-
SN65HVD11-HT 3.3-V RS-485 Transceiver
- 1 Features
- 2 Applications
- 3 Description
- 4 Revision History
- 5 Pin Configuration and Functions
- 6 Specifications
- 7 Parameter Measurement Information
- 8 Detailed Description
- 9 Application and Implementation
- 10Power Supply Recommendations
- 11Layout
- 12Device and Documentation Support
- 13Mechanical, Packaging, and Orderable Information
- IMPORTANT NOTICE
パッケージ・オプション
メカニカル・データ(パッケージ|ピン)
サーマルパッド・メカニカル・データ
発注情報
SN65HVD11-HT 3.3-V RS-485 Transceiver
1 Features
- Operates With a 3.3-V Supply
- Bus-Pin ESD Protection Exceeds 16-kV Human-Body Model (HBM)
- 1/8 Unit-Load Option Available (up to 256 Nodes on Bus)
- Optional Driver Output Transition Times for Signaling Rates (1) of 1 Mbps, 10 Mbps, and
32 Mbps - Based on ANSI TIA/EIA-485-A
- Bus-Pin Short Circuit Protection From
–7 V to 12 V - Open-Circuit, Idle-Bus, and Shorted-Bus Fail-Safe Receiver
- Glitch-Free Power-Up and Power-Down Protection for Hot-Plugging Applications
- SN75176 Footprint
- Supports Extreme Temperature Applications:
- Controlled Baselines
- One Assembly and Test Sites
- One Fabrication Sites
- Available in Extreme (–55°C/210°C) Temperature Range (2)
- Extended Product Life Cycles
- Extended Product-Change Notifications
- Product Traceability
- Texas Instruments' High Temperature Products Use Highly Optimized Silicon (Die) Solutions With Design and Process Enhancements to Maximize Performance Over Extended Temperatures.
2 Applications
- Down-Hole Drilling
- High Temperature Environments
- Digital Motor Controls
- Utility Meters
- Chassis-to-Chassis Interconnects
- Electronic Security Stations
- Industrial Process Controls
- Building Automation
- Point-of-Sale (POS) Terminals and Networks
3 Description
The SN65HVD11-HT device combines a 3-state differential line driver and differential input line receiver that operates with a single 3.3-V power supply. It is designed for balanced transmission lines and meets or exceeds ANSI TIA/EIA-485-A and ISO 8482:1993, with the exception that the thermal shutdown is removed. This differential bus transceiver is a monolithic integrated circuit designed for bidirectional data communication on multipoint bus-transmission lines. The driver and receiver have active-high and active-low enables, respectively, that can be externally connected together to function as direction control.
The driver differential outputs and receiver differential inputs connect internally to form a differential input/ output (I/O) bus port that is designed to offer minimum loading to the bus when the driver is disabled or VCC = 0.
Device Information(1)
| PART NUMBER | PACKAGE | BODY SIZE (NOM) |
|---|---|---|
| SN65HVD11-HT | SOIC (8) | 4.90 mm × 3.91 mm |
| CFP (8) (2) | 6.90 mm × 5.65 mm | |
| CFP (8) (3) | 6.90 mm × 5.65 mm | |
| CDIP SB (8) | 11.81 mm × 7.49 mm |
- For all available packages, see the orderable addendum at the end of the data sheet.
