-
LMK61XX High-Performance Ultra-Low Jitter Oscillator SNAS676D October 2015 – October 2017 LMK61A2-100M , LMK61A2-125M , LMK61A2-156M , LMK61A2-312M , LMK61A2-644M , LMK61E0-050M , LMK61E0-155M , LMK61E0-156M , LMK61E2-100M , LMK61E2-125M , LMK61E2-156M , LMK61E2-312M , LMK61I2-100M
PRODUCTION DATA.
-
LMK61XX High-Performance Ultra-Low Jitter Oscillator
- 1 Features
- 2 Applications
- 3 Description
- 4 Revision History
- 5 Pin Configuration and Functions
-
6 Specifications
- 6.1 Absolute Maximum Ratings
- 6.2 ESD Ratings
- 6.3 Recommended Operating Conditions
- 6.4 Thermal Information
- 6.5 Electrical Characteristics - Power Supply
- 6.6 LVPECL Output Characteristics
- 6.7 LVDS Output Characteristics
- 6.8 HCSL Output Characteristics
- 6.9 OE Input Characteristics
- 6.10 Frequency Tolerance Characteristics
- 6.11 Power-On/Reset Characteristics (VDD)
- 6.12 PSRR Characteristics
- 6.13 PLL Clock Output Jitter Characteristics
- 6.14 Typical 156.25-MHz Output Phase Noise Characteristics
- 6.15 Additional Reliability and Qualification
- 6.16 Typical Characteristics
- 7 Parameter Measurement Information
- 8 Power Supply Recommendations
- 9 Layout
- 10Device and Documentation Support
- 11Mechanical, Packaging, and Orderable Information
- IMPORTANT NOTICE
パッケージ・オプション
デバイスごとのパッケージ図は、PDF版データシートをご参照ください。
メカニカル・データ(パッケージ|ピン)
- SIA|6
サーマルパッド・メカニカル・データ
発注情報
LMK61XX High-Performance Ultra-Low Jitter Oscillator
1 Features
- Ultra-low Noise, High Performance
- Jitter: 90 fs RMS Typical Fout > 100 MHz
- PSRR: –70 dBc, Robust Supply Noise Immunity
- Supported Output Format
- LVPECL up to 1 GHz
- LVDS up to 900 MHz
- HCSL up to 400 MHz
- Total Frequency Tolerance of ± 50 ppm (LMK61X2) and ± 25 ppm (LMK61X0)
- 3.3-V Operating Voltage
- Industrial Temperature Range (–40ºC to +85ºC)
- 7 mm × 5 mm 6-Pin Package, Pin-Compatible With Industry Standard 7050 XO Package
2 Applications
- High-Performance Replacement for Crystal, SAW, or Silicon-Based Oscillators
- Switches, Routers, Network Line Cards, Base Band Units (BBU), Servers, Storage/SAN
- Test and Measurement
- Medical Imaging
- FPGA, Processor Attach
3 Description
The LMK61XX is an ultra-low jitter oscillator that generates a commonly used reference clock. The device is pre-programmed in factory to support any reference clock frequency; supported output formats are LVPECL up to 1 GHz, LVDS up to 900 MHz, and HCSL up to 400 MHz. Internal power conditioning provide excellent power supply ripple rejection (PSRR), reducing the cost and complexity of the power delivery network. The device operates from a single 3.3 V ± 5% supply.
Device Information(1)
- For all available packages, see the orderable addendum at the end of the data sheet.
4 Revision History
Changes from C Revision (September 2017) to D Revision
Changes from B Revision (March 2017) to C Revision
- Added LMK61E0-155M Go
Changes from A Revision (November 2015) to B Revision
- Updated data sheet text to the latest documentation and translations standards Go
- Added LMK61E0-050M Go
- Updated key graphic Go
- Added Receiving Notification of Documentation Updates section Go
Changes from * Revision (October 2015) to A Revision
- Product Preview to Production Data Datasheet Go
5 Pin Configuration and Functions

Pin Functions
| PIN | I/O | DESCRIPTION | |
|---|---|---|---|
| NAME | NO. | ||
| POWER | |||
| GND | 3 | Ground | Device Ground. |
| VDD | 6 | Analog | 3.3 V Power Supply. |
| OUTPUT BLOCK | |||
| OUTP, OUTN | 4, 5 | Universal | Differential Output Pair (LVPECL, LVDS or HCSL). |
| DIGITAL CONTROL / INTERFACES | |||
| NC | 2 | N/A | No Connect. |
| OE | 1 | LVCMOS | Output Enable (internal pullup). When set to low, output pair is disabled and set at high impedance. |
6 Specifications
6.1 Absolute Maximum Ratings
over operating free-air temperature range (unless otherwise noted)(1)| MIN | MAX | UNIT | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| VDD | Device supply voltage | –0.3 | 3.6 | V |
| VIN | Output voltage for logic inputs | –0.3 | VDD + 0.3 | V |
| VOUT | Output voltage for clock outputs | –0.3 | VDD + 0.3 | V |
| TJ | Junction temperature | 150 | °C | |
| TSTG | Storage temperature | –40 | 125 | °C |
6.2 ESD Ratings
| VALUE | UNIT | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| V(ESD) | Electrostatic discharge | Human-body model (HBM), per ANSI/ESDA/JEDEC JS-001(1) | ±4000 | V |
| Charged-device model (CDM), per JEDEC specification JESD22-C101(2) | ±1500 | |||
6.3 Recommended Operating Conditions
over operating free-air temperature range (unless otherwise noted)| MIN | NOM | MAX | UNIT | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| VDD | Device supply voltage | 3.135 | 3.3 | 3.465 | V | |
| TA | Ambient temperature | –40 | 25 | 85 | °C | |
| TJ | Junction temperature | LMK61X2 | 125 | °C | ||
| LMK61X0 | 115 | °C | ||||
| tRAMP | VDD power-up ramp time | 0.1 | 100 | ms | ||
6.4 Thermal Information
| THERMAL METRIC(1) | LMK61XX (2) (3) (4) | UNIT | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| SIA (QFM) | |||||
| 6 PINS | |||||
| Airflow (LFM) 0 | Airflow (LFM) 200 | Airflow (LFM) 400 | |||
| RθJA | Junction-to-ambient thermal resistance | 55.2 | 46.4 | 43.7 | °C/W |
| RθJC(top) | Junction-to-case (top) thermal resistance | 34.6 | n/a | n/a | °C/W |
| RθJB | Junction-to-board thermal resistance | 37.7 | n/a | n/a | °C/W |
| ψJT | Junction-to-top characterization parameter | 11.3 | 17.6 | 22.5 | °C/W |
| ψJB | Junction-to-board characterization parameter | 37.7 | 41.5 | 40.1 | °C/W |
| RθJC(bot) | Junction-to-case (bottom) thermal resistance | n/a | n/a | n/a | °C/W |
6.5 Electrical Characteristics - Power Supply(1)
VDD = 3.3 V ± 5%, TA = -40C to 85°C| PARAMETER | TEST CONDITIONS | MIN | TYP | MAX | UNIT | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| IDD | Device current consumption | LVPECL(2) | 162 | 208 | mA | |
| LVDS | 152 | 196 | ||||
| HCSL | 155 | 196 | ||||
| IDD-PD | Device current consumption when output is disabled | OE = GND | 136 | mA | ||
6.6 LVPECL Output Characteristics(1)
VDD = 3.3 V ± 5%, TA = -40C to 85°C| PARAMETER | TEST CONDITIONS | MIN | TYP | MAX | UNIT | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| fOUT | Output frequency(2) | 10 | 1000 | MHz | ||
| VOD | Output voltage swing (VOH – VOL)(2) |
