JAJSFD3G August 2016 – March 2019 DRA780 , DRA781 , DRA782 , DRA783 , DRA785 , DRA786 , DRA787 , DRA788
PRODUCTION DATA.
- 1デバイスの概要
- 2改訂履歴
- 3Device Comparison
-
4Terminal Configuration and Functions
- 4.1 Pin Diagram
- 4.2 Pin Attributes
- 4.3
Signal Descriptions
- 4.3.1 VIP
- 4.3.2 DSS
- 4.3.3 SD_DAC
- 4.3.4 ADC
- 4.3.5 Camera Control
- 4.3.6 CPI
- 4.3.7 CSI2
- 4.3.8 EMIF
- 4.3.9 GPMC
- 4.3.10 Timers
- 4.3.11 I2C
- 4.3.12 UART
- 4.3.13 McSPI
- 4.3.14 QSPI
- 4.3.15 McASP
- 4.3.16 DCAN and MCAN
- 4.3.17 GMAC_SW
- 4.3.18 SDIO Controller
- 4.3.19 GPIO
- 4.3.20 ePWM
- 4.3.21 ATL
- 4.3.22 Test Interfaces
- 4.3.23 System and Miscellaneous
- 4.3.24 Power Supplies
- 4.4 Pin Multiplexing
- 4.5 Connections for Unused Pins
-
5Specifications
- 5.1 Absolute Maximum Ratings
- 5.2 ESD Ratings
- 5.3 Power on Hour (POH) Limits
- 5.4 Recommended Operating Conditions
- 5.5 Operating Performance Points
- 5.6 Power Consumption Summary
- 5.7
Electrical Characteristics
- Table 5-6 LVCMOS DDR DC Electrical Characteristics
- Table 5-7 Dual Voltage LVCMOS I2C DC Electrical Characteristics
- Table 5-8 IQ1833 Buffers DC Electrical Characteristics
- Table 5-9 IHHV1833 Buffers DC Electrical Characteristics
- Table 5-10 LVCMOS Analog OSC Buffers DC Electrical Characteristics
- Table 5-11 Dual Voltage LVCMOS DC Electrical Characteristics
- Table 5-12 Analog-to-Digital ADC Subsystem Electrical Specifications
- 5.8 Thermal Characteristics
- 5.9
Timing Requirements and Switching Characteristics
- 5.9.1 Timing Parameters and Information
- 5.9.2 Interface Clock Specifications
- 5.9.3 Power Supply Sequences
- 5.9.4 Clock Specifications
- 5.9.5 Recommended Clock and Control Signal Transition Behavior
- 5.9.6
Peripherals
- 5.9.6.1 Timing Test Conditions
- 5.9.6.2 VIP
- 5.9.6.3 DSS
- 5.9.6.4 EMIF
- 5.9.6.5 GPMC
- 5.9.6.6 GP Timers
- 5.9.6.7 I2C
- 5.9.6.8 UART
- 5.9.6.9 McSPI
- 5.9.6.10 QSPI
- 5.9.6.11
McASP
- Table 5-50 Timing Requirements for McASP1
- Table 5-51 Timing Requirements for McASP2
- Table 5-52 Timing Requirements for McASP3
- Table 5-53 Switching Characteristics Over Recommended Operating Conditions for McASP1
- Table 5-54 Switching Characteristics Over Recommended Operating Conditions for McASP2
- Table 5-55 Switching Characteristics Over Recommended Operating Conditions for McASP3
- 5.9.6.12 DCAN and MCAN
- 5.9.6.13
GMAC_SW
- 5.9.6.13.1 GMAC MDIO Interface Timings
- 5.9.6.13.2
GMAC RGMII Timings
- Table 5-63 Timing Requirements for rgmiin_rxc - RGMIIn Operation
- Table 5-64 Timing Requirements for GMAC RGMIIn Input Receive for 10/100/1000 Mbps
- Table 5-65 Switching Characteristics Over Recommended Operating Conditions for rgmiin_txctl - RGMIIn Operation for 10/100/1000 Mbit/s
- Table 5-66 Switching Characteristics for GMAC RGMIIn Output Transmit for 10/100/1000 Mbps
- 5.9.6.14 SDIO Controller
- 5.9.6.15 GPIO
- 5.9.6.16 ATL
- 5.9.7
Emulation and Debug Subsystem
- 5.9.7.1
JTAG Electrical Data/Timing
- Table 5-78 Timing Requirements for IEEE 1149.1 JTAG
- Table 5-79 Switching Characteristics Over Recommended Operating Conditions for IEEE 1149.1 JTAG
