SNLS396D January 2012 – January 2016 DS100MB203
PRODUCTION DATA.
- 1 Features
- 2 Applications
- 3 Description
- 4 Revision History
- 5 Pin Configuration and Functions
- 6 Specifications
- 7 Detailed Description
- 8 Application and Implementation
- 9 Power Supply Recommendations
- 10Layout
- 11Device and Documentation Support
- 12Mechanical, Packaging, and Orderable Information
6 Specifications
6.1 Absolute Maximum Ratings
See (1)(2)(3).| MIN | MAX | UNIT | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Supply voltage (VDD – 2.5-V mode) | –0.5 | 2.75 | V | |
| Supply voltage (VIN – 3.3-V mode) | –0.5 | 4 | V | |
| LVCMOS input / output voltage | –0.5 | 4 | V | |
| CML input voltage | –0.5 | (VDD + 0.5) | V | |
| CML input current | –30 | 30 | mA | |
| Junction temperature | 125 | °C | ||
| Lead temperature | Soldering (4 sec.)(3) | 260 | °C | |
| Storage temperature, Tstg | –40 | 150 | °C | |
(1) Stresses beyond those listed under Absolute Maximum Ratings may cause permanent damage to the device. These are stress ratings only, which do not imply functional operation of the device at these or any other conditions beyond those indicated under Recommended Operating Conditions. Exposure to absolute-maximum-rated conditions for extended periods may affect device reliability.
(2) If Military/Aerospace specified devices are required, please contact the Texas Instruments Sales Office/Distributors for availability and specifications.
(3) Soldering Information: SNOA549
6.2 ESD Ratings
| VALUE | UNIT | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| V(ESD) | Electrostatic discharge | Human body model (HBM), per ANSI/ESDA/JEDEC JS-001(1) | ±3000 | V |
| Charged-device model (CDM), per JEDEC specification JESD22-C101(2) | ±1000 | |||
(1) JEDEC document JEP155 states that 500-V HBM allows safe manufacturing with a standard ESD control process.
(2) JEDEC document JEP157 states that 250-V CDM allows safe manufacturing with a standard ESD control process.
6.3 Recommended Operating Conditions
| MIN | NOM | MAX | UNIT | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Supply voltage | 2.5-V mode | 2.375 | 2.5 | 2.625 | V |
| 3.3-V mode | 3 | 3.3 | 3.6 | V | |
| Ambient temperature | –40 | 25 | 85 | °C | |
| SMBus (SDA, SCL) | 3.6 | V | |||
| Supply noise up to 50 MHz(3) | 100 | mVp-p | |||
6.4 Thermal Information
| THERMAL METRIC(1) | DS100MB203 | UNIT | |
|---|---|---|---|
| NYJ (WQFN) | |||
| 54 PINS | |||
| RθJA | Junction-to-ambient thermal resistance, No Airflow, 4 layer JEDEC | 26.6 | °C/W |
| RθJC(top) | Junction-to-case (top) thermal resistance | 10.8 | °C/W |
| RθJB | Junction-to-board thermal resistance | 4.4 | °C/W |
| ψJT | Junction-to-top characterization parameter | 0.2 | °C/W |
| ψJB | Junction-to-board characterization parameter | 4.3 | °C/W |
| RθJC(bot) | Junction-to-case (bottom) thermal resistance | 1.5 | °C/W |
(1) For more information about traditional and new thermal metrics, see the Semiconductor and IC Package Thermal Metrics application report, SPRA953.