700 | 800 | 1200 | mV | |
| VOUT, DIFF, PP | Differential output peak-to-peak swing | 2 × |VOD| | V | |||
| VOS | Output common-mode voltage | VDD – 1.55 | V | |||
| tR / tF | Output rise/fall time (20% to 80%)(3) | 120 | 200 | ps | ||
| PN-Floor | Output phase noise floor (fOFFSET > 10 MHz) | 156.25 MHz | –165 | dBc/Hz | ||
| ODC | Output duty cycle(3) | 45% | 55% | |||
6.7 LVDS Output Characteristics(1)
VDD = 3.3 V ± 5%, TA = –40°C to 85°C| PARAMETER | TEST CONDITIONS | MIN | TYP | MAX | UNIT | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| fOUT | Output frequency(1) | 10 | 900 | MHz | ||
| VOD | Output voltage swing (VOH – VOL)(1) |
300 | 390 | 480 | mV | |
| VOUT, DIFF, PP | Differential output peak-to-peak swing | 2 × |VOD| | V | |||
| VOS | Output common-mode voltage | 1.2 | V | |||
| tR / tF | Output rise/fall time (20% to 80%)(2) | 150 | 250 | ps | ||
| PN-Floor | Output phase noise floor (fOFFSET > 10 MHz) | 156.25 MHz | –162 | dBc/Hz | ||
| ODC | Output duty cycle(2) | 45% | 55% | |||
| ROUT | Differential output impedance | 125 | Ohm | |||
6.8 HCSL Output Characteristics(1)
VDD = 3.3 V ± 5%, TA = –40°C to 85°C| PARAMETER | TEST CONDITIONS | MIN | TYP | MAX | UNIT | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| fOUT | Output frequency | 10 | 400 | MHz | ||
| VOH | Output high voltage | 600 | 850 | mV | ||
| VOL | Output low voltage | –100 | 100 | mV | ||
| VCROSS | Absolute crossing voltage(2)(3) | 250 | 475 | mV | ||
| VCROSS-DELTA | Variation of VCROSS(2)(3) | 0 | 140 | mV | ||
| dV/dt | Slew rate(4) | 0.8 | 2 | V/ns | ||
| PN-Floor | Output phase noise floor (fOFFSET > 10 MHz) | 100 MHz | –164 | dBc/Hz | ||
| ODC | Output duty cycle(4) | 45% | 55% | |||
6.9 OE Input Characteristics
VDD = 3.3 V ± 5%, TA = –40°C to 85°C| PARAMETER | TEST CONDITIONS | MIN | TYP | MAX | UNIT | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| VIH | Input high voltage | 1.4 | V | |||
| VIL | Input low voltage | 0.6 | V | |||
| IIH | Input high current | VIH = VDD | –40 | 40 | uA | |
| IIL | Input low current | VIL = GND | –40 | 40 | uA | |
| CIN | Input capacitance | 2 | pF | |||
6.10 Frequency Tolerance Characteristics(1)
VDD = 3.3 V ± 5%, TA = –40°C to 85°C| PARAMETER | TEST CONDITIONS | MIN | TYP | MAX | UNIT | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| fT | Total frequency tolerance | LMK61X2: All output formats, frequency bands and device junction temperature up to 125°C; includes initial freq tolerance, temperature & supply voltage variation, solder reflow and aging (10 years) | –50 | 50 | ppm | |
| LMK61X0: All output formats, frequency bands and device junction temperature up to 115°C; includes initial freq tolerance, temperature & supply voltage variation, solder reflow and aging (5 years at 40°C) | –25 | 25 | ppm | |||
6.11 Power-On/Reset Characteristics (VDD)
VDD = 3.3 V ± 5%, TA = –40°C to 85°C| PARAMETER | TEST CONDITIONS | MIN | TYP | MAX | UNIT | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| VTHRESH | Threshold voltage(1) | 2.72 | 2.95 | V | ||
| VDROOP | Allowable voltage droop(2) | 0.1 | V | |||
| tSTARTUP | Start-up time (1) | Time elapsed from VDD at 3.135 V to output enabled | 10 | ms | ||
| tOE-EN | Output enable time(2) | Time elapsed from OE at VIH to output enabled | 50 | us | ||
| tOE-DIS | Output disable time(2) | Time elapsed from OE at VIL to output disabled | 50 | us | ||
6.12 PSRR Characteristics(1)