- HKJ Package
- HKQ Package
Typical Application Diagram

4 Revision History
Changes from E Revision (June 2012) to F Revision
- Added ESD Ratings table, Feature Description section, Device Functional Modes, Application and Implementation section, Power Supply Recommendations section, Layout section, Device and Documentation Support section, and Mechanical, Packaging, and Orderable Information section Go
5 Pin Configuration and Functions


Pin Functions
| PIN | TYPE | DESCRIPTION | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| NAME | SOIC, PDIP |
HKQ | ||
| A | 6 | 6 | Bus input/output | Driver output or receiver input (complementary to B) |
| B | 7 | 7 | Bus input/output | Driver output or receiver input (complementary to A) |
| D | 4 | 4 | Digital input | Driver data input |
| DE | 3 | 3 | Digital input | Active-high driver enable |
| GND | 5 | 5 | Reference potential | Local device ground |
| R | 1 | 1 | Digital output | Receive data output |
| RE | 2 | 2 | Digital input | Active-low receiver enable |
| VCC | 8 | 8 | Supply | 3-V to 3.6-V supply |
Bare Die Information
| DIE THICKNESS | BACKSIDE FINISH | BACKSIDE POTENTIAL | BOND PAD METALLIZATION COMPOSITION |
|---|---|---|---|
| 15 mils. | Silicon with backgrind | GND | Cu-Ni-Pd |
Bond Pad Coordinates in Microns - Rev A
| DESCRIPTION(1) | PAD NUMBER | a | b | c | d |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| R | 1 | 69.3 | 372.15 | 185.3 | 489.15 |
| ~RE | 2 | 388.75 | 71.5 | 503.75 | 186.5 |
| DNC | 3 | 722.4 | 55.4 | 839.4 | 172.4 |
| DNC | 4 | 891.4 | 55.4 | 1008.4 | 172.4 |
| DE | 5 | 1174.8 | 71.5 | 1289.8 | 186.5 |
| DNC | 6 | 1754.35 | 65.4 | 1869.35 | 180.4 |
| DNC | 7 | 1907.35 | 65.4 | 2022.35 | 180.4 |
| D | 8 | 2280.55 | 69.5 | 2395.55 | 184.5 |
| DNC | 9 | 2733.5 | 371.5 | 2848.5 | 486.5 |
| GND | 10 | 2691 | 1693.1 | 2808 | 1810.1 |
| GND | 11 | 2535 | 1693.1 | 2652 | 1810.1 |
| DNC | 12 | 2253.45 | 1685.65 | 2368.45 | 1800.65 |
| A | 13 | 1961.55 | 1693.1 | 2078.55 | 1810.1 |
| B | 14 | 799.55 | 1693.1 | 916.55 | 1810.1 |
| DNC | 15 | 498.35 | 1681.2 | 613.35 | 1796.2 |
| VCC | 16 | 244.8 | 1668.5 | 359.8 | 1783.5 |
| VCC | 17 | 91.8 | 1668.5 | 206.8 | 1783.5 |

6 Specifications
6.1 Absolute Maximum Ratings
over operating free-air temperature range (unless otherwise noted)(1)| MIN | MAX | UNIT | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| VCC | Supply voltage | –0.3 | 6 | V | ||
| Voltage at A or B | –9 | 14 | V | |||
| Input voltage at D, DE, R, or RE | –0.5 | VCC + 0.5 | V | |||
| Voltage input, transient pulse, A and B, through 100 Ω (see Figure 20) | –50 | 50 | V | |||
| IO | Receiver output current | –11 | 11 | mA | ||
| Continuous total power dissipation | See Thermal Information | |||||
6.2 ESD Ratings
| VALUE | UNIT | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| V(ESD) | Electrostatic discharge | Human-body model (HBM), per ANSI/ESDA/JEDEC JS-001(1) | A, B, and GND | ±16000 | V |
| All pins | ±4000 | ||||
| Charged-device model (CDM), per JEDEC specification JESD22-C101(2) | ±1000 | ||||
6.3 Recommended Operating Conditions
| MIN | NOM | MAX | UNIT | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| VCC | Supply voltage | 3 | 3.6 | V | ||
| VI or VIC | Voltage at any bus terminal (separately or common-mode) | –7(1) | 12 | V | ||
| VIH | High-level input voltage | D, DE, RE | 2 | VCC | V | |
| VIL | Low-level input voltage | D, DE, RE | 0 | 0.8 | V | |
| VID | Differential input voltage | Figure 16 | –12 | 12 | V | |
| IOH | High-level output current | Driver | –60 | mA | ||
| Receiver | –8 | |||||
| IOL | Low-level output current | Driver | 60 | mA | ||
| Receiver | 8 | |||||
| RL | Differential load resistance | 54 | 60 | Ω | ||
| CL | Differential load capacitance | 50 | pF | |||
| Signaling rate | 10 | Mbps | ||||
| TJ(2) | Operating junction temperature | TA = –55°C to 125°C | 129 | °C | ||
| TA = 175°C | 179 | |||||
| TA = 210°C | 214 | |||||
6.4 Thermal Information
| THERMAL METRIC(1) | SN65HVD11-HT | UNIT | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| D (SOIC) | JD (CDIP SB) | HKJ (CFP) | HKQ (CFP) | |||
| 8 PINS | 8 PINS | 8 PINS | 8 PINS | |||
| RθJA | Junction-to-ambient thermal resistance | 101.5 | 73.9 | N/A | 170 | °C/W |
| RθJC(top) | Junction-to-case (top) thermal resistance | 53.6 | N/A | N/A | 6.2 | °C/W |
| RθJB | Junction-to-board thermal resistance | 45.1 | 39.8 | N/A | 195 | °C/W |
| ψJT | Junction-to-top characterization parameter | 4.8 | 6.9 | N/A | 3.8 | °C/W |
| ψJB | Junction-to-board characterization parameter | 41.8 | 49.2 | N/A | 146.8 | °C/W |
| RθJC(bot) | Junction-to-case (bottom) thermal resistance | N/A | 9.1 | 6.2 | N/A | °C/W |
6.5 Driver Electrical Characteristics
over recommended operating conditions (unless otherwise noted)| PARAMETER | TEST CONDITIONS | MIN | TYP | MAX | UNIT | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| VIK | Input clamp voltage | II = –18 mA | –1.5 | V | |||||
| |VOD| | Differential output voltage | IO = 0 | 2 | VCC | V | ||||
| RL = 54 Ω, See Figure 10 | 1 | ||||||||
| Vtest = –7 V to 12 V, See Figure 11 |
1 | ||||||||
| Δ|VOD| | Change in magnitude of differential output voltage | Vtest = –7 V to 12 V, See Figure 10 and Figure 11 |
–0.2 | 0.2 | V | ||||
| VOC(PP) | Peak-to-peak common mode output voltage | See Figure 12 | 400 | mV | |||||
| VOC(SS) | Steady-state common mode output voltage | See Figure 12 | 1.4 | 2.5 | V | ||||
| ΔVOC(SS) | Change in steady-state common mode output voltage | See Figure 12 | –0.06 | 0.06 | V | ||||
| IOZ | High-impedance output current | See receiver input currents | |||||||
| II | Input current | D | TA = –55°C to 125°C | –100 | 0 | μA | |||
| TA = 175°C(1) | –100 | 3 | |||||||
| TA = 210°C(2) | –100 | 3 | |||||||
| DE | 0 | 100 | |||||||
| IOS | Short circuit output current | –7 V ≤ VO ≤ 12 V | –250 | 250 | mA | ||||
| C(OD) | Differential output capacitance | VOD = 0.4 sin (4E6πt) + 0.5 V, DE = 0 V |
18 | pF | |||||
| ICC | Supply current | RE = VCC, D and DE = VCC, No load |
Receiver disabled and driver enabled | TA = –55°C to 125°C | 11 | 15.5 | mA | ||
| TA = 175°C(1) | 11.5 | 17.5 | |||||||
| TA = 210°C(2) | 14 | 18 | |||||||
| RE = VCC, D = VCC, DE = 0 V, No load |
Receiver disabled and driver disabled (standby) | TA = –55°C to 125°C | 2.5 | 20 | μA | ||||
| TA = 175°C(1) | 20 | 150 | |||||||
| TA = 210°C(2) | 175 | 450 | |||||||
| RE = 0 V, D and DE = VCC, No load |
Receiver enabled and driver enabled | TA = –55°C to 125°C | 11 | 15.5 | mA | ||||
| TA = 175°C(1) | 11 | 17.5 | |||||||
| TA = 210°C(2) | 11 | 18 | |||||||
6.6 Receiver Electrical Characteristics
over recommended operating conditions (unless otherwise noted)| PARAMETER | TEST CONDITIONS | MIN | TYP | MAX | UNIT | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| VIT+ | Positive-going input threshold voltage | IO = –8 mA | –0.01 | V | ||||
| VIT– | Negative-going input threshold voltage | IO = 8 mA | –0.2 | V | ||||
| Vhys | Hysteresis voltage (VIT+ –VIT–) |
TA = –55°C to 125°C | 35 | mV | ||||
| TA = 175°C(1) | 41 | |||||||
| TA = 210°C(2) | 41 | |||||||
