JAJSEA9A December 2017 – March 2018 MSP430FR5969-SP
PRODUCTION DATA.
- 1デバイスの概要
- 2改訂履歴
- 3Terminal Configuration and Functions
-
4Specifications
- 4.1 Absolute Maximum Ratings
- 4.2 ESD Ratings
- 4.3 Recommended Operating Conditions
- 4.4 Active Mode Supply Current Into VCC Excluding External Current
- 4.5 Typical Characteristics – Active Mode Supply Currents
- 4.6 Low-Power Mode (LPM0, LPM1) Supply Currents Into VCC Excluding External Current
- 4.7 Low-Power Mode (LPM2, LPM3, LPM4) Supply Currents (Into VCC) Excluding External Current
- 4.8 Low-Power Mode (LPM3.5, LPM4.5) Supply Currents (Into VCC) Excluding External Current
- 4.9 Typical Characteristics, Current Consumption per Module
- 4.10 Thermal Resistance Characteristics
- 4.11
Timing and Switching Characteristics
- 4.11.1 Power Supply Sequencing
- 4.11.2 Reset Timing
- 4.11.3 Clock Specifications
- 4.11.4 Wake-up Characteristics
- 4.11.5 Digital I/Os
- 4.11.6 Timer_A and Timer_B
- 4.11.7 eUSCI
- 4.11.8
ADC
- Table 4-22 12-Bit ADC, Power Supply and Input Range Conditions
- Table 4-23 12-Bit ADC, Timing Parameters
- Table 4-24 12-Bit ADC, Linearity Parameters With External Reference
- Table 4-25 12-Bit ADC, Dynamic Performance for Differential Inputs With External Reference
- Table 4-26 12-Bit ADC, Dynamic Performance for Differential Inputs With Internal Reference
- Table 4-27 12-Bit ADC, Dynamic Performance for Single-Ended Inputs With External Reference
- Table 4-28 12-Bit ADC, Dynamic Performance for Single-Ended Inputs With Internal Reference
- Table 4-29 12-Bit ADC, Dynamic Performance With 32.768-kHz Clock
- Table 4-30 12-Bit ADC, Temperature Sensor and Built-In V1/2
- Table 4-31 12-Bit ADC, External Reference
- 4.11.9 Reference
- 4.11.10 Comparator
- 4.11.11 FRAM
- 4.12 Emulation and Debug
-
5Detailed Description
- 5.1 Overview
- 5.2 CPU
- 5.3 Operating Modes
- 5.4 Interrupt Vector Table and Signatures
- 5.5 Memory Organization
- 5.6 Bootloader (BSL)
- 5.7 JTAG Operation
- 5.8 FRAM
- 5.9 Memory Protection Unit Including IP Encapsulation
- 5.10
Peripherals
- 5.10.1 Digital I/O
- 5.10.2 Oscillator and Clock System (CS)
- 5.10.3 Power-Management Module (PMM)
- 5.10.4 Hardware Multiplier (MPY)
- 5.10.5 Real-Time Clock (RTC_B) (Only MSP430FR596x and MSP430FR594x)
- 5.10.6 Watchdog Timer (WDT_A)
- 5.10.7 System Module (SYS)
- 5.10.8 DMA Controller
- 5.10.9 Enhanced Universal Serial Communication Interface (eUSCI)
- 5.10.10 TA0, TA1
- 5.10.11 TA2, TA3
- 5.10.12 TB0
- 5.10.13 ADC12_B
- 5.10.14 Comparator_E
- 5.10.15 CRC16
- 5.10.16 AES256 Accelerator
- 5.10.17 True Random Seed
- 5.10.18 Shared Reference (REF)
- 5.10.19 Embedded Emulation
- 5.10.20 Peripheral File Map
- 5.11
Input and Output Diagrams
- 5.11.1 Port P1 (P1.0 to P1.2) Input/Output With Schmitt Trigger
- 5.11.2 Port P1 (P1.3 to P1.5) Input/Output With Schmitt Trigger
- 5.11.3 Port P1 (P1.6 and P1.7) Input/Output With Schmitt Trigger
- 5.11.4 Port P2 (P2.0 to P2.2) Input/Output With Schmitt Trigger
- 5.11.5 Port P2 (P2.3 and P2.4) Input/Output With Schmitt Trigger
- 5.11.6 Port P2 (P2.5 and P2.6) Input/Output With Schmitt Trigger
- 5.11.7 Port P2 (P2.7) Input/Output With Schmitt Trigger
- 5.11.8 Port P3 (P3.0 to P3.3) Input/Output With Schmitt Trigger
- 5.11.9 Port P3 (P3.4 to P3.7) Input/Output With Schmitt Trigger
- 5.11.10 Port P4 (P4.0 to P4.3) Input/Output With Schmitt Trigger
- 5.11.11 Port P4 (P4.4 to P4.7) Input/Output With Schmitt Trigger
- 5.11.12 Port PJ, PJ.4 and PJ.5 Input/Output With Schmitt Trigger
- 5.11.13 Port PJ (PJ.6 and PJ.7) Input/Output With Schmitt Trigger
- 5.11.14 Port PJ (PJ.0 to PJ.3) JTAG Pins TDO, TMS, TCK, TDI/TCLK, Input/Output With Schmitt Trigger
- 5.12 Device Descriptor (TLV)
- 5.13 Identification
- 6Applications, Implementation, and Layout
- 7デバイスおよびドキュメントのサポート
- 8メカニカル、パッケージ、および注文情報
パッケージ・オプション
メカニカル・データ(パッケージ|ピン)
サーマルパッド・メカニカル・データ
発注情報
4.3 Recommended Operating Conditions
Typical data are based on VCC = 3.0 V, TA = 25°C (unless otherwise noted)| MIN | NOM | MAX | UNIT | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| VCC | Supply voltage range applied at all DVCC and AVCC pins(1)(2)(3) | 1.8(6) | 3.6 | V | ||
| VSS | Supply voltage applied at all DVSS and AVSS pins | 0 | V | |||
| TJ | Operating junction temperature | –55 | 105 | °C | ||
| CDVCC | Capacitor value at DVCC(4) | 1–20% | µF | |||
| fSYSTEM | Processor frequency (maximum MCLK frequency)(5) | No FRAM wait states
(NWAITSx = 0) |
0 | 8(8) | MHz | |
| With FRAM wait states
(NWAITSx = 1)(7) |
0 | 16(9) | ||||
| fACLK | Maximum ACLK frequency | 50 | kHz | |||
| fSMCLK | Maximum SMCLK frequency | 16(9) | MHz | |||
(1) TI recommends powering AVCC and DVCC pins from the same source. At a minimum, during power up, power down, and device operation, the voltage difference between AVCC and DVCC must not exceed the limits specified in Absolute Maximum Ratings. Exceeding the specified limits may cause malfunction of the device including erroneous writes to RAM and FRAM.
(2) See Table 4-1 for additional important information.
(3) Modules may have a different supply voltage range specification. See the specification of the respective module in this data sheet.
(4) Connect a low-ESR capacitor with at least the value specified and a maximum tolerance of 20% as close as possible to the DVCC pin.
(5) Modules may have a different maximum input clock specification. See the specification of the respective module in this data sheet.
(6) The minimum supply voltage is defined by the supervisor SVS levels. See Table 4-2 for the exact values.
(7) Wait states only occur on actual FRAM accesses; that is, on FRAM cache misses. RAM and peripheral accesses are always executed without wait states.
(8) DCO settings and HF crystals with a typical value less or equal the specified MAX value are permitted.
(9) DCO settings and HF crystals with a typical value less or equal the specified MAX value are permitted. If a clock sources with a larger typical value is used, the clock must be divided in the clock system.
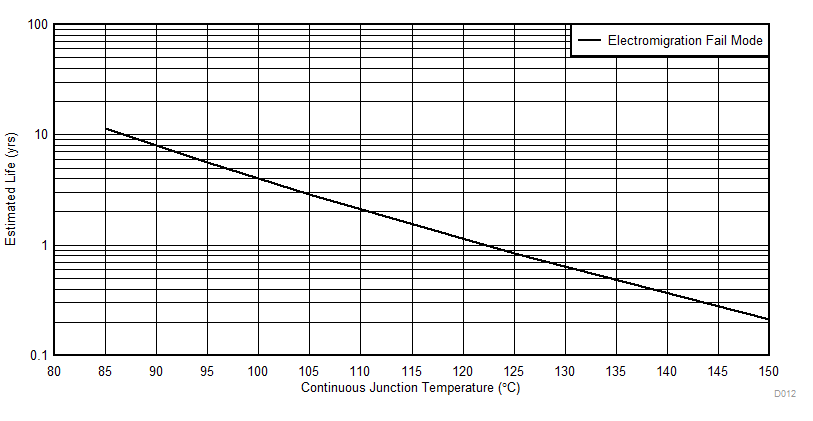
1. See data sheet for absolute maximum and minimum recommended operating conditions.
2. The predicted operating lifetime vs junction temperature is based on reliability modeling using electromigration as the dominant failure mechanism affecting device wear-out for the specific device process and design characteristics.
Figure 4-1 MSP430FR5969-SP EM Lifetime Derating Chart