JAJSFU7E December 2013 – March 2019 DLPC2607
PRODUCTION DATA.
- 1 特長
- 2 アプリケーション
- 3 概要
- 4 改訂履歴
- 5 Pin Configuration and Functions
-
6 Specifications
- 6.1 Absolute Maximum Ratings
- 6.2 ESD Ratings
- 6.3 Recommended Operating Conditions
- 6.4 Thermal Information
- 6.5 Typical Current and Power Dissipation
- 6.6 I/O Characteristics
- 6.7 Internal Pullup and Pulldown Characteristics
- 6.8 Parallel I/F Frame Timing Requirements
- 6.9 Parallel I/F General Timing Requirements
- 6.10 Parallel I/F Maximum Parallel Interface Horizontal Line Rate
- 6.11 BT.656 I/F General Timing Requirements
- 6.12 100- to 120-Hz Operational Limitations
- 6.13 Flash Interface Timing Requirements
- 6.14 DMD Interface Timing Requirements
- 6.15 mDDR Memory Interface Timing Requirements
- 7 Detailed Description
- 8 Application and Implementation
- 9 Power Supply Recommendations
-
10Layout
- 10.1
Layout Guidelines
- 10.1.1 Internal ASIC PLL Power
- 10.1.2 General Handling Guidelines for Unused CMOS-Type Pins
- 10.1.3 SPI Signal Routing
- 10.1.4 mDDR Memory and DMD Interface Considerations
- 10.1.5 PCB Design
- 10.1.6 General PCB Routing (Applies to All Corresponding PCB Signals)
- 10.1.7 Maximum, Pin-to-Pin, PCB Interconnects Etch Lengths
- 10.1.8 I/F Specific PCB Routing
- 10.1.9 Number of Layer Changes
- 10.1.10 Stubs
- 10.1.11 Termination Requirements:
- 10.2 Layout Example
- 10.1
Layout Guidelines
- 11デバイスおよびドキュメントのサポート
- 12メカニカル、パッケージ、および注文情報
デバイスごとのパッケージ図は、PDF版データシートをご参照ください。
メカニカル・データ(パッケージ|ピン)
- ZVB|176
サーマルパッド・メカニカル・データ
6.15 mDDR Memory Interface Timing Requirements
The DLPC2607 controller mDDR memory interface consists of a 16-bit wide, mDDR interface (that is, LVCMOS signaling) operated at 133.33 MHz (nominal). (see (1)(2)(3))| MIN | MAX | UNIT | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| tCYCLE | Cycle-time reference | 7500 | ps | |
| tCH | CK high pulse width(4) | 2700 | ps | |
| tCL | CK low pulse width(4) | 2700 | ps | |