- Table 5-80 Timing Requirements for IEEE 1149.1 JTAG With RTCK
- Table 5-81 Switching Characteristics Over Recommended Operating Conditions for IEEE 1149.1 JTAG With RTCK
- 5.9.7.2 Trace Port Interface Unit (TPIU)
- 5.9.7.1
JTAG Electrical Data/Timing
-
6Detailed Description
- 6.1 Description
- 6.2 Functional Block Diagram
- 6.3 DSP Subsystem
- 6.4 IPU
- 6.5 EVE
- 6.6 Memory Subsystem
- 6.7 Interprocessor Communication
- 6.8 Interrupt Controller
- 6.9 EDMA
- 6.10 Peripherals
- 6.11 On-Chip Debug
-
7Applications, Implementation, and Layout
- 7.1 Introduction
- 7.2 Power Optimizations
- 7.3 Core Power Domains
- 7.4 Single-Ended Interfaces
- 7.5 Differential Interfaces
- 7.6 Clock Routing Guidelines
- 7.7 DDR2 Board Design and Layout Guidelines
- 7.8
DDR3 Board Design and Layout Guidelines
- 7.8.1 DDR3 General Board Layout Guidelines
- 7.8.2
DDR3 Board Design and Layout Guidelines
- 7.8.2.1 Board Designs
- 7.8.2.2 DDR3 Device Combinations
- 7.8.2.3 DDR3 Interface Schematic
- 7.8.2.4 Compatible JEDEC DDR3 Devices
- 7.8.2.5 PCB Stackup
- 7.8.2.6 Placement
- 7.8.2.7 DDR3 Keepout Region
- 7.8.2.8 Bulk Bypass Capacitors
- 7.8.2.9 High-Speed Bypass Capacitors
- 7.8.2.10 Net Classes
- 7.8.2.11 DDR3 Signal Termination
- 7.8.2.12 VTT
- 7.8.2.13 CK and ADDR_CTRL Topologies and Routing Definition
- 7.8.2.14 Data Topologies and Routing Definition
- 7.8.2.15 Routing Specification
- 7.9 CVIDEO/SD-DAC Guidelines and Electrical Data/Timing
- 8Device and Documentation Support
- 9Mechanical, Packaging, and Orderable Information
パッケージ・オプション
デバイスごとのパッケージ図は、PDF版データシートをご参照ください。
メカニカル・データ(パッケージ|ピン)
- ABF|367
サーマルパッド・メカニカル・データ
発注情報
7.2.3 Step 3: Static Analysis
Delivering reliable power to circuits is always of critical importance because voltage drops (also known as IR drops) can happen at every level within an electronic system, on-chip, within a package, and across the board. Robust system performance can only be ensured by understanding how the system elements will perform under typical stressful Use Cases. Therefore, it is a good practice to perform a Static or DC Analysis.
Static or DC analysis and design methodology results in a PDN design that minimizes voltage or IR drops across power and ground planes, traces and vias. This ensures the application processor’s internal transistors will be operating within their specified voltage ranges for proper functionality. The amount of IR drop that will be encounter is based upon amount power drawn for a desired Use Case and PCB trace (widths, geometry and number of parallel traces) and via (size, type and number) characteristics.
Components that are distant from their power source are particularly susceptible to IR drop. Designs that rely on battery power must minimize voltage drops to avoid unacceptable power loss that can negatively impact system performance. Early assessments a PDN’s static (DC) performance helps to determine basic power distribution parameters such as best system input power point, optimal PCB layer stackup, and copper area needed for load currents.