VDD = 3.3 V, TA = 25°C, FS[1:0] = NC, NC| PARAMETER | TEST CONDITIONS | MIN | TYP | MAX | UNIT | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| PSRR | Spurs induced by 50-mV power supply ripple(2)(3) at 156.25-MHz output, all output types | Sine wave at 50 kHz | –70 | dBc | ||
| Sine wave at 100 kHz | –70 | |||||
| Sine wave at 500 kHz | –70 | |||||
| Sine wave at 1 MHz | –70 | |||||
6.13 PLL Clock Output Jitter Characteristics(1)(3)
VDD = 3.3 V ± 5%, TA = –40°C to 85°C| PARAMETER | TEST CONDITIONS | MIN | TYP | MAX | UNIT | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| RJ | RMS phase jitter(2)
(12 kHz – 20 MHz) (1 kHz – 5 MHz) |
fOUT < 100 MHz, all output types | 200 | 300 | fs RMS | |
| RJ | RMS phase jitter(2)
(12 kHz – 20 MHz) (1 kHz – 5 MHz) |
fOUT ≥ 100 MHz (except 155.52 MHz and 644.53125 MHz), all output types | 100 | 200 | fs RMS | |
| RJ | RMS phase jitter(2)
(12 kHz – 20 MHz) (1 kHz – 5 MHz) |
fOUT = 155.52 MHz or 644.53125 MHz, all output types | 150 | 300 | fs RMS | |
6.14 Typical 156.25-MHz Output Phase Noise Characteristics(1)(2)
VDD = 3.3 V, TA = 25°C, Output Type = LVPECL/LVDS/HCSL| PARAMETER | OUTPUT TYPE | UNITS | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| LVPECL | LVDS | HCSL | |||
| phn10k | Phase noise at 10-kHz offset | –143 | –143 | –143 | dBc/Hz |
| Phn20k | Phase noise at 20-kHz offset | –143 | –143 | –143 | dBc/Hz |
| phn100k | Phase noise at 100-kHz offset | –144 | –144 | –144 | dBc/Hz |
| Phn200k | Phase noise at 200-kHz offset | –145 | –145 | –145 | dBc/Hz |
| phn1M | Phase noise at 1-MHz offset | –150 | –150 | –150 | dBc/Hz |
| phn2M | Phase noise at 2-MHz offset | –154 | –154 | –154 | dBc/Hz |
| phn10M | Phase noise at 10-MHz offset | –165 | –162 | –164 | dBc/Hz |
| phn20M | Phase noise at 20-MHz offset | –165 | –162 | –164 | dBc/Hz |
6.15 Additional Reliability and Qualification
| PARAMETER | CONDITION / TEST METHOD |
|---|---|
| Mechanical Shock | MIL-STD-202, Method 213 |
| Mechanical Vibration | MIL-STD-202, Method 204 |
| Moisture Sensitivity Level | J-STD-020, MSL3 |
6.16 Typical Characteristics









7 Parameter Measurement Information
7.1 Device Output Configurations
 Figure 10. LVPECL Output DC Configuration During Device Test
Figure 10. LVPECL Output DC Configuration During Device Test
 Figure 11. LVDS Output DC Configuration During Device Test
Figure 11. LVDS Output DC Configuration During Device Test
 Figure 12. HCSL Output DC Configuration During Device Test
Figure 12. HCSL Output DC Configuration During Device Test
 Figure 13. LVPECL Output AC Configuration During Device Test
Figure 13. LVPECL Output AC Configuration During Device Test
 Figure 14. LVDS Output AC Configuration During Device Test
Figure 14. LVDS Output AC Configuration During Device Test
 Figure 15. HCSL Output AC Configuration During Device Test
Figure 15. HCSL Output AC Configuration During Device Test
 Figure 16. PSRR Test Setup
Figure 16. PSRR Test Setup
 Figure 17. Differential Output Voltage and Rise/Fall Time
Figure 17. Differential Output Voltage and Rise/Fall Time
8 Power Supply Recommendations
For best electrical performance of LMK61XX, TI recommends using a combination of 10 µF, 1 µF and 0.1 µF on its power supply bypass network. TI also recommends using component side mounting of the power supply bypass capacitors and it is best to use 0201 or 0402 body size capacitors to facilitate signal routing. Keep the connections between the bypass capacitors and the power supply on the device as short as possible. Ground the other side of the capacitor using a low impedance connection to the ground plane. Figure 18 shows the layout recommendation for power supply decoupling of LMK61XX.
