SNOS998I February 2002 – October 2015 LMV761 , LMV762 , LMV762Q-Q1
PRODUCTION DATA.
- 1 Features
- 2 Applications
- 3 Description
- 4 Revision History
- 5 Pin Configuration and Functions
-
6 Specifications
- 6.1 Absolute Maximum Ratings
- 6.2 ESD Ratings: LMV761, LMV762
- 6.3 ESD Ratings: LMV762Q-Q1
- 6.4 Recommended Operating Conditions
- 6.5 Thermal Information
- 6.6 2.7-V Electrical Characteristics
- 6.7 5-V Electrical Characteristics
- 6.8 2-V Switching Characteristics
- 6.9 5-V Switching Characteristics
- 6.10 Typical Characteristics
- 7 Detailed Description
- 8 Application and Implementation
- 9 Power Supply Recommendations
- 10Layout
- 11Device and Documentation Support
- 12Mechanical, Packaging, and Orderable Information
パッケージ・オプション
メカニカル・データ(パッケージ|ピン)
サーマルパッド・メカニカル・データ
発注情報
6 Specifications
6.1 Absolute Maximum Ratings
See (1)(2)| MIN | MAX | UNIT | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Supply voltage (V+ – V−) | 5.5 | V | ||
| Differential input voltage | Supply Voltage | |||
| Voltage between any two pins | Supply Voltage | |||
| Output short circuit duration(3) | Current at input pin | ±5 | mA | |
| Soldering information | Infrared or convection (20 sec.) | 235 | °C | |
| Wave soldering (10 sec.) (Lead temp) | 260 | °C | ||
| Junction temperature | 150 | °C | ||
| Storage temperature, Tstg | −65 | 150 | °C | |
(1) Stresses beyond those listed under Absolute Maximum Ratings may cause permanent damage to the device. These are stress ratings only, which do not imply functional operation of the device at these or any other conditions beyond those indicated under Recommended Operating Conditions. Exposure to absolute-maximum-rated conditions for extended periods may affect device reliability.
(2) If Military/Aerospace specified devices are required, please contact the Texas Instruments Sales Office/Distributors for availability and specifications.
(3) Applies to both single supply and split supply operation. Continuous short circuit operation at elevated ambient temperature can result in exceeding the maximum allowed junction temperature of 150°C. Output current in excess of ±25 mA over long term may adversely affect reliability.
6.2 ESD Ratings: LMV761, LMV762
| VALUE | UNIT | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| V(ESD) | Electrostatic discharge(2) | Human body model (HBM), per ANSI/ESDA/JEDEC JS-001(1) | ± 2000 | V |
| Machine model | ± 200 | |||
(1) JEDEC document JEP155 states that 500-V HBM allows safe manufacturing with a standard ESD control process.
(2) Unless otherwise specified human body model is 1.5 kΩ in series with 100 pF. Machine model 200 pF.
6.3 ESD Ratings: LMV762Q-Q1
| VALUE | UNIT | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| V(ESD) | Electrostatic discharge | Human-body model (HBM), per AEC Q100-002(1) | ± 2000 | V |
| Machine model | ± 200 | |||
(1) AEC Q100-002 indicates that HBM stressing shall be in accordance with the ANSI/ESDA/JEDEC JS-001 specification.
6.4 Recommended Operating Conditions
| MIN | MAX | UNIT | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Supply voltage (V+ – V−) | 2.7 | 5.25 | V | |
| Temperature range | −40 | 125 | °C | |
6.5 Thermal Information
| THERMAL METRIC(1) | LMV761 | LMV762, LMV762Q-Q1 | UNIT | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| D (SOIC) | DBV (SOT-23) | DGK (VSSOP) | |||
| 8 PINS | 6 PINS | 8 PINS | |||
| RθJA | Junction-to-ambient thermal resistance (2) | 190 | 265 | 235 | °C/W |
(1) For more information about traditional and new thermal metrics, see the Semiconductor and IC Package Thermal Metrics application report, SPRA953.
(2) The maximum power dissipation is a function of TJ(MAX), θJA, and TA. The maximum allowable power dissipation at any ambient temperature is PD = (TJ(MAX) – TA) RθJA. All numbers apply for packages soldered directly into a PCB.
