1 特長
- 2 アプリケーション
- 3 概要
- 4 改訂履歴
- 5 概要(続き)
- 6 Pin Configuration and Functions
- 7 Specifications
-
8 Detailed Description
- 8.1 Overview
- 8.2 Functional Block Description
- 8.3
Feature Description
- 8.3.1 Supply and Monitoring
- 8.3.2 Illumination
- 8.3.3 External Power MOSFET Selection
- 8.3.4 DMD Supplies
- 8.3.5 Buck Converters
- 8.3.6 Auxiliary LDOs
- 8.3.7 Measurement System
- 8.4 Device Functional Modes
- 8.5 Programming
- 8.6 Register Maps
- 9 Application and Implementation
- 10Power Supply Recommendations
- 11Layout
- 12デバイスおよびドキュメントのサポート
- 13メカニカル、パッケージ、および注文情報
11.1.2 General Purpose Buck 2
Use short traces. Separate individual power grounds to avoid ground shift problems. Ground shift problems occur when ground currents of different buck converters interfere. High currents flow through the inductor (L7) and the output capacitors (C130, C131).Make the traces to and from inductor and capacitors as short as possible to avoid losses due to trace resistance. Use high-quality capacitors with a low ESR value to minimize losses in the capacitors and to maintain an acceptable amount of voltage ripple.
The next paragraph explains how to place and connect components near PWR6 Buck converter which are those component connected to pins 62, 63, 64, 65, and 66.
Connect the supply voltage i to pin 64 with sufficient copper to make it stable and of low resistance. Use multiple vias to the ground layer to connect pin 62 to ground. Use multiple layers create low resistive paths. Make sure the ground connection of the output capacitors and the ground connection of the DLPA4000 (pin 62) are close together. Connect both points using a wide trace. All buck converters in the layout use a separated ground trace to their respective ground connection on the DLPA4000. All these ground connections are connected together on the ground plane below the DLPA4000 package.
Figure 30 shows the position of the converter inductor and the accompanying capacitors (L7, C130, and C131) positioned as close as possible to pin 62 and pin 64 using the thickest traces that are feasible. Make these ground connections by using multiple vias to the ground layer to ensure a low-resistance path.
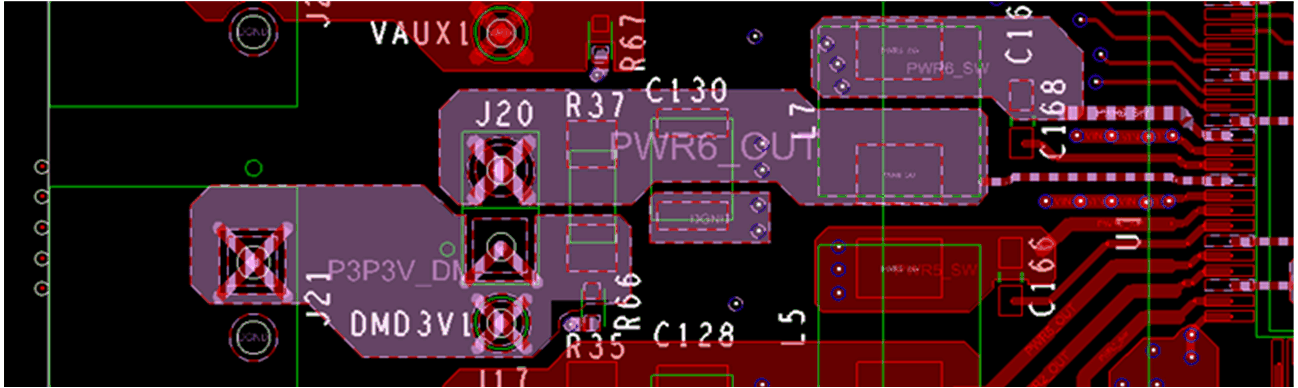 Figure 30. General Purpose Buck Layout
Figure 30. General Purpose Buck Layout