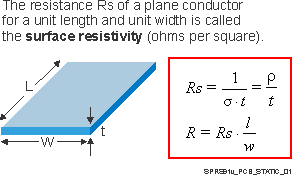 Figure 7-3 Depiction of Sheet Resistivity and Resistance
Figure 7-3 Depiction of Sheet Resistivity and Resistance Ohm’s Law (V = I × R) relates conduction current to voltage drop. At DC, the relation coefficient is a constant and represents the resistance of the conductor. Even current carrying conductors will dissipate power at high currents even though their resistance may be very small. Both voltage drop and power dissipation are proportional to the resistance of the conductor.
Figure 7-4 shows a PCB-level static IR drop budget defined between the power management device (PMIC) pins and the application processor’s balls when the PMIC is supplying power.
- It is highly recommended to physically place the PMIC as close as possible to the processor and on the same side. The orientation of the PMIC vs. the processor should be aligned to minimize distance for the highest current rail.
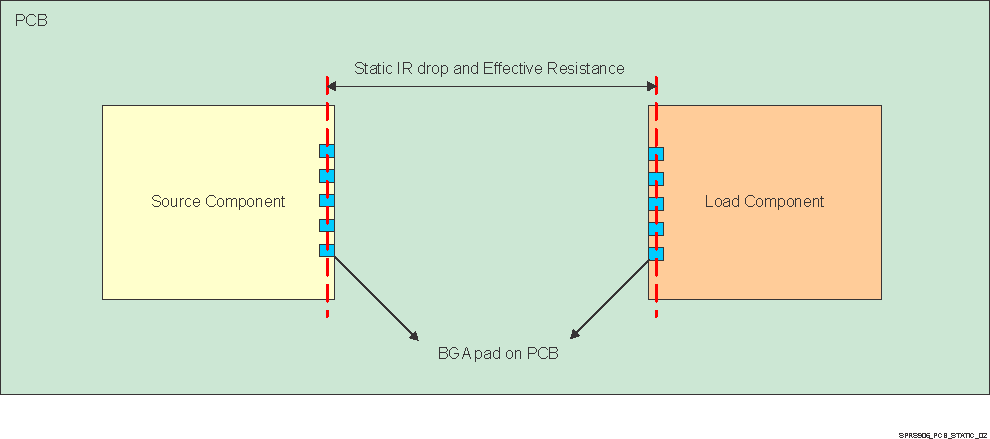 Figure 7-4 Static IR Drop Budget for PCB Only
Figure 7-4 Static IR Drop Budget for PCB Only The system-level IR drop budget is made up of three portions: on-chip, package, and PCB board. Static IR or dc analysis/design methodology consists of designing the PDN such that the voltage drop (under dc operating conditions) across power and ground pads of the transistors of the application processor device is within a specified value of the nominal voltage for proper functionality of the device.
A PCB system-level voltage drop budget for proper device functionality is typically 1.5% of nominal voltage. For a 1.35-V supply, this would be ≤20 mV.
To accurately analyze PCB static IR drop, the actual geometry of the PDN must be modeled properly and simulated to accurately characterize long distribution paths, copper weight impacts, electro-migration violations of current-carrying vias, and "Swiss-cheese” effects via placement has on power rails. It is recommended to perform the following analyses:
- Lumped resistance/IR drop analysis
- Distributed resistance/IR drop analysis
NOTE
The PMIC companion device supporting Processor has been designed with voltage sensing feedback loop capabilities that enable a remote sense of the SMPS output voltage at the point of use.
The NOTE above means the SMPS feedback signals and returns must be routed across PCB and connected to the Device input power ball for which a particular SMPS is supplying power. This feedback loop provides compensation for some of the voltage drop encountered across the PDN within limits. As such, the effective resistance of the PDN within this loop should be determined in order to optimize voltage compensation loop performance. The resistance of two PDN segments are of interest: one from the power inductor/bulk power filtering capacitor node to the Processor’s input power and second is the entire PDN route from SMPS output pin/ball to the Processor input power.
In the following sections each methodology is described in detail and an example has been provided of analysis flow that can be used by the PCB designer to validate compliance to the requirements on their PCB PDN design.