SLTS278J November 2010 – March 2020 PTH08T250W
PRODUCTION DATA.
- 1 Features
- 2 Applications
- 3 Description
- 4 Revision History
- 5 Description (continued)
- 6 Pin Configuration and Functions
- 7 Specifications
- 8 Detailed Description
-
9 Application and Implementation
- 9.1
Typical Application
- 9.1.1
Detailed Design Procedure
- 9.1.1.1 Adjusting the Output Voltage
- 9.1.1.2
Capacitor Recommendations for the PTH08T250W Power Module
- 9.1.1.2.1 Capacitor Technologies
- 9.1.1.2.2 Input Capacitor (Required)
- 9.1.1.2.3 Input Capacitor Information
- 9.1.1.2.4 Output Capacitor (Required)
- 9.1.1.2.5 Output Capacitor Information
- 9.1.1.2.6 TurboTrans Output Capacitance
- 9.1.1.2.7 Non-TurboTrans Output Capacitance
- 9.1.1.2.8 Designing for Fast Load Transients
- 9.1.1.2.9 Capacitor Table
- 9.1.1.3 TurboTrans™ Technology
- 9.1.1.4 TurboTrans™ Selection
- 9.1.1.5 Undervoltage Lockout (UVLO)
- 9.1.1.6 On/Off Inhibit
- 9.1.1.7 Current Sharing
- 9.1.1.8 Prebias Startup Capability
- 9.1.1.9 SmartSync Technology
- 9.1.1.10 Auto-Track™ Function
- 9.1.1
Detailed Design Procedure
- 9.1
Typical Application
- 10Device and Documentation Support
- 11Mechanical, Packaging, and Orderable Information
デバイスごとのパッケージ図は、PDF版データシートをご参照ください。
メカニカル・データ(パッケージ|ピン)
- BCU|22
- ECT|22
- ECU|22
サーマルパッド・メカニカル・データ
6 Pin Configuration and Functions
ECT, ECU or EBU Package
22 Pin
(Top View)
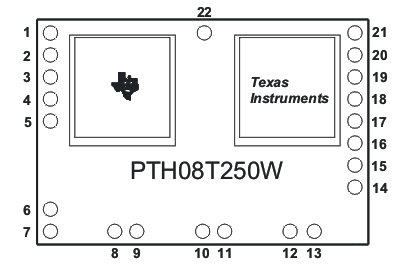
Table 1. Pin Functions
| PIN | DESCRIPTION | |
|---|---|---|
| NAME | NO. | |
| VI | 6, 7, 14, 15 | The positive input voltage power node to the module, which is referenced to common GND. |
| VO | 10, 11 | The regulated positive power output with respect to GND |
| GND | 8, 9, 12, 13 | This is the common ground connection for the VI and VO power connections. It is also the 0 Vdc reference for the control inputs. |
| Inhibit(1) and UVLO | 21 | The Inhibit pin is an open-collector/drain, negative logic input that is referenced to GND. Applying a low level ground signal to this input disables the module’s output and turns off the output voltage. When the Inhibit control is active, the input current drawn by the regulator is significantly reduced. If the Inhibit pin is left open-circuit, the module produces an output whenever a valid input source is applied. |
| This pin is also used for input undervoltage lockout (UVLO) programming. Connecting a resistor from this pin to GND (pin 13) allows the ON threshold of the UVLO to be adjusted higher than the default value. For more information, see the Application and Implementation section. | ||
| Vo Adjust | 18 | A 0.05 W, 1% resistor must be directly connected between this pin and pin 4 (AGND) to set the output voltage to a value higher than 0.7 V. The temperature stability of the resistor should be 100 ppm/°C (or better). The setpoint range for the output voltage is from 0.7 V to 3.6 V. If left open circuit, the output voltage defaults to its lowest value. For further information, on output voltage adjustment see the related application note. |
| Specifications gives the preferred resistor values for a number of standard output voltages. | ||
| + Sense | 17 | The sense input allows the regulation circuit to compensate for voltage drop between the module and the load. The +Sense pin should always be connected to VO, either at the load for optimal voltage accuracy, or at the module (pin 11). |
| – Sense | 16 | The sense input allows the regulation circuit to compensate for voltage drop between the module and the load. The –Sense pin should always be connected to GND, either at the load for optimal voltage accuracy, or at the module (pin 13). |
| Track | 20 | This is an analog control input that enables the output voltage to follow an external voltage. This pin becomes active typically 25 ms after a valid input voltage has been applied, and allows direct control of the output voltage from 0 V up to the nominal set-point voltage. Within this range the module's output voltage follows the voltage at the Track pin on a volt-for-volt basis. When the control voltage is raised above this range, the module regulates at its set-point voltage. The feature allows the output voltage to rise simultaneously with other modules powered from the same input bus. If unused, this input should be connected to VI. |
| NOTE: Due to the undervoltage lockout feature, the output of the module cannot follow its own input voltage during power up. For more information, see the related application note. | ||
| TurboTrans | 19 | This input pin adjusts the transient response of the regulator. To activate the TurboTrans feature, a 1%, 50 mW resistor, must be connected between this pin and pin 17 (+Sense) very close to the module. For a given value of output capacitance, a reduction in peak output voltage deviation is achieved by utilizing this feature. If unused, this pin must be left open-circuit. The resistance requirement can be selected from the TurboTrans resistor table in the Application Information section. External capacitance must never be connected to this pin unless the TurboTrans resistor value is a short, 0 Ω. |
| SmartSync | 22 | This input pin synchronizes the switching frequency of the module to an external clock frequency. The SmartSync feature can be used to synchronize the switching frequency of multiple modules, aiding EMI noise suppression efforts. The external synchronization frequency must be present before a valid input voltage is present, or before the release of inhibit control. If unused, this pin MUST be connected to GND. For more information, please review the Application Information section. |
| CONFIG | 1 | When two modules are connected together to share load current, one must be configured as the MASTER and the other as the SLAVE. This pin is used to configure the module as either MASTER or SLAVE. To configure the module as the MASTER, connect this pin to GND. To configure the module as the SLAVE, connect this pin to VI (pin 6). When not sharing current, this pin should be connected to GND. |
| Share | 2 | This pin is used when connecting two modules together to share load current. When two modules are sharing current the Share pin of both modules must be connected together. When not sharing current, this pin MUST be left open (floating). |
| Comp | 3 | This pin is used when connecting two modules together to share load current. When two modules are sharing current the Comp pin of both modules must be connected together. When not sharing current, this pin MUST be left open (floating). |
| AGND | 4 | This pin is the internal analog ground of the module. This pin provides the return path for the VOAdjust resistor (RSET). When two modules are sharing current the AGND pin of both modules must be connected together. Also, when two modules are connected, RSET must be connected only on the MASTER module. |
| CLKIO | 5 | This pin is used when connecting two modules together to share load current. When two modules are sharing current the CLKIO pin of both modules must be connected together. When not sharing current, this pin MUST be left open (floating). |
(1) Denotes negative logic: Open = Normal operation, Ground = Function active