JAJSBZ5C April 2014 – April 2019 LM46002
PRODUCTION DATA.
- 1 特長
- 2 アプリケーション
- 3 概要
- 4 改訂履歴
- 5 Pin Configuration and Functions
- 6 Specifications
-
7 Detailed Description
- 7.1 Overview
- 7.2 Functional Block Diagram
- 7.3
Feature Description
- 7.3.1 Fixed-Frequency, Peak-Current-Mode-Controlled, Step-Down Regulator
- 7.3.2 Light Load Operation
- 7.3.3 Adjustable Output Voltage
- 7.3.4 Enable (ENABLE)
- 7.3.5 VCC, UVLO, and BIAS
- 7.3.6 Soft Start and Voltage Tracking (SS/TRK)
- 7.3.7 Switching Frequency (RT) and Synchronization (SYNC)
- 7.3.8 Minimum ON-Time, Minimum OFF-Time, and Frequency Foldback at Dropout Conditions
- 7.3.9 Internal Compensation and CFF
- 7.3.10 Bootstrap Voltage (BOOT)
- 7.3.11 Power Good (PGOOD)
- 7.3.12 Overcurrent and Short-Circuit Protection
- 7.3.13 Thermal Shutdown
- 7.4 Device Functional Modes
-
8 Applications and Implementation
- 8.1 Application Information
- 8.2
Typical Applications
- 8.2.1 Design Requirements
- 8.2.2
Detailed Design Procedure
- 8.2.2.1 Custom Design With WEBENCH® Tools
- 8.2.2.2 Output Voltage Setpoint
- 8.2.2.3 Switching Frequency
- 8.2.2.4 Input Capacitors
- 8.2.2.5 Inductor Selection
- 8.2.2.6 Output Capacitor Selection
- 8.2.2.7 Feed-Forward Capacitor
- 8.2.2.8 Bootstrap Capacitors
- 8.2.2.9 VCC Capacitor
- 8.2.2.10 BIAS Capacitors
- 8.2.2.11 Soft-Start Capacitors
- 8.2.2.12 Undervoltage Lockout Setpoint
- 8.2.2.13 PGOOD
- 8.2.3 Application Performance Curves
- 9 Power Supply Recommendations
- 10Layout
- 11デバイスおよびドキュメントのサポート
- 12メカニカル、パッケージ、および注文情報
パッケージ・オプション
デバイスごとのパッケージ図は、PDF版データシートをご参照ください。
メカニカル・データ(パッケージ|ピン)
- PWP|16
サーマルパッド・メカニカル・データ
発注情報
7.3.3 Adjustable Output Voltage
The voltage regulation loop in the LM46002 regulates output voltage by maintaining the voltage on FB pin (VFB) to be the same as the internal REF voltage (VREF). Use a resistor divider pair to program the ratio from output voltage VOUT to VFB. The resistor divider is connected from the VOUT of the LM46002 to ground with the mid-point connecting to the FB pin.
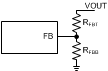 Figure 35. Output Voltage Setting
Figure 35. Output Voltage Setting The voltage reference system produces a precise voltage reference over temperature. The internal REF voltage is 1.011 V typically. To program the output voltage of the LM46002 to be a certain value VOUT, RFBB can be calculated with a selected RFBT by Equation 1:
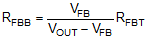
The choice of the RFBT depends on the application. TI recommends RFBT in the range from 10 kΩ to 100 kΩ for most applications. A lower RFBT value can be used if static loading is desired to reduce VOUT offset in PFM operation. Lower RFBT reduces efficiency at very light load. Less static current goes through a larger RFBT and might be more desirable when light load efficiency is critical. But RFBT larger than 1 MΩ is not recommended because it makes the feedback path more susceptible to noise. Larger RFBT value requires more carefully designed feedback path on the PCB. The tolerance and temperature variation of the resistor dividers affect the output voltage regulation. TI recommends using divider resistors with 1% tolerance or better and temperature coefficient of 100 ppm or lower.
If the resistor divider is not connected properly, output voltage cannot be regulated because the feedback loop is broken. If the FB pin is shorted to ground, the output voltage is driven close to VIN because the regulator detects very low voltage on the FB pin and tries to regulate it up. The load connected to the output could be damaged under such a condition. Do not short FB pin to ground when the LM46002 is enabled. It is important to route the feedback trace away from the noisy area of the PCB. For more layout recommendations, see Layout section.