| VIK | Enable-input clamp voltage | II = –18 mA | –1.5 | V | ||||
| VOH | High-level output voltage | VID = 200 mV, IOH = –8 mA, See Figure 16 |
2.4 | V | ||||
| VOL | Low-level output voltage | VID = –200 mV, IOL = 8 mA, See Figure 16 |
0.4 | V | ||||
| IOZ | High-impedance state output current | VO = 0 or VCC,RE = VCC | –1 | 1 | μA | |||
| II | Bus input current | VA or VB = 12 V | Other input at 0 V |
TA = –55°C to 125°C | 0.075 | 0.11 | mA | |
| TA = 175°C(1) | 0.1 | 0.15 | ||||||
| TA = 210°C(2) | 0.1 | 0.15 | ||||||
| VA or VB = 12 V, VCC = 0 V |
TA = –55°C to 125°C | 0.085 | 0.13 | |||||
| TA = 175°C(1) | 0.12 | 0.16 | ||||||
| TA = 210°C(2) | 0.12 | 0.16 | ||||||
| VA or VB = –7 V | TA = –55°C to 125°C | –0.1 | –0.05 | |||||
| TA = 175°C(1) | –0.3 | –0.15 | ||||||
| TA = 210°C(2) | –0.3 | –0.15 | ||||||
| VA or VB = –7 V, VCC = 0 V |
TA = –55°C to 125°C | –0.1 | –0.05 | |||||
| TA = 175°C(1) | –0.3 | –0.15 | ||||||
| TA = 210°C(2) | –0.3 | –0.15 | ||||||
| IIH | High-level input current, RE | VIH = 2 V | TA = –55°C to 125°C | –30 | 0 | μA | ||
| TA = 175°C(1) | –30 | 3 | ||||||
| TA = 210°C(2) | –30 | 3 | ||||||
| IIL | Low-level input current, RE | VIL = 0.8 V | –30 | 0 | μA | |||
| CID | Differential input capacitance | VID = 0.4 sin (4E6πt) + 0.5 V, DE at 0 V |
TA = –55°C to 125°C | 15 | pF | |||
| TA = 175°C(1) | 18 | |||||||
| TA = 210°C(2) | 18 | |||||||
| ICC | Supply current | RE = 0 V, D and DE = 0 V, No load |
Receiver enabled and driver disabled | TA = –55°C to 125°C | 5 | 8 | mA | |
| TA = 175°C(1) | 7.5 | 8.5 | ||||||
| TA = 210°C(2) | 7.5 | 10 | ||||||
| RE = VCC, D = VCC, DE = 0 V, No load |
Receiver disabled and driver disabled (standby) | TA = –55°C to 125°C | 2.5 | 20 | μA | |||
| TA = 175°C(1) | 12.5 | 200 | ||||||
| TA = 210°C(2) | 175 | 450 | ||||||
| RE = 0 V, D and DE = VCC, No load |
Receiver enabled and driver enabled | TA = –55°C to 125°C | 11 | 15.5 | mA | |||
| TA = 175°C(1) | 11.5 | 17.5 | ||||||
| TA = 210°C(2) | 14 | 18 | ||||||
6.7 Driver Switching Characteristics
over recommended operating conditions (unless otherwise noted)| PARAMETER | TEST CONDITIONS | MIN | TYP | MAX | UNIT | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| tPLH | Propagation delay time, low-to-high-level output | RL = 54 Ω, CL = 50 pF, See Figure 13 |
18 | 25 | 40 | ns | ||
| tPHL | Propagation delay time, high-to-low-level output | 18 | 25 | 40 | ns | |||
| tr | Differential output signal rise time | TA = –55°C to 125°C | 10 | 21 | 30 | ns | ||
| TA = 175°C(1) | 10 | 22 | 30 | |||||
| TA = 210°C(2) | 10 | 22 | 30 | |||||
| tf | Differential output signal fall time | TA = –55°C to 125°C | 10 | 21 | 30 | ns | ||
| TA = 175°C(1) | 10 | 22 | 30 | |||||
| TA = 210°C(2) | 10 | 22 | 30 | |||||
| tsk(p) | Pulse skew (|tPHL – tPLH|) | 2.5 | ns | |||||
| tsk(pp)(3) | Part-to-part skew (tPHL or tPLH) | 11 | ns | |||||
| tPZH | Propagation delay time, high-impedance to high-level output | RL = 110 Ω, RE = 0 V, See Figure 14 |
55 | ns | ||||
| tPHZ | Propagation delay time, high-level to high-impedance output | 55 | ns | |||||
| tPZL | Propagation delay time, high-impedance to low-level output | RL = 110 Ω, RE = 0 V, See Figure 15 |
55 | ns | ||||
| tPLZ | Propagation delay time, low-level to high-impedance output | 75 | ns | |||||
| tPZH | Propagation delay time, standby to high-level output | RL = 110 Ω, RE = 3 V, See Figure 14 |
6 | μs | ||||
| tPZL | Propagation delay time, standby to low-level output | RL = 110 Ω, RE = 3 V, See Figure 15 |
6 | μs | ||||
6.8 Receiver Switching Characteristics
over recommended operating conditions (unless otherwise noted)| PARAMETER | TEST CONDITIONS | MIN | TYP | MAX | UNIT | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| tPLH | Propagation delay time, low-to-high-level output | VID = –1.5 V to 1.5 V, CL = 15 pF, See Figure 17 |
30 | 55 | 70 | ns | ||
| tPHL | Propagation delay time, high-to-low-level output | 30 | 55 | 70 | ns | |||
| tsk(p) | Pulse skew (|tPHL – tPLH|) | 4 | ns | |||||
| tsk(pp)(3) | Part-to-part skew | 15 | ns | |||||
| tr | Output signal rise time | CL = 15 pF, See Figure 17 |
TA = –55°C to 125°C | 1 | 3 | 5 | ns | |
| TA = 175°C(1) | 1 | 4 | 5 | |||||
| TA = 210°C(2) | 1 | 4 | 5 | |||||
| tf | Output signal fall time | TA = –55°C to 125°C | 1 | 3 | 5 | ns | ||
| TA = 175°C(1) | 1 | 4 | 5 | |||||
| TA = 210°C(2) | 1 | 4 | 5 | |||||
| tPZH(2) | Output enable time to high level | CL = 15 pF, DE = 3 V, See Figure 18 |
15 | ns | ||||
| tPZL(2) | Output enable time to low level | 15 | ns | |||||
| tPHZ | Output disable time from high level | 20 | ns | |||||
| tPLZ | Output disable time from low level | 15 | ns | |||||
| tPZH(3) | Propagation delay time, standby-to-high-level output | CL = 15 pF, DE = 0, See Figure 19 |
