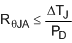JAJSAB5F December 2006 – November 2016 LP38853
PRODUCTION DATA.
- 1 特長
- 2 アプリケーション
- 3 概要
- 4 改訂履歴
- 5 Pin Configuration and Functions
- 6 Specifications
- 7 Detailed Description
- 8 Application and Implementation
- 9 Power Supply Recommendations
- 10Layout
- 11デバイスおよびドキュメントのサポート
- 12メカニカル、パッケージ、および注文情報
- 12メカニカル、パッケージ、および注文情報
パッケージ・オプション
メカニカル・データ(パッケージ|ピン)
サーマルパッド・メカニカル・データ
発注情報
8.2.2.2 Power Dissipation and Heat Sinking
Additional copper area for heat sinking may be required, depending on the maximum device dissipation (PD) and the maximum anticipated ambient temperature (TA) for the device. Under all possible conditions, the junction temperature must be within the range specified under operating conditions.
The total power dissipation of the device is the sum of three different points of dissipation in the device.
The first part is the power that is dissipated in the NMOS pass element and can be determined with Equation 8:
The second part is the power that is dissipated in the bias and control circuitry and can be determined with Equation 9:
where
- IGND(BIAS) is the portion of the operating ground current of the device that is related to VBIAS.
The third part is the power that is dissipated in portions of the output stage circuitry and can be determined with Equation 10:
where
- IGND(IN) is the portion of the operating ground current of the device that is related to VIN.
The total power dissipation is shown by Equation 11:
The maximum allowable junction temperature rise (ΔTJ) depends on the maximum anticipated ambient temperature (TA(MAX)) for the application, and the maximum allowable operating junction temperature (TJ(MAX))(see Equation 12):
The maximum allowable value for junction-to-ambient thermal resistance, RθJA, can be calculated using Equation 13: