SNLS374D May 1998 – January 2015 DS8921
PRODUCTION DATA.
- 1 Features
- 2 Applications
- 3 Description
- 4 Revision History
- 5 Pin Configuration and Functions
-
6 Specifications
- 6.1 Absolute Maximum Ratings
- 6.2 ESD Ratings
- 6.3 Recommended Operating Conditions
- 6.4 Electrical Characteristics
- 6.5 Receiver Switching Characteristics
- 6.6 Driver Switching Characteristics: Single-Ended Characteristics
- 6.7 Driver Switching Characteristics: Differential Characteristics
- 6.8 Typical Characteristics
- 7 Parameter Measurement Information
- 8 Detailed Description
- 9 Application and Implementation
- 10Power Supply Recommendations
- 11Layout
- 12Device and Documentation Support
- 13Mechanical, Packaging, and Orderable Information
11 Layout
11.1 Layout Guidelines
High-speed interconnects should be treated as transmission lines with a controlled impedance. The differential interconnect can be a pair of printed-circuit board (PCB) traces, twisted-pair wires, or a parallel wire cable. A termination resistor should be placed at the differential input, and the resistor value should be approximately the same as the differential impedance of the transmission line to minimize reflections.
It is preferable to connect the VCC and GND pins to the power and ground planes using plated-through-holes. Additionally, a 0.1-µF bypass capacitor should be placed close to the VCC pin across VCC and GND.
Place a terminating resistor at the receiving end of the interconnect transmission line, as close as possible to the input pins of the receiver. The terminating resistor value should be approximately the same as the differential pair impedance to minimize reflection, and the transmission line should have a controlled impedance with minimum impedance discontinuities.
The input and output differential signals of the device should have traces that are routed exclusively on one layer of the board, and the differential pairs should also be routed away from other differential pairs in order to minimize crosstalk between transmission lines. Additionally, the differential pairs should have a controlled impedance with minimum impedance discontinuities and be terminated with a resistor that is closely matched to the differential pair impedance in order to minimize transmission line reflections. The differential pairs should be routed with uniform trace width and spacing to minimize impedance mismatch.
11.2 Layout Example
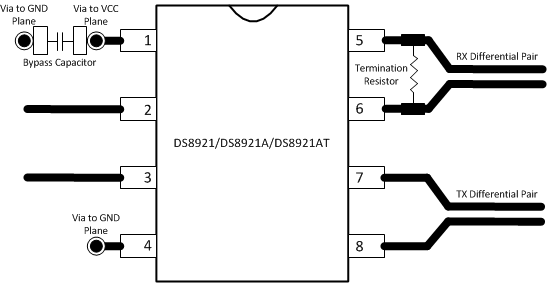 Figure 16. DS8921 Example Layout
Figure 16. DS8921 Example Layout