JAJSAH6H January 2006 – October 2017 LM3100
PRODUCTION DATA.
- 1 特長
- 2 アプリケーション
- 3 概要
- 4 改訂履歴
- 5 Pin Configuration and Functions
- 6 Specifications
- 7 Detailed Description
- 8 Applications and Implementation
- 9 Layout
- 10デバイスおよびドキュメントのサポート
- 11メカニカル、パッケージ、および注文情報
パッケージ・オプション
メカニカル・データ(パッケージ|ピン)
- PWP|20
サーマルパッド・メカニカル・データ
- PWP|20
発注情報
7.3.1 Hysteretic Control Circuit Overview
The LM3100 buck DC-DC regulator employs a control scheme in which the high-side switch on-time varies inversely with the line voltage (VIN). Control is based on a comparator and the one-shot on-timer, with the output voltage feedback (FB) compared with an internal reference of 0.8 V. If the FB level is below the reference the buck switch is turned on for a fixed time determined by the input voltage and a programming resistor (RON). Following the on-time, the switch remains off for a minimum of 260 ns. If FB is below the reference at that time the switch turns on again for another on-time period. The switching will continue until regulation is achieved.
The regulator will operate in discontinuous conduction mode at light load currents, and continuous conduction mode with heavy load current. In discontinuous conduction mode (DCM), current through the output inductor starts at zero and ramps up to a peak during the on-time, then ramps back to zero before the end of the off-time. The next on-time period starts when the voltage at FB falls below the internal reference. Until then the inductor current remains zero and the load is supplied entirely by the output capacitor. In this mode the operating frequency is lower than in continuous conduction mode, and varies with load current. Conversion efficiency is maintained since the switching losses are reduced with the reduction in load and switching frequency. The discontinuous operating frequency can be calculated approximately as follows:
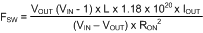
In continuous conduction mode (CCM), current always flows through the inductor and never reaches zero during the off-time. In this mode, the operating frequency remains relatively constant with load and line variations. The CCM operating frequency can be calculated approximately as follows:
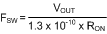
The output voltage is set by two external resistors (RFB1, RFB2). The regulated output voltage is calculated as follows: