JAJSKO0C October 2021 – November 2022 LMR51420
PRODUCTION DATA
- 1 特長
- 2 アプリケーション
- 3 概要
- 4 Revision History
- 5 Device Comparison Table
- 6 Pin Configuration and Functions
- 7 Specifications
- 8 Detailed Description
- 9 Application and Implementation
- 10Device and Documentation Support
- 11Mechanical, Packaging, and Orderable Information
9.2.2.4 Inductor Selection
The most critical parameters for the inductor are the inductance, saturation current, and the RMS current. The inductance is based on the desired peak-to-peak ripple current, ΔiL. Because the ripple current increases with the input voltage, the maximum input voltage is always used to calculate the minimum inductance, LMIN. Use Equation 11 to calculate the minimum value of the output inductor. KIND is a coefficient that represents the amount of inductor ripple current relative to the maximum output current of the device. A reasonable value of KIND must be 20% to 60% of maximum IOUT supported by the converter. During an instantaneous overcurrent operation event, the RMS and peak inductor current can be high. The inductor saturation current must be higher than peak current limit level.
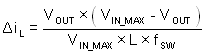
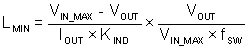
In general, choose lower inductance in switching power supplies because it usually corresponds to faster transient response, smaller DCR, and reduced size for more compact designs. Too low of an inductance can generate too large of an inductor current ripple such that overcurrent protection at the full load can be falsely triggered and generates more inductor core loss because the current ripple is larger. Larger inductor current ripple also implies larger output voltage ripple with the same output capacitors. With peak current mode control, ensure there is an adequate amount of inductor ripple current. A larger inductor ripple current improves the comparator signal-to-noise ratio.
For this design example, choose KIND = 0.3. The minimum inductor value is calculated to be 9.7 µH. Choose the nearest standard 10-µH ferrite inductor with a capability of 3-A RMS current and 4-A saturation current.