6 | μs | ||||
| tPZL(3) | Propagation delay time, standby-to-low-level output | 6 | μs | |||||
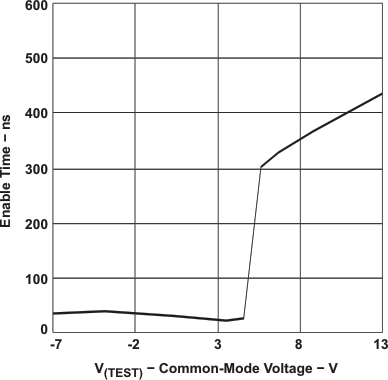
xxx
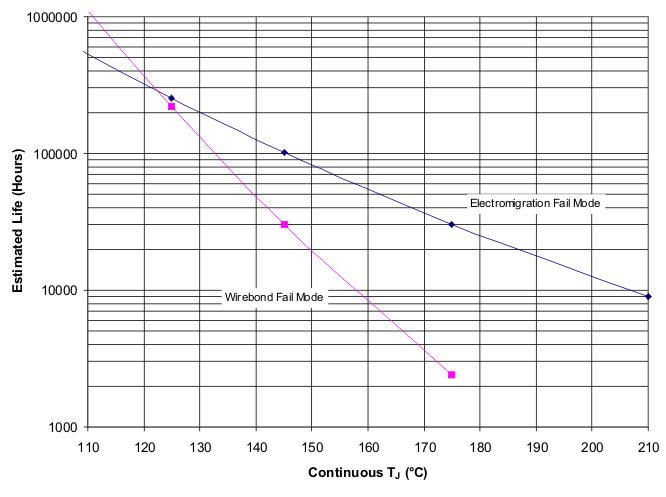
Operating Life Derating Chart
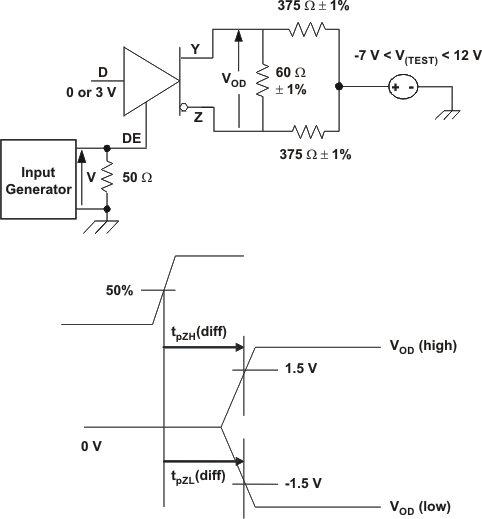
NOTE:
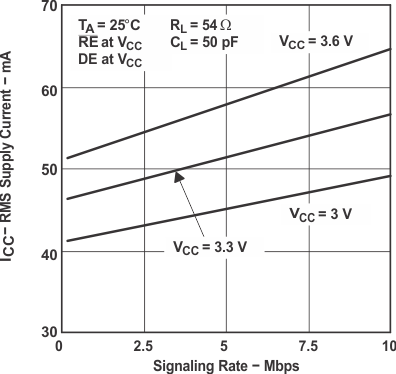
The time tpZL(x) is the measure from DE to VOD(x). VOD is valid when it is greater than 1.5 V.6.9 Typical Characteristics
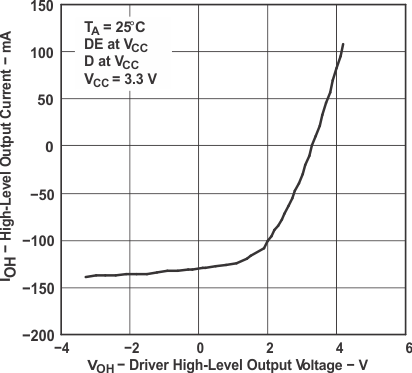
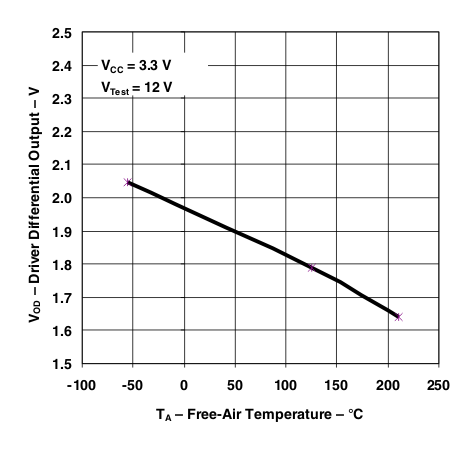
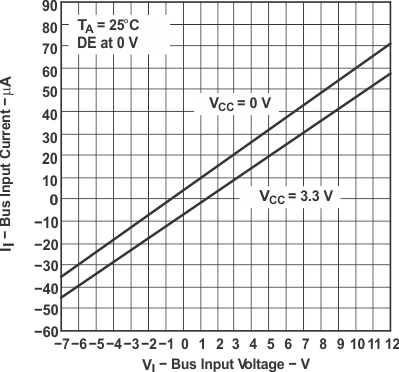
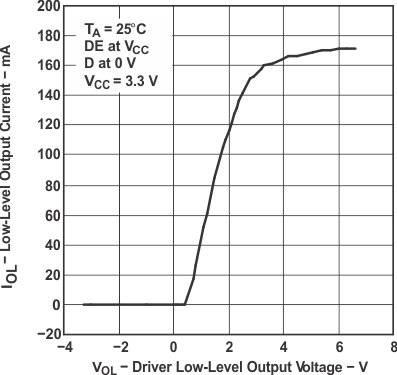
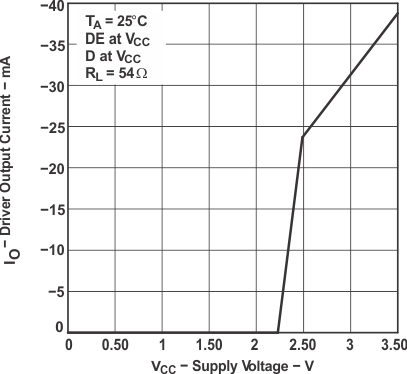
7 Parameter Measurement Information
 Figure 10. Driver VOD Test Circuit and Voltage and Current Definitions
Figure 10. Driver VOD Test Circuit and Voltage and Current Definitions
 Figure 11. Driver VOD With Common Mode Loading Test Circuit
Figure 11. Driver VOD With Common Mode Loading Test Circuit
 Figure 12. Test Circuit and Definitions for Driver Common Mode Output Voltage
Figure 12. Test Circuit and Definitions for Driver Common Mode Output Voltage
 Figure 13. Driver Switching Test Circuit and Voltage Waveforms
Figure 13. Driver Switching Test Circuit and Voltage Waveforms
 Figure 14. Driver High-Level Enable and Disable Time Test Circuit and Voltage Waveforms
Figure 14. Driver High-Level Enable and Disable Time Test Circuit and Voltage Waveforms
 Figure 15. Driver Low-Level Output Enable and Disable Time Test Circuit and Voltage Waveforms
Figure 15. Driver Low-Level Output Enable and Disable Time Test Circuit and Voltage Waveforms
 Figure 16. Receiver Voltage and Current Definitions
Figure 16. Receiver Voltage and Current Definitions
 Figure 17. Receiver Switching Test Circuit and Voltage Waveforms
Figure 17. Receiver Switching Test Circuit and Voltage Waveforms
 Figure 18. Receiver Enable and Disable Time Test Circuit and Voltage Waveforms With Drivers Enabled
Figure 18. Receiver Enable and Disable Time Test Circuit and Voltage Waveforms With Drivers Enabled
 Figure 19. Receiver Enable Time From Standby (Driver Disabled)
Figure 19. Receiver Enable Time From Standby (Driver Disabled)
 Figure 20. Test Circuit, Transient Overvoltage Test
Figure 20. Test Circuit, Transient Overvoltage Test
 Figure 21. Equivalent Input and Output Schematic Diagrams
Figure 21. Equivalent Input and Output Schematic Diagrams