6.6 2.7-V Electrical Characteristics
Unless otherwise specified, all limited ensured for TJ = 25°C, VCM = V+ / 2, V+ = 2.7 V, V− = 0 V−.| PARAMETER | TEST CONDITIONS | MIN(4) | TYP(3) | MAX(4) | UNIT | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| VOS | Input offset voltage | 0.2 | mV | ||||
| apply at the temperature extremes(2) | 1 | ||||||
| IB | Input bias current(5) | 0.2 | 50 | pA | |||
| IOS | Input offset current(5) | 0.001 | 5 | pA | |||
| CMRR | Common-mode rejection ratio | 0 V < VCM < VCC – 1.3 V | 80 | 100 | dB | ||
| PSRR | Power supply rejection ratio | V+ = 2.7 V to 5 V | 80 | 110 | dB | ||
| CMVR | Input common-mode voltage range | CMRR > 50 dB | apply at the temperature extremes(2) | −0.3 | 1.5 | V | |
| VO | Output swing high | IL = 2 mA, VID = 200 mV | V+ – 0.35 | V+ – 0.1 | V | ||
| Output swing low | IL = −2 mA, VID = –200 mV | 90 | 250 | mV | |||
| ISC | Output short circuit current(1) | Sourcing, VO = 1.35 V, VID = 200 mV | 6 | 20 | mA | ||
| Sinking, VO = 1.35 V, VID = –200 mV | 6 | 15 | |||||
| IS | Supply current LMV761 (single comparator) | 275 | 700 | μA | |||
| LMV762, LMV762Q-Q1 (both comparators) | 550 | μA | |||||
| apply at the temperature extremes(2) | 1400 | ||||||
| IOUT LEAKAGE | Output leakage I at shutdown | SD = GND, VO = 2.7 V | 0.2 | μA | |||
| IS LEAKAGE | Supply leakage I at shutdown | SD = GND, VCC = 2.7 V | 0.2 | 2 | μA | ||
(1) Electrical Table values apply only for factory testing conditions at the temperature indicated. Factory testing conditions result in very limited self-heating of the device such that TJ = TA. No ensured specification of parametric performance is indicated in the electrical tables under conditions of internal self-heating where TJ > TA. See Recommended Operating Conditions for information on temperature de-rating of this device. Absolute Maximum Rating indicate junction temperature limits beyond which the device may be permanently degraded, either mechanically or electrically.
(2) Maximum temperature ensured range is −40°C to +125°C.
(3) Typical values represent the most likely parametric norm.
(4) All limits are specified by testing or statistical analysis.
(5) Specified by design.
6.7 5-V Electrical Characteristics
Unless otherwise specified, all limited ensured for TJ = 25°C, VCM = V+ / 2, V+ = 5 V, V− = 0 V−.| PARAMETER | TEST CONDITIONS | MIN(4) | TYP(3) | MAX(4) | UNIT | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| VOS | Input offset voltage | 0.2 | mV | ||||
| apply at the temperature extremes(2) | 1 | ||||||
| IB | Input bias current(5) | 0.2 | 50 | pA | |||
| IOS | Input offset current(5) | 0.01 | 5 | pA | |||
| CMRR | Common-mode rejection ratio | 0 V < VCM < VCC – 1.3 V | 80 | 100 | dB | ||
| PSRR | Power supply rejection ratio | V+ = 2.7 V to 5 V | 80 | 110 | dB | ||
| CMVR | Input common-mode voltage range | CMRR > 50 dB | apply at the temperature extremes(2) | −0.3 | 3.8 | V | |
| VO | Output swing high | IL = 4 mA, VID = 200 mV | V+ – 0.35 | V+ – 0.1 | V | ||
| Output swing low | IL = –4 mA, VID = –200 mV | 120 | 250 | mV | |||
| ISC | Output short circuit current(1) | Sourcing, VO = 2.5 V, VID = 200 mV | 6 | 60 | mA | ||
| Sinking, VO = 2.5 V, VID = −200 mV | 6 | 40 | |||||
| IS | Supply current LMV761 (single comparator) | 225 | 700 | μA | |||
| LMV762, LMV762Q-Q1 (both comparators) | 450 | μA | |||||
| apply at the temperature extremes(2) | 1400 | ||||||
| IOUT LEAKAGE | Output leakage I at shutdown | SD = GND, VO = 5 V | 0.2 | μA | |||
| IS LEAKAGE | Supply leakage I at shutdown | SD = GND, VCC = 5 V | 0.2 | 2 | μA | ||
(1) Electrical Table values apply only for factory testing conditions at the temperature indicated. Factory testing conditions result in very limited self-heating of the device such that TJ = TA. No ensured specification of parametric performance is indicated in the electrical tables under conditions of internal self-heating where TJ > TA. See Recommended Operating Conditions for information on temperature de-rating of this device. Absolute Maximum Rating indicate junction temperature limits beyond which the device may be permanently degraded, either mechanically or electrically.