| tDQSH | DQS high pulse width(4) | 2700 | ps | |
| tDQSL | DQS low pulse width(4) | 2700 | ps | |
| tWAC | CK to address and control outputs active | –2870 | 2870 | ps |
| tQAC | CK to DQS output active | 200 | ps | |
| tDAC | DQS to DQ and DM output active | –1225 | 1225 | ps |
| tDQSRS | Input (read) DQS and DQ skew(5) | 1000 | ps | |
(1) This includes the 200 ppm of the external oscillator (but no jitter).
(2) Output setup and hold numbers already account for controller clock jitter. Only routing skew and memory setup/hold must be considered in system timing analysis.
(3) Assumes a 30-Ω series termination on all signal lines.
(4) CK and DQS pulse duration specifications for the DLPC2607 assume it is interfacing to a 166-MHz mDDR device. Even though these memories are only operated at 133.33 MHz, according to memory vendors, the rated tCK specification (that is 6 ns) can be applied to determine minimum CK and DQS pulse duration requirements to the memory.
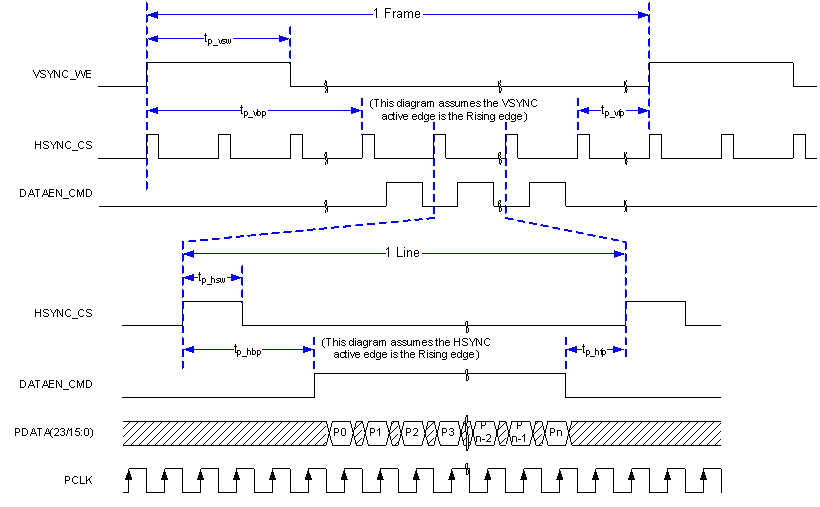 Figure 1. Parallel I/F Frame Timing
Figure 1. Parallel I/F Frame Timing 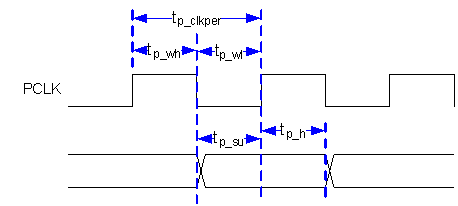 Figure 2. Parallel and BT.656 I/F General Timing
Figure 2. Parallel and BT.656 I/F General Timing 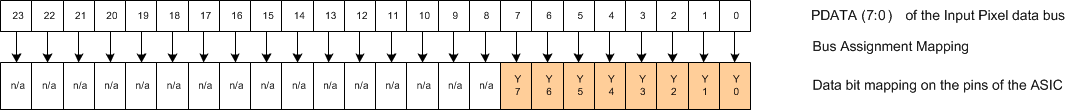 Figure 3. DLPC2607 PDATA Bus – BT.656 I/F Mode Bit Mapping (YCrCb 4:2:2 Source)
Figure 3. DLPC2607 PDATA Bus – BT.656 I/F Mode Bit Mapping (YCrCb 4:2:2 Source) 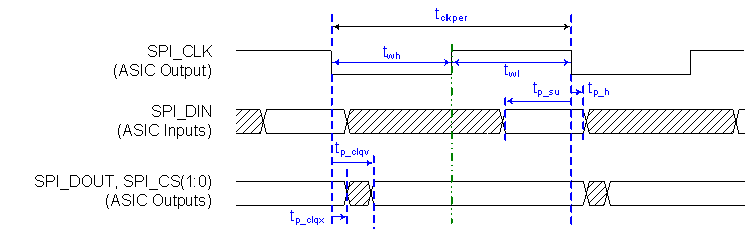 Figure 4. Flash I/F Timing
Figure 4. Flash I/F Timing 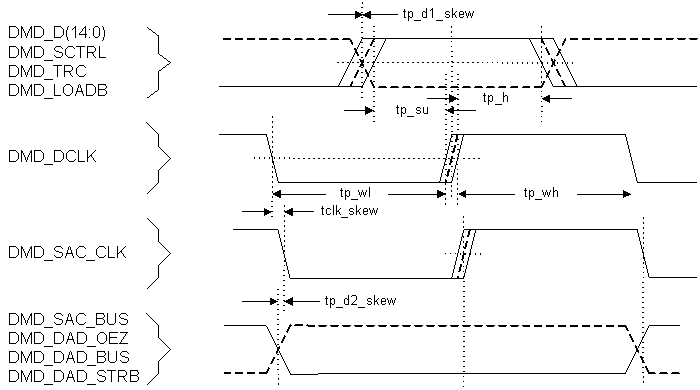 Figure 5. DMD I/F Timing
Figure 5. DMD I/F Timing 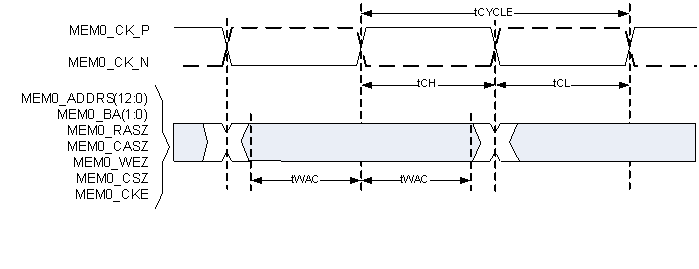 Figure 6. mDRR Memory Address and Control Timing
Figure 6. mDRR Memory Address and Control Timing 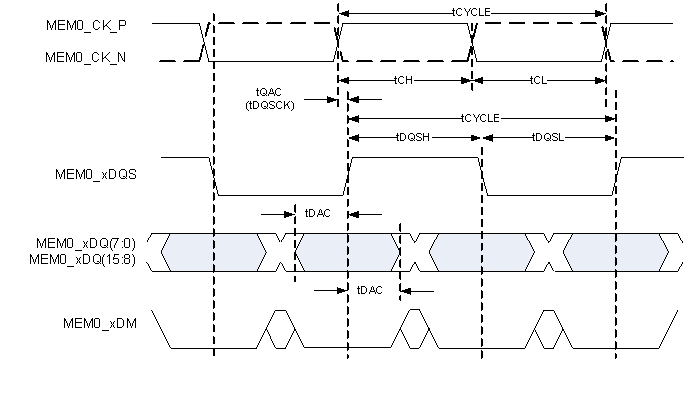 Figure 7. mDRR Memory Write Dtat Timing
Figure 7. mDRR Memory Write Dtat Timing 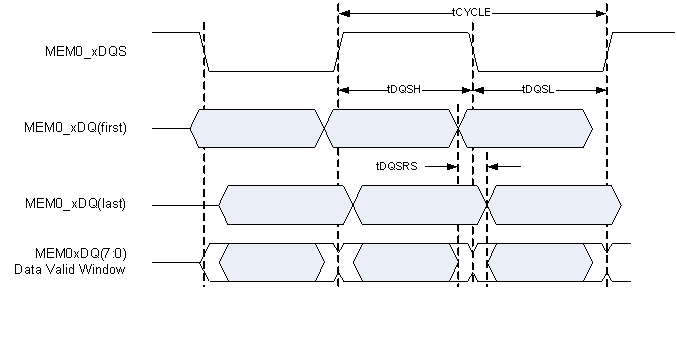 Figure 8. mDDR Memory Read Data Timing
Figure 8. mDDR Memory Read Data Timing