JAJSIO5B July 2019 – February 2020 LMR36506-Q1
ADVANCE INFORMATION for pre-production products; subject to change without notice.
- 1 特長
- 2 アプリケーション
- 3 概要
- 4 改訂履歴
- 5 Device Comparison Table
- 6 Pin Configuration and Functions
- 7 Specifications
-
8 Detailed Description
- 8.1 Overview
- 8.2 Functional Block Diagram
- 8.3
Feature Description
- 8.3.1 Output Voltage Selection
- 8.3.2 Enable and Start-up
- 8.3.3 External CLK SYNC (with MODE/SYNC)
- 8.3.4 Adjustable Switching Frequency (with RT)
- 8.3.5 Power-Good Flag Output
- 8.3.6 Internal LDO, VCC UVLO, and VOUT/BIAS Input
- 8.3.7 Bootstrap Voltage and VCBOOT-UVLO (CBOOT Terminal)
- 8.3.8 Spread Spectrum
- 8.3.9 Soft Start and Recovery from Dropout
- 8.3.10 Current Limit and Short Circuit
- 8.3.11 Thermal Shutdown
- 8.4 Device Functional Modes
-
9 Application and Implementation
- 9.1 Application Information
- 9.2
Typical Application
- 9.2.1 Design Requirements
- 9.2.2 Detailed Design Procedure
- 9.3 What to Do and What Not to Do
- 10Power Supply Recommendations
- 11Layout
- 12デバイスおよびドキュメントのサポート
- 13メカニカル、パッケージ、および注文情報
パッケージ・オプション
メカニカル・データ(パッケージ|ピン)
- RPE|9
サーマルパッド・メカニカル・データ
- RPE|9
発注情報
9.2.2.4 Output Capacitor Selection
The value of the output capacitor and its ESR determine the output voltage ripple and load transient performance. The output capacitor bank is usually limited by the load transient requirements and stability rather than the output voltage ripple. Equation 4 can be used to estimate a lower bound on the total output capacitance and an upper bound on the ESR, which is required to meet a specified load transient. Use as a starting point to determine the required output capacitor for each design.
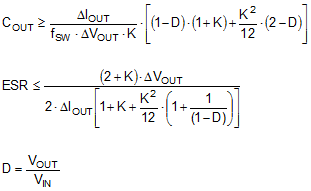
where
- ΔVOUT = output voltage transient
- ΔIOUT = output current transient
- K = ripple factor from Inductor Selection
Once the output capacitor and ESR have been calculated, use Equation 5 to check the output voltage ripple.
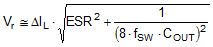
where
- Vr = peak-to-peak output voltage ripple
The output capacitor and ESR can then be adjusted to meet both the load transient and output ripple requirements.
In practice, the output capacitor has the most influence on the transient response and loop-phase margin. Load transient testing and bode plots are the best way to validate any given design and must always be completed before the application goes into production. In addition to the required output capacitance, a small ceramic placed on the output can help reduce high-frequency noise. Small-case size ceramic capacitors in the range of 1 nF to 100 nF can be very helpful in reducing spikes on the output caused by inductor and board parasitics.
Limit the maximum value of total output capacitance to about 10 times the design value, or 1000 µF, whichever is smaller. Large values of output capacitance can adversely affect the start-up behavior of the regulator as well as the loop stability. If values larger than noted here must be used, then a careful study of start-up at full load and loop stability must be performed.