JAJSFO1G September 2012 – June 2018 SN65DSI84
PRODUCTION DATA.
- 1 特長
- 2 アプリケーション
- 3 概要
- 4 改訂履歴
- 5 Pin Configuration and Functions
- 6 Specifications
- 7 Detailed Description
- 8 Application and Implementation
- 9 Power Supply Recommendations
- 10Layout
- 11デバイスおよびドキュメントのサポート
- 12メカニカル、パッケージ、および注文情報
7.4.6 DSI Video Transmission Specifications
The SN65DSI84 supports burst video mode and non-burst video mode with sync events or with sync pulses packet transmission as described in the DSI specification. The burst mode supports time-compressed pixel stream packets that leave added time per scan line for power savings LP mode. The SN65DSI84 requires a transition to LP mode once per frame to enable PHY synchronization with the DSI host processor; however, for a robust and low-power implementation, the transition to LP mode is recommended on every video line.
Figure 17 illustrates the DSI video transmission applied to SN65DSI84 applications. In all applications, the LVDS output rate must be less than or equal to the DSI input rate. The first line of a video frame shall start with a VSS packet, and all other lines start with VSE or HSS. The position of the synchronization packets in time is of utmost importance since this has a direct impact on the visual performance of the display panel; that is, these packets generate the HS and VS (horizontal and vertical sync) signals on the LVDS interface after the delay programmed into CHA_SYNC_DELAY_LOW/HIGH (CSR 0x28.7:0 and 0x29.3:0).
As required in the DSI specification, the SN65DSI84 requires that pixel stream packets contain an integer number of pixels (i.e. end on a pixel boundary); it is recommended to transmit an entire scan line on one pixel stream packet. When a scan line is broken in to multiple packets, inter-packet latency shall be considered such that the video pipeline (ie. pixel queue or partial line buffer) does not run empty (i.e. under-run); during scan line processing, if the pixel queue runs empty, the SN65DSI84 transmits zero data (18’b0 or 24’b0) on the LVDS interface.
NOTE
When the HS clock is used as a source for the LVDS pixel clock, the LP mode transitions apply only to the data lanes, and the DSI clock lane remains in the HS mode during the entire video transmission.
The DSI84 does not support the DSI Virtual Channel capability or reverse direction (peripheral to processor) transmissions.
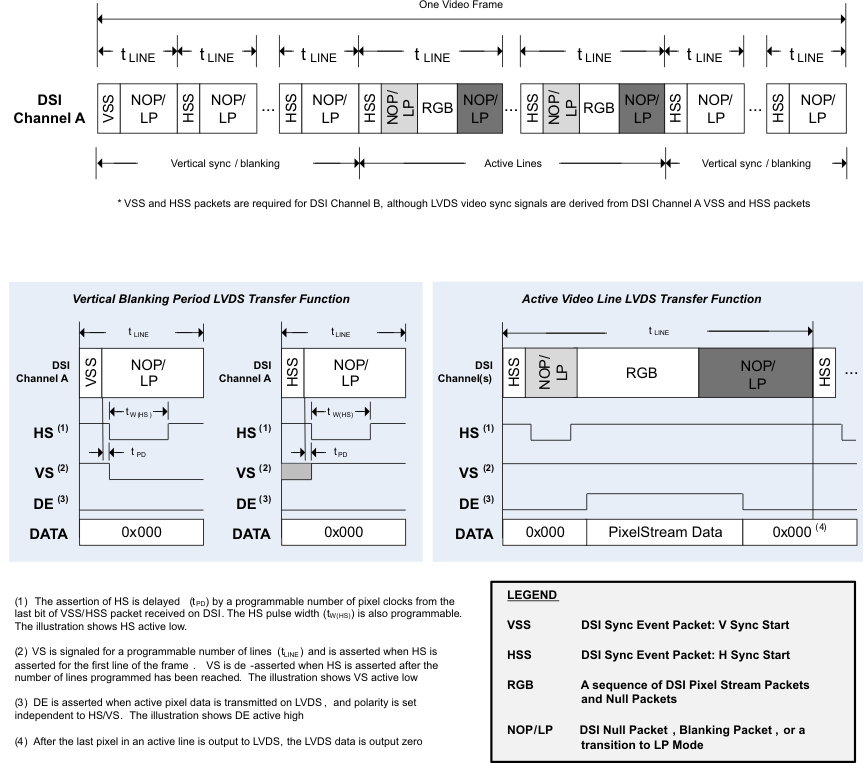 Figure 17. DSI Channel Transmission and Transfer Function
Figure 17. DSI Channel Transmission and Transfer Function