JAJSGM4 December 2018 SN55HVD233-SEP
PRODUCTION DATA.
- 1 特長
- 2 アプリケーション
- 3 概要
- 4 改訂履歴
- 5 概要(続き)
- 6 Pin Configuration and Functions
-
7 Specifications
- 7.1 Absolute Maximum Ratings
- 7.2 ESD Ratings
- 7.3 Recommended Operating Conditions
- 7.4 Thermal Information
- 7.5 Driver Electrical Characteristics
- 7.6 Receiver Electrical Characteristics
- 7.7 Driver Switching Characteristics
- 7.8 Receiver Switching Characteristics
- 7.9 Device Switching Characteristics
- 7.10 Typical Characteristics
- 8 Parameter Measurement Information
- 9 Detailed Description
- 10Application and Implementation
- 11Power Supply Recommendations
- 12Layout
- 13デバイスおよびドキュメントのサポート
- 14メカニカル、パッケージ、および注文情報
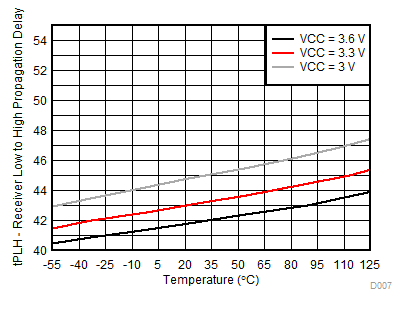
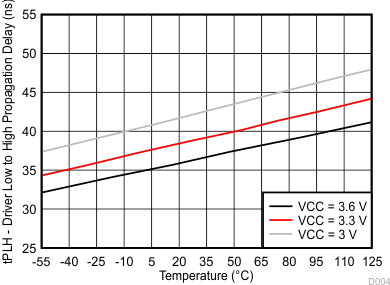
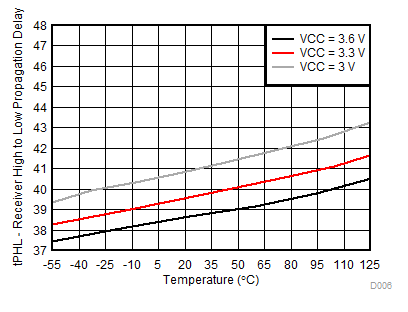
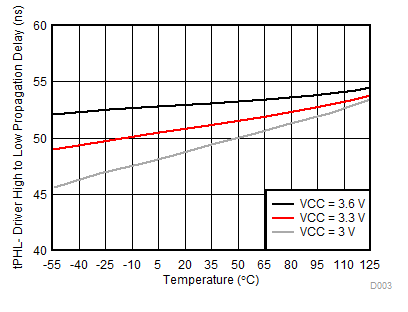
7.10 Typical Characteristics
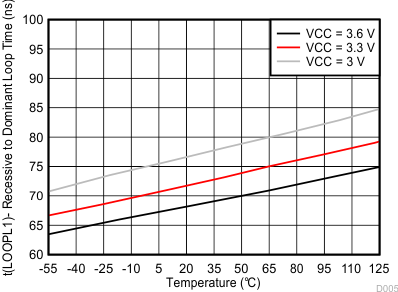
| V(RS), V(LBK) = 0 V |
Temperature
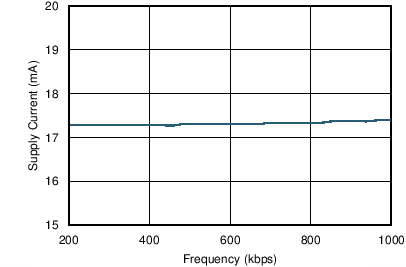
| VCC = 3.3 V | V(RS), V(LBK) = 0 V | TA = 25°C |
| 60-Ω load |
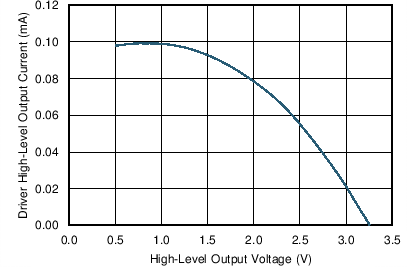
| VCC = 3.3 V | V(RS), V(LBK) = 0 V | TA = 25°C |
High-Level Output Voltage
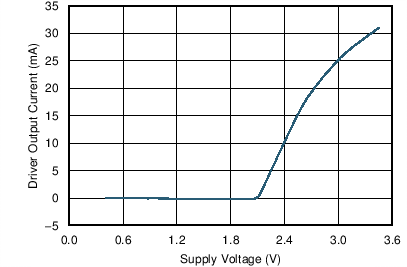
| V(RS), V(LBK) = 0 V | TA = 25°C | RL = 60 Ω |
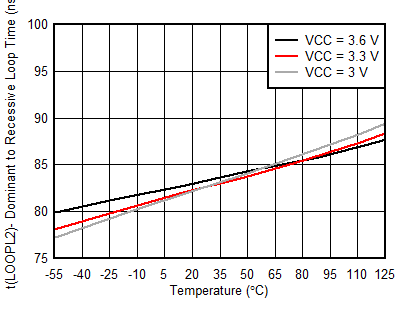
| V(RS), V(LBK) = 0 V |
Temperature
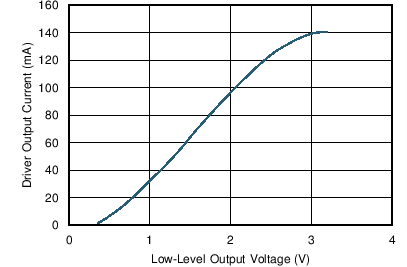
| VCC = 3.3 V | V(RS), V(LBK) = 0 V | TA = 25°C |
Low-Level Output Voltage
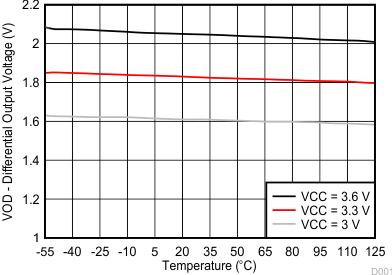
| RL = 60 Ω | V(RS), V(LBK) = 0 V | |
Temperature