SLVSHQ2 December 2024 DRV8351-SEP
PRODUCTION DATA
- 1
- 1 Features
- 2 Applications
- 3 Description
- 4 Device Comparison Table
- 5 Pin Configuration and Functions
- 6 Specifications
- 7 Detailed Description
- 8 Application and Implementation
- 9 Power Supply Recommendations
- 10Layout
- 11Device and Documentation Support
- 12Revision History
- 13Mechanical, Packaging, and Orderable Information
8.2.2 Bootstrap Capacitor and GVDD Capacitor Selection
The bootstrap capacitor must be sized to maintain the bootstrap voltage above the undervoltage lockout for normal operation. Equation 1 calculates the maximum allowable voltage drop across the bootstrap capacitor:
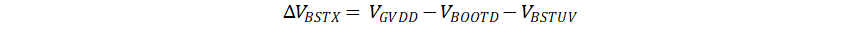
=12V – 0.85V – 4.5V = 6.65V
where
- VGVDD is the supply voltage of the gate drive
- VBOOTD is the forward voltage drop of the bootstrap diode
- VBSTUV is the threshold of the bootstrap undervoltage lockout
In this example the allowed voltage drop across bootstrap capacitor is 6.65V. It is generally recommended that ripple voltage on both the bootstrap capacitor and GVDD capacitor should be minimized as much as possible. Many commercial, industrial, and automotive applications use ripple values between 0.5V to 1V.
The total charge needed per switching cycle can be estimated with Equation 2:
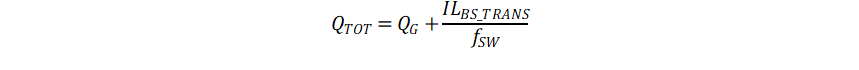
=48nC + 220μA/20kHz = 50nC + 11nC = 59nC
where
- QG is the total MOSFET gate charge
- ILBS_TRAN is the bootstrap pin leakage current
- fSW is the is the PWM frequency
The minimum bootstrap capacitor an then be estimated as below assuming 1V ΔVBSTx:
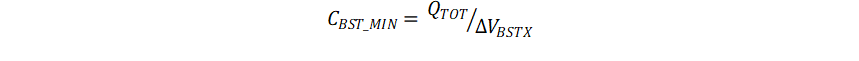
= 59nC / 1V = 59nF
The calculated value of the minimum bootstrap capacitor is 59nF. It should be noted that this value of capacitance is needed at full bias voltage. In practice, the value of the bootstrap capacitor must be greater than the calculated value to allow for situations where the power stage may skip pulse due to various transient conditions. It is recommended to use a 100nF bootstrap capacitor in this example. It is also recommended to include enough margin and place the bootstrap capacitor as close to the BSTx and SHx pins as possible.
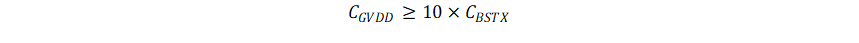
= 10*100nF= 1μF
For this example application choose 1µF CGVDD capacitor. Choose a capacitor with a voltage rating at least twice the maximum voltage that it will be exposed to because most ceramic capacitors lose significant capacitance when biased. This value also improves the long term reliability of the system.