JAJSF93 April 2018 LMV7239-Q1
PRODUCTION DATA.
- 1 特長
- 2 アプリケーション
- 3 概要
- 4 改訂履歴
- 5 Pin Configuration and Functions
- 6 Specifications
- 7 Detailed Description
- 8 Application and Implementation
- 9 Power Supply Recommendations
- 10Layout
- 11デバイスおよびドキュメントのサポート
- 12メカニカル、パッケージ、および注文情報
パッケージ・オプション
メカニカル・データ(パッケージ|ピン)
サーマルパッド・メカニカル・データ
発注情報
8.2.1.2 Detailed Design Procedure
The maximum frequency is limited by the large signal propagation delay of the comparator and by the capacitive loading at the output, which limits the output slew rate.
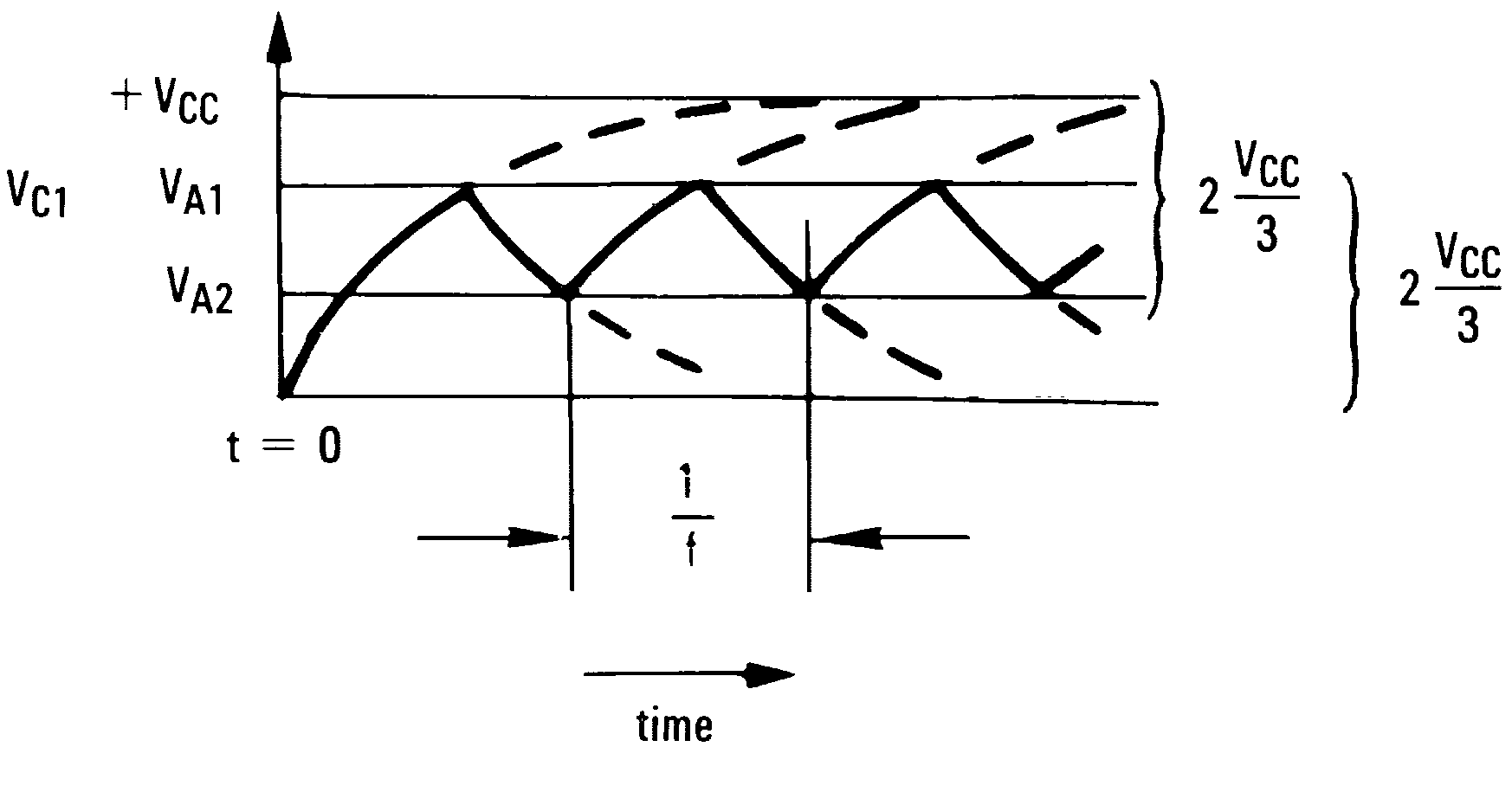 Figure 25. Square Wave Oscillator Timing Thresholds
Figure 25. Square Wave Oscillator Timing Thresholds
Consider the output of Figure 24 to be high to analyze the circuit. That implies that the inverted input (VC) is lower than the noninverting input (VA). This causes the C1 to be charged through R4, and the voltage VC increases until it is equal to the noninverting input. The value of VA at this point is:
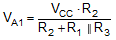
If R1 = R2 = R3, then V A1 = 2 Vcc/3
At this point the comparator switches pulling down the output to the negative rail. The value of VA at this point is:
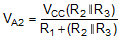
If R1 = R2 = R3, then VA2 = VCC/3.
The capacitor C1 now discharges through R4, and the voltage VC decreases until it is equal to VA2, at which point the comparator switches again, bringing it back to the initial stage. The time period is equal to twice the time it takes to discharge C1 from 2VCC/3 to VCC/3, which is given by R4C1·ln2. Hence the formula for the frequency is:
The LMV7239 should be used for a symmetrical output. The LMV7235 will require a pullup resistor on the output to function, and will have a slightly asymmetrical output due to the reduced sourcing current.