9 Layout
9.1 Layout Guidelines
The following sections provides recommendations for board layout, solder reflow profile and power supply bypassing when using LMK61XX to ensure good thermal / electrical performance and overall signal integrity of entire system.
9.1.1 Ensuring Thermal Reliability
The LMK61XX is a high performance device. Therefore, pay careful attention to device configuration and printed-circuit board (PCB) layout with respect to power consumption. The ground pin needs to be connected to the ground plane of the PCB through three vias or more, as shown in Figure 18, to maximize thermal dissipation out of the package.
Equation 1 describes the relationship between the PCB temperature around the LMK61XX and its junction temperature.
where
- TB: PCB temperature around the LMK61XX
- TJ: Junction temperature of LMK61XX
- ΨJB: Junction-to-board thermal resistance parameter of LMK61XX (37.7°C/W without airflow)
- P: On-chip power dissipation of LMK61XX
To ensure that the maximum junction temperature of LMK61X2 is below 125°C, the maximum PCB temperature without airflow should be at 99°C or below (89°C or below for LMK61X0) when the device is optimized for best performance resulting in maximum on-chip power dissipation of 0.68 W.
9.1.2 Best Practices for Signal Integrity
For best electrical performance and signal integrity of entire system with LMK61XX, TI recommends routing vias into decoupling capacitors and then into the LMK61XX. TI also recommends increasing the via count and width of the traces wherever possible. These steps ensure lowest impedance and shortest path for high frequency current flow. Figure 18 shows the layout recommendation for LMK61XX.
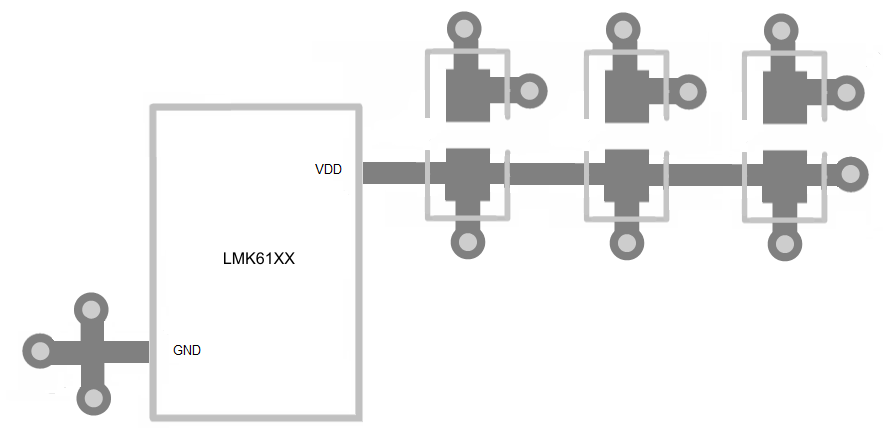 Figure 18. LMK61XX Layout Recommendation for Power Supply and Ground
Figure 18. LMK61XX Layout Recommendation for Power Supply and Ground
9.1.3 Recommended Solder Reflow Profile
TI recommends following the solder paste supplier's recommendations to optimize flux activity and to achieve proper melting temperatures of the alloy within the guidelines of J-STD-20. It is preferrable for the LMK61XX to be processed with the lowest peak temperature possible while also remaining below the components peak temperature rating as listed on the MSL label. The exact temperature profile would depend on several factors including maximum peak temperature for the component as rated on the MSL label, Board thickness, PCB material type, PCB geometries, component locations, sizes, densities within PCB, as well solder manufactures recommended profile, and capability of the reflow equipment to as confirmed by the SMT assembly operation.