(2) Maximum temperature ensured range is −40°C to +125°C.
(3) Typical values represent the most likely parametric norm.
(4) All limits are specified by testing or statistical analysis.
(5) Specified by design.
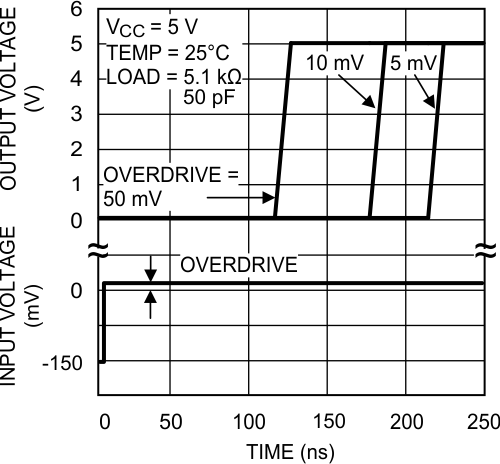
6.8 2-V Switching Characteristics
over operating free-air temperature range (unless otherwise noted)| PARAMETER | TEST CONDITIONS | MIN | TYP | MAX | UNIT | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| tPD | Propagation delay RL = 5.1 kΩ CL = 50 pF |
Overdrive = 5 mV | 270 | ns | ||
| Overdrive = 10 mV | 205 | |||||
| Overdrive = 50 mV | 120 | |||||
| tSKEW | Propagation delay skew | 5 | ns | |||
| tr | Output rise time | 10% to 90% | 1.7 | ns | ||
| tf | Output fall time | 90% to 10% | 1.8 | ns | ||
| ton | Turnon time from shutdown | 6 | μs | |||
6.9 5-V Switching Characteristics
over operating free-air temperature range (unless otherwise noted)| PARAMETER | TEST CONDITIONS | MIN | TYP | MAX | UNIT | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| tPD | Propagation delay RL = 5.1 kΩ CL = 50 pF |
Overdrive = 5 mV | 225 | ns | ||
| Overdrive = 10 mV | 190 | |||||
| Overdrive = 50 mV | 120 | |||||
| tSKEW | Propagation delay skew | 5 | ns | |||
| tr | Output rise time | 10% to 90% | 1.7 | ns | ||
| tf | Output fall time | 90% to 10% | 1.5 | ns | ||
| ton | Turnon time from shutdown | 4 | μs | |||
6.10 Typical Characteristics
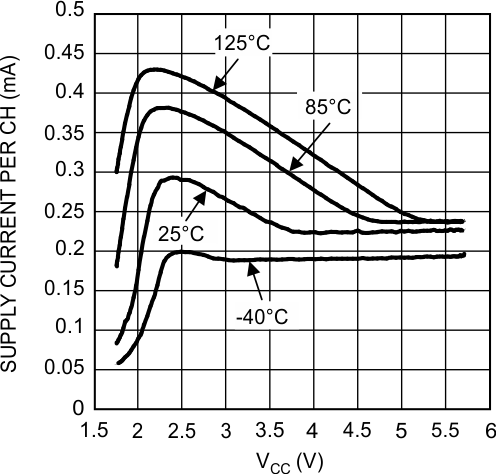
| VO = High | |||||









| VO = Low |