JAJSH28D November 2013 – March 2019 LM3697
PRODUCTION DATA.
- 1 特長
- 2 アプリケーション
- 3 概要
- 4 改訂履歴
- 5 Pin Configuration and Functions
- 6 Specifications
-
7 Detailed Description
- 7.1 Overview
- 7.2 Functional Block Diagram
- 7.3 Feature Descriptions
- 7.4 Device Functional Modes
- 7.5 Register Maps
- 8 Application and Implementation
- 9 Power Supply Recommendations
- 10Layout
- 11デバイスおよびドキュメントのサポート
- 12メカニカル、パッケージ、および注文情報
パッケージ・オプション
デバイスごとのパッケージ図は、PDF版データシートをご参照ください。
メカニカル・データ(パッケージ|ピン)
- YFQ|12
サーマルパッド・メカニカル・データ
発注情報
8.2.2.1.1 Peak Current Limited
In the case of a peak current limited situation, when the peak of the inductor current hits the LM3697 device's current limit, the NFET switch turns off for the remainder of the switching period. If this happens each switching cycle the LM3697 regulates the peak of the inductor current instead of the headroom across the current sinks. This can result in the dropout of the boost output connected current sinks, and the LED current dropping below its programmed level.
The peak current in a boost converter is dependent on the value of the inductor, total LED current in the boost (IOUT), the boost output voltage (VOUT) (which is the highest voltage LED string + VHR ), the input voltage (VIN), the switching frequency (ƒSW), and the efficiency (output power/input power). Additionally, the peak current is different depending on whether the inductor current is continuous during the entire switching period (CCM), or discontinuous (DCM) where it goes to 0 before the switching period ends. For CCM the peak inductor current is given by:
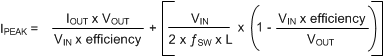
For DCM the peak inductor current is given by:
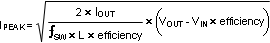
To determine which mode the circuit is operating in (CCM or DCM) it is necessary to perform a calculation to test whether the inductor current ripple is less than the anticipated input current (IIN). If ΔIL is less than IIN then the device is operating in CCM. If ΔIL is greater than IIN then the device is operating in DCM.
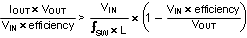
Typically at currents high enough to reach the LM3697's peak current limit, the device is operating in CCM.
Figure 14 and Figure 15 show the output current and voltage derating for a 10-µH and a 22-µH inductor. These plots take Equation 9 and Equation 10 and plot VOUT and IOUT with varying VIN, a constant peak current of 880 mA (ICL_MIN), 500-kHz switching frequency, and a constant efficiency of 85%. Using these curves can give a good design guideline on selecting the correct inductor for a given output power requirement. A 10-µH inductor will typically be a smaller device with lower on resistance, but the peak currents is higher. A 22-µH inductor provides for lower peak currents but a larger sized device is required to match the DC resistance of a 10-µH inductor.
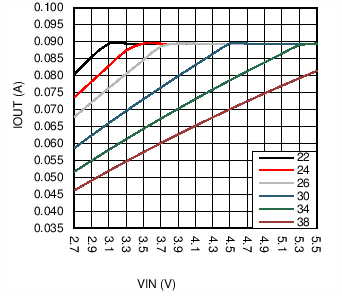 Figure 14. Maximum Output Power (22 µH)
Figure 14. Maximum Output Power (22 µH) 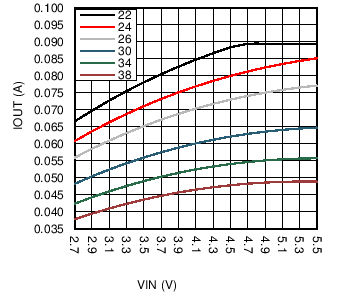 Figure 15. Maximum Output Power (10 µH)
Figure 15. Maximum Output Power (10 µH)