JAJSDP6D February 2016 – March 2018 LM36274
PRODUCTION DATA.
- 1 特長
- 2 アプリケーション
- 3 概要
- 4 改訂履歴
- 5 Pin Configuration and Functions
- 6 Specifications
-
7 Detailed Description
- 7.1 Overview
- 7.2 Functional Block Diagram
- 7.3
Features Description
- 7.3.1 Enabling the LM36274
- 7.3.2 Backlight
- 7.3.3 LCM Bias
- 7.3.4 Software Reset
- 7.3.5 HWEN Input
- 7.3.6 Thermal Shutdown (TSD)
- 7.4 Device Functional Modes
- 7.5 Programming
- 7.6
Register Maps
- 7.6.1 Revision Register (Address = 0x01)[Reset = 0x01]
- 7.6.2 Backlight Configuration1 Register (Address = 0x02)[Reset = 0x28]
- 7.6.3 Backlight Configuration 2 Register (Address = 0x03)[Reset = 0x8D]
- 7.6.4 Backlight Brightness LSB Register (Address = 0x04)[Reset = 0x07]
- 7.6.5 Backlight Brightness MSB Register (Address = 0x05)[Reset = 0xFF]
- 7.6.6 Backlight Auto-Frequency Low Threshold Register (Address = 0x06)[Reset = 0x00]
- 7.6.7 Backlight Auto-Frequency High Threshold Register (Address = 0x07)[Reset = 0x00]
- 7.6.8 Backlight Enable Register (Address = 0x08)[Reset = 0x00]
- 7.6.9 Bias Configuration 1 Register (Address = 0x09)[Reset = 0x18]
- 7.6.10 Bias Configuration 2 register (Address = 0x0A)[Reset = 0x11]
- 7.6.11 Bias Configuration 3 Register (Address = 0x0B)[Reset = 0x00]
- 7.6.12 LCM Boost Bias Register (Address = 0x0C)[Reset = 0x28]
- 7.6.13 VPOS Bias Register (Address = 0x0D)[Reset = 0x1E]
- 7.6.14 VNEG Bias Register (Address = 0x0E)[Reset = 0x1C]
- 7.6.15 Flags Register (Address = 0x0F)[Reset = 0x00]
- 7.6.16 Option 1 Register (Address = 0x10)[Reset = 0x06]
- 7.6.17 Option 2 Register (Address = 0x11)[Reset = 0x35]
- 7.6.18 PWM-to-Digital Code Readback LSB Register (Address = 0x12)[Reset = 0x00]
- 7.6.19 PWM-to-Digital Code Readback MSB Register (Address = 0x13)[Reset = 0x00]
- 8 Application and Implementation
- 9 Power Supply Recommendations
- 10Layout
- 11デバイスおよびドキュメントのサポート
- 12メカニカル、パッケージ、および注文情報
7.3.2.8 Regulated Headroom Voltage
In order to optimize efficiency, current accuracy, and string-to-string matching the LED current sink regulated headroom voltage (VHR) varies with the target LED current. Figure 39 details the typical variation of VHR with LED current. This allows for increased solution efficiency as the dropout voltage of the LED driver changes. Furthermore, in order to ensure that all current sinks remain in regulation whenever there is a mismatch in string voltages, the minimum headroom voltage between VLED1, VLED2, VLED3, VLED4 becomes the regulation point for the boost converter. For example, if the LEDs connected to LED1 require 12 V, the LEDs connected to LED2 require 12.5 V, the LEDs connected to LED3 require 13 V and the LEDs connected to LED4 require 13.5 V at the programmed current, then the voltage at LED1 is VHR + 1.5 V, the voltage at LED2 is VHR + 1 V, the voltage at LED3 is VHR + 0.5, and the voltage at LED4 is regulated at VHR. In other words, the boost makes the cathode of the highest voltage LED string the regulation point.
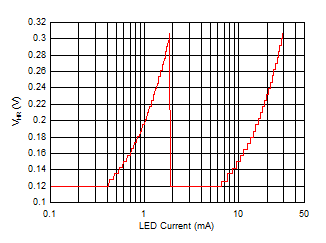 Figure 39. LM36274 Typical Exponential Regulated Headroom Voltage vs Programmed LED Current
Figure 39. LM36274 Typical Exponential Regulated Headroom Voltage vs Programmed LED Current