6.5 Electrical Characteristics(1)(2)
| PARAMETER | TEST CONDITIONS | MIN | TYP | MAX | UNIT | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| POWER | |||||||
| PD | Power dissipation | EQ Enabled, VOD = 1 Vp-p, RESET = 0 | VDD = 2.5-V supply | 390 | 499 | mW | |
| VIN = 3.3-V supply | 515 | 684 | mW | ||||
| LVCMOS / LVTTL DC SPECIFICATIONS | |||||||
| Vih | High-level input voltage | 2 | VDD | V | |||
| Vil | Low-level input voltage | 0 | 0.8 | V | |||
| Voh | High-level output voltage (ALL_DONE pin) | Ioh= −4mA | 2 | V | |||
| Vol | Low-level output voltage (ALL_DONE pin) | Iol= 4mA | 0.4 | V | |||
| Iih | Input high current (RESET pin) | VIN = 3.6 V, LVCMOS = 3.6 V |
–15 | 15 | µA | ||
| Input high current with internal resistors (4–level input pin) | VIN = 3.6 V, LVCMOS = 3.6 V |
20 | 150 | µA | |||
| Iil | Input low current (RESET pin) | VIN = 3.6 V, LVCMOS = 0 V |
–15 | 15 | µA | ||
| Input low current with internal resistors (4–level input pin) | VIN = 3.6 V, LVCMOS = 0 V |
–160 | –40 | µA | |||
| CML RECEIVER INPUTS (IN_n+, IN_n–) | |||||||
| RLrx-diff | RX differential return loss | 0.05 - 1.25 GHz | –16 | dB | |||
| 1.25 - 2.5 GHz | –16 | dB | |||||
| 2.5 - 4.0 GHz | –14 | dB | |||||
| RLrx-cm | RX common-mode return loss | 0.05 - 2.5 GHz | –12 | dB | |||
| 2.5 - 4.0 GHz | –8 | dB | |||||
| Zrx-dc | RX DC common-mode impedance | Tested at VDD = 2.5 V | 40 | 50 | 60 | Ω | |
| Zrx-diff-dc | RX DC differntial mode impedance | Tested at VDD = 2.5 V | 80 | 100 | 120 | Ω | |
| Vrx-signal-det-diff-pp | Signal detect assert level for active data signal | 0101 pattern at 8 Gbps | 180 | mVp-p | |||
| Vrx-idle-det-diff-pp | Signal detect de-assert level for electrical idle | 0101 pattern at 8 Gbps | 110 | mVp-p | |||
| HIGH-SPEED OUTPUTS | |||||||
| Vtx-diff-pp | Output voltage differential swing | Differential measurement with OUT_n+ and OUT_n-, terminated by 50 Ω to GND, AC-Coupled, VID = 1 Vp-p, DEM_x[1:0] = R, F(5) |
0.8 | 1 | 1.2 | Vp-p | |
| Vtx-de-ratio_3.5 | TX de-emphasis ratio | VOD = 1 Vp-p, DEM_x[1:0] = R, F |
–3.5 | dB | |||
| Vtx-de-ratio_6 | TX de-emphasis ratio | VOD = 1 Vp-p, DEM_x[1:0] = F, 0 |
–6 | dB | |||
| tTX-DJ | Deterministic jitter | VID = 800 mV, PRBS15 pattern, 8.0 0.05 Gbps, VOD = 1 V, UIpp EQ = 0x00, DE = 0 dB (no input or output trace loss) | 0.05 | UIpp | |||
| tTX-RJ | Random jitter | VID = 800 mV, 0101 pattern, 8.0 Gbps, 0.3 VOD = 1 V, ps RMS EQ = 0x00, DE = 0 dB, (no input or output trace loss) | 0.3 | ps RMS | |||
| TTX-RISE-FALL | TX rise/fall time | 20% to 80% of differential output voltage | 35 | 45 | ps | ||
| TRF-MISMATCH | TX rise/fall mismatch | 20% to 80% of differential output voltage | 0.01 | 0.1 | UI | ||
| RLTX-DIFF | TX differential return loss | 0.05 - 1.25 GHz | –16 | dB | |||
| 1.25 - 2.5 GHz | –12 | dB | |||||
| 2.5 - 4 GHz | –11 | dB | |||||
| RLTX-CM | TX common-mode return loss | 0.05 - 2.5 GHz | –12 | dB | |||
| 2.5 - 4 GHz | –8 | dB | |||||
| ZTX-DIFF-DC | DC differential TX impedance | 100 | Ω | ||||
| VTX-CM-AC-PP | TX AC common-mode voltage | VOD = 1 Vp-p, DEM_x[1:0] = R, F |
100 | mVpp | |||
| ITX-SHORT | TX short circuit current limit | Total current the transmitter can supply when shorted to VDD or GND | 20 | mA | |||
| VTX-CM-DC-ACTIVE-IDLE-DELTA | Absolute delta of DC common-mode voltage during L0 and electrical idle | 100 | mV | ||||
| VTX-CM-DC-LINE-DELTA | Absolute delta of DC common-mode voltage between TX+ and TX- | 25 | mV | ||||
| TTX-IDLE-DATA | Max time to transition to differential DATA signal after IDLE | VID = 1 Vp-p, 8 Gbps | 3.5 | ns | |||
| TTX-DATA-IDLE | Max time to transition to IDLE after differential DATA signal | VID = 1 Vp-p, 8 Gbps | 6.2 | ns | |||
| TPLHD/PHLD | High-to-low and low-to-high differential propagation delay | EQ = 00(4) | 200 | ps | |||
| TLSK | Lane-to-lane skew | T = 25°C, VDD = 2.5 V | 25 | ps | |||
| TPPSK | Part-to-part propagation delay skew | T = 25°C, VDD = 2.5 V | 40 | ps | |||
| TMUX-SWITCH | Mux / switch time | 100 | ns | ||||
| EQUALIZATION | |||||||
| DJE1 | Residual deterministic jitter at 10.3125 Gbps | 35-in 4 mils FR4, VID = 0.8 Vp-p, PRBS15, EQ = 1F'h, DEM = 0 dB |
0.3 | UI | |||
| DJE2 | Residual deterministic jitter at 8 Gbps | 35-in 4 mils FR4, VID = 0.8 Vp-p, PRBS15, EQ = 1F'h, DEM = 0 dB |
0.14 | UI | |||
| DJE3 | Residual deterministic jitter at 5 Gbps | 35-in 4 mils FR4, VID = 0.8 Vp-p, PRBS15,EQ = 1F'h, DEM = 0 dB |
0.1 | UI | |||
| DJE4 | Residual deterministic jitter at 2.5 Gbps | 35-in 4 mils FR4, VID = 0.8 Vp-p, PRBS15, EQ = 1F'h, DEM = 0 dB |
0.05 | UI | |||
| DJE5 | Residual deterministic jitter at 10.3125 Gbps | 10 meters 30 awg cable, VID = 0.8 Vp-p, PRBS15, EQ = 2F'h, DEM = 0 dB |
0.3 | UI | |||
| DJE6 | Residual deterministic jitter at 8 Gbps | 10 meters 30 awg cable, VID = 0.8 Vp-p, PRBS15, EQ = 2F'h, DEM = 0 dB |
0.16 | UI | |||
| DJE7 | Residual deterministic jitter at 5 Gbps | 10 meters 30 awg cable, VID = 0.8 Vp-p, PRBS15, EQ = 2F'h, DEM = 0 dB |
0.1 | UI | |||
| DJE8 | Residual deterministic jitter at 2.5 Gbps | 10 meters 30 awg cable, VID = 0.8 Vp-p, PRBS15, EQ = 2F'h, DEM = 0 dB |
0.05 | UI | |||
| DE-EMPHASIS (MODE = 0) | |||||||
| DJD1 | Residual deterministic jitter at 2.5 Gbps and 5.0 Gbps | 10-in 4 mils FR4, VID = 0.8 Vp-p, PRBS15, EQ = 00, VOD = 1 Vp-p, DEM = −3.5 dB |
0.1 | UI | |||
| DJD2 | Residual deterministic jitter at 2.5 Gbps and 5.0 Gbps | 20-in 4 mils FR4, VID = 0.8 Vp-p, PRBS15, EQ = 00, VOD = 1 Vp-p, DEM = −9 dB |
0.1 | UI | |||
| DJD3 | Residual deterministic jitter at 10.3125 Gbps | 20-in 4 mils FR4, VID = 0.8 Vp-p, PRBS15, EQ = 00, VOD = 1 Vp-p, DEM = −9 dB |
0.1 | UI | |||
(1) Typical values represent most likely parametric norms at VDD = 2.5V, TA = 25°C., and at the Recommended Operation Conditions at the time of product characterization and are not ensured.
(2) The Electrical Characteristics tables list ensured specifications under the listed Recommended Operating Conditions except as otherwise modified or specified by the Electrical Characteristics Conditions and/or Notes. Typical specifications are estimations only and are not ensured.
(3) Allowed supply noise (mVp-p sine wave) under typical conditions.
(4) Propagation Delay measurements will change slightly based on the level of EQ selected. EQ = 00 will result in the shortest propagation delays.
(5) In GEN3 mode, the output VOD level is not fixed. It will be adjusted automatically based on the VID input amplitude level. The output VOD level set by DEM_x[1:0] in GEN3 mode is dependent on the VID level and the frequency content. The DS100MB203 repeater in GEN3 mode is designed to be transparent, so the TX-FIR (de-emphasis) is passed to the RX to support the PCIe GEN3 handshake negotiation link training.
6.6 Electrical Characteristics – Serial Management Bus Interface
Over recommended operating supply and temperature ranges unless other specified.| PARAMETER | TEST CONDITIONS | MIN | TYP | MAX | UNIT | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| SERIAL BUS INTERFACE DC SPECIFICATIONS | ||||||
| VIL | Data, clock input low voltage | 0.8 | V | |||
| VIH | Data, clock input high voltage | 2.1 | 3.6 | V | ||
| IPULLUP | Current through pullup resistor or current source | High power specification | 4 | mA | ||
| VDD | Nominal bus voltage | 2.375 | 3.6 | V | ||
| ILEAK-Bus | Input leakage per bus segment | See (1) | –200 | 200 | µA | |
| ILEAK-Pin | Input leakage per device Pin | –15 | µA | |||
| CI | Capacitance for SDA and SCL | See (1)(2) | 10 | pF | ||
| RTERM | External termination resistance pull to VDD = 2.5 V ± 5% OR 3.3 V ± 10% | Pullup VDD = 3.3 V(1)(2)(3) | 2000 | Ω | ||
| Pullup VDD = 2.5 V(1)(2)(3) | 1000 | Ω | ||||
(1) Recommended value.
(2) Recommended maximum capacitance load per bus segment is 400pF.
(3) Maximum termination voltage should be identical to the device supply voltage.
6.7 Timing Requirements – Serial Bus Interface
| MIN | NOM | MAX | UNIT | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| FSMB | Bus operating frequency | ENSMB = VDD (slave mode) | 400 | kHz | ||
| ENSMB = FLOAT (master mode) | 280 | 400 | 520 | kHz | ||
| TBUF | Bus free time between stop and start condition | 1.3 | µs | |||
| THD:STA | Hold time after (repeated) start condition. After this period, the first clock is generated. | At IPULLUP, maximum | 0.6 | µs | ||
| TSU:STA | Repeated start condition set-up time | 0.6 | µs | |||
| TSU:STO | Stop condition set-up time | 0.6 | µs | |||
| THD:DAT | Data hold time | 0 | ns | |||
| TSU:DAT | Data set-up time | 100 | ns | |||
| TLOW | Clock low period | 1.3 | µs | |||
| THIGH | Clock high period | See (1) | 0.6 | 50 | µs | |
| tF | Clock / data fall time | 300 | ns | |||
| tR | Clock / data rise time | 300 | ns | |||
| tPOR | Time in which a device must be operational after power-on reset | See (1)(2) | 500 | ms | ||
(1) Compatible with SMBus 2.0 physical layer specification. See System Management Bus (SMBus) Specification Version 2.0, section 3.1.1 SMBus Common AC Specifications for details
(2) Specified by Design. Parameter not tested in production.
 Figure 1. CML Output and Rise and FALL Transition Time
Figure 1. CML Output and Rise and FALL Transition Time
 Figure 2. Propagation Delay Timing Diagram
Figure 2. Propagation Delay Timing Diagram
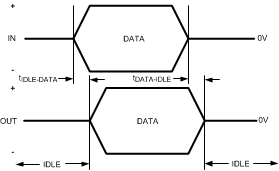 Figure 3. Transmit IDLE-DATA and DATA-IDLE Response Time
Figure 3. Transmit IDLE-DATA and DATA-IDLE Response Time
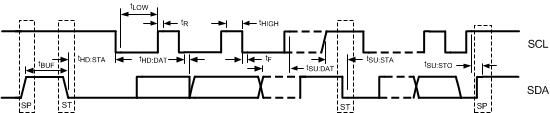 Figure 4. SMBus Timing Parameters
Figure 4. SMBus Timing Parameters
6.8 Typical Characteristics
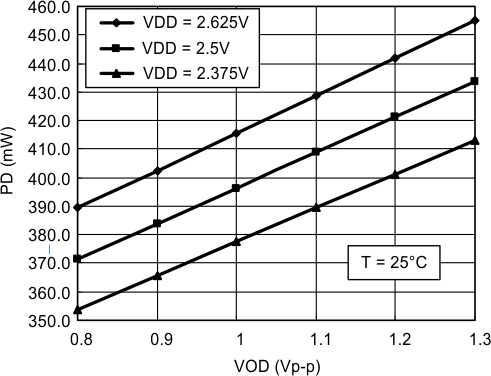 Figure 5. Power Dissipation (PD) vs Output Differential Voltage (VOD)
Figure 5. Power Dissipation (PD) vs Output Differential Voltage (VOD)
 Figure 7. Output Differential Voltage (VOD = 1 Vp-p) vs Temperature
Figure 7. Output Differential Voltage (VOD = 1 Vp-p) vs Temperature
 Figure 6. Output Differential Voltage (VOD = 1 Vp-p) vs Supply Voltage (VDD)
Figure 6. Output Differential Voltage (VOD = 1 Vp-p) vs Supply Voltage (VDD)