JAJSCO0D November 2016 – August 2021 LM5170-Q1
PRODUCTION DATA
- 1 特長
- 2 アプリケーション
- 3 概要
- 4 Revision History
- 5 概要 (続き)
- 6 Pin Configuration and Functions
- 7 Specifications
-
8 Detailed Description
- 8.1 Overview
- 8.2 Functional Block Diagram
- 8.3
Feature Description
- 8.3.1 Bias Supply (VCC, VCCA)
- 8.3.2 Undervoltage Lockout (UVLO) and Master Enable or Disable
- 8.3.3 High Voltage Input (VIN, VINX)
- 8.3.4 Current Sense Amplifier
- 8.3.5 Control Commands
- 8.3.6 Channel Current Monitor (IOUT1, IOUT2)
- 8.3.7 Cycle-by-Cycle Peak Current Limit (IPK)
- 8.3.8 Error Amplifier
- 8.3.9 Ramp Generator
- 8.3.10 Soft Start
- 8.3.11 Gate Drive Outputs, Dead Time Programming and Adaptive Dead Time (HO1, HO2, LO1, LO2, DT)
- 8.3.12 PWM Comparator
- 8.3.13 Oscillator (OSC)
- 8.3.14 Synchronization to an External Clock (SYNCIN, SYNCOUT)
- 8.3.15 Diode Emulation
- 8.3.16 Power MOSFET Failure Detection and Failure Protection (nFAULT, BRKG, BRKS)
- 8.3.17 Overvoltage Protection (OVPA, OVPB)
- 8.4 Device Functional Modes
- 8.5 Programming
-
9 Application and Implementation
- 9.1 Application Information
- 9.2
Typical Application
- 9.2.1
60-A, Dual-Phase, 48-V to 12-V Bidirectional Converter
- 9.2.1.1 Design Requirements
- 9.2.1.2
Detailed Design Procedure
- 9.2.1.2.1 Determining the Duty Cycle
- 9.2.1.2.2 Oscillator Programming
- 9.2.1.2.3 Power Inductor, RMS and Peak Currents
- 9.2.1.2.4 Current Sense (RCS)
- 9.2.1.2.5 Current Setting Limits (ISETA or ISETD)
- 9.2.1.2.6 Peak Current Limit
- 9.2.1.2.7 Power MOSFETS
- 9.2.1.2.8 Bias Supply
- 9.2.1.2.9 Boot Strap
- 9.2.1.2.10 RAMP Generators
- 9.2.1.2.11 OVP
- 9.2.1.2.12 Dead Time
- 9.2.1.2.13 IOUT Monitors
- 9.2.1.2.14 UVLO Pin Usage
- 9.2.1.2.15 VIN Pin Configuration
- 9.2.1.2.16 Loop Compensation
- 9.2.1.2.17 Soft Start
- 9.2.1.2.18 ISET Pins
- 9.2.1.3 Application Curves
- 9.2.1
60-A, Dual-Phase, 48-V to 12-V Bidirectional Converter
- 10Power Supply Recommendations
- 11Layout
- 12Device and Documentation Support
- 13Mechanical, Packaging, and Orderable Information
パッケージ・オプション
メカニカル・データ(パッケージ|ピン)
- PHP|48
サーマルパッド・メカニカル・データ
- PHP|48
発注情報
8.5.1 Dynamic Dead Time Adjustment
In addition to a fixed dead time programming by RDT, the dead time can be dynamically adjusted either by applying an analog voltage or a PWM signal as shown in Figure 8-27. Varying the analog voltage or the duty ratio of the PWM signal will adjust the DT programming. For analog adjustment, a single stage RC filter is recommended to filter out any possible noise. For PWM adjustment, a two-stage RC filter is recommended to minimize the ripple voltage resulted on the DT pin.
 Figure 8-27 Dynamic Dead Time Adjustment
Figure 8-27 Dynamic Dead Time AdjustmentWhen an analog voltage is applied, the resulted dead time is determined by Equation 19:

where
- VADJ is the analog voltage used to adjust the dead time
When a PWM signal is applied, the resulted dead time is determined by Equation 20:
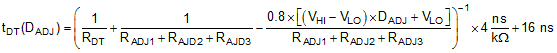
where
- VHI and VLO are the high and low voltage levels of the PWM signal, respectively,
- DADJ is the duty factor of